Campo, Vallemaggia
Campo is a municipality in the district of Vallemaggia in the canton of Ticino in Switzerland.
Campo | |
|---|---|
-coat_of_arms.svg.png) Coat of arms | |
Location of Campo 
| |
 Campo  Campo | |
| Coordinates: 46°17′N 8°29′E | |
| Country | Switzerland |
| Canton | Ticino |
| District | Vallemaggia |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Sindaco |
| Area | |
| • Total | 43.34 km2 (16.73 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 1,321 m (4,334 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 53 |
| • Density | 1.2/km2 (3.2/sq mi) |
| Postal code | 6684 |
| SFOS number | 5307 |
| Surrounded by | Bosco/Gurin, Cerentino, Cevio, Maggia, Montecrestese (IT-VB), Premia (IT-VB), Santa Maria Maggiore (IT-VB), Vergeletto |
| Website | www SFSO statistics |
History
In the 15th century, the Valle di Campo along with Cevio, Bignasco and Cavergno formed the Roana Superior, a kind of administrative district. Until 1513, Campo belonged to the parish of Cevio. Cimalmotto and Niva separated from Campo's church in 1767 to form an independent parish. They also formed independent political municipalities until the beginning of the 19th century. The church of S. Bernardo in Campo was probably built in the 14th century. In the first half of the 16th century, in 1620 and 1740-45 it was enlarged. It contains frescoes by Giuseppe Mattia Borgnis (1745), who also worked on the churches of Cimalmotto and Niva, the Baroque chapel of San Giovanni and the facade of Palazzi Pedrazzini.[3]
In the 17th and 18th Centuries, the lack of arable land caused a strong migratory flow toward Germany and Italy. Some of the residents, especially merchants and emigrants, became wealthy. Many of the village buildings were richly decorated with frescoes. At this time a wealthy and influential middle class emerged with political and religious power. Currently, a few families still work in agriculture. The majority of houses in the village are second homes. Even in the 18th century the area was popular as a holiday destination. Since 1850, the population has declined with many residents moving to the cities. The great distances (42 km (26 mi) from Locarno) and adverse road make it difficult for the village to become a commuter town.[3]
The unfavorable geological conditions, exacerbated by reckless logging and resultant flooding caused numerous landslides since the beginning of the 19th century.[3]
Geography
Campo has an area, as of 1997, of 43.27 square kilometers (16.71 sq mi). Of this area, 1.07 km2 (0.41 sq mi) or 2.5% is used for agricultural purposes, while 19.22 km2 (7.42 sq mi) or 44.4% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 0.36 km2 (0.14 sq mi) or 0.8% is settled (buildings or roads), 0.79 km2 (0.31 sq mi) or 1.8% is either rivers or lakes and 17.21 km2 (6.64 sq mi) or 39.8% is unproductive land. Of the built up area, housing and buildings made up 0.4% and transportation infrastructure made up 0.3%. Out of the forested land, 28.0% of the total land area is heavily forested, while 10.6% is covered in small trees and shrubbery and 5.8% is covered with orchards or small clusters of trees. Of the agricultural land, 2.1% is used for growing crops. Of the water in the municipality, 0.2% is in lakes and 1.7% is in rivers and streams. Of the unproductive areas, 19.3% is unproductive vegetation and 20.5% is too rocky for vegetation.[4]
The municipality is located in the Vallemaggia district, in the upper Valle di Campo. It consists of the villages of Campo (Mezzo), Cimalmotto (1,405 m (4,610 ft)), Piano and Niva (955 m (3,133 ft)). The villages are all geographically isolated from each other.
Coat of arms
The blazon of the municipal coat of arms is Azure a fleur de lis or.[5]
Demographics
Campo has a population (as of December 2018) of 53.[6] As of 2008, 8.8% of the population are resident foreign nationals.[7] Over the last 10 years (1997–2007) the population has changed at a rate of -9.5%.[8] Most of the population (as of 2000) speaks Italian language (52 or 89.7%), with German being second most common (5 or 8.6%) and English being third (1 or 1.7%). There are people who speak French and people who speak Romansh.[9]
As of 2008, the gender distribution of the population was 55.8% male and 44.2% female. The population was made up of 27 Swiss men (51.9% of the population), and 2 (3.8%) non-Swiss men. There were 23 Swiss women (44.2%), and (0.0%) non-Swiss women.[10] Of the population in the municipality 26 or about 44.8% were born in Campo and lived there in 2000. There were 9 or 15.5% who were born in the same canton, while 11 or 19.0% were born somewhere else in Switzerland, and 8 or 13.8% were born outside of Switzerland.[9]
In 2008 there was 1 live birth to Swiss citizens and 1 death of a Swiss citizen. Ignoring immigration and emigration, the population of Swiss citizens remained the same while the foreign population remained the same. There was 1 Swiss woman who immigrated back to Switzerland. The total Swiss population remained the same in 2008 and the non-Swiss population remained the same. This represents a population growth rate of 0.0%.[7]
The age distribution, as of 2009, in Campo is; 1 child is between 0 and 9 years old and 1 teenager is between 10 and 19. Of the adult population, 4 people or 7.7% of the population are between 20 and 29 years old. 9 people or 17.3% are between 30 and 39, 7 people or 13.5% are between 40 and 49, and 10 people or 19.2% are between 50 and 59. The senior population distribution is 7 people or 13.5% of the population are between 60 and 69 years old, 1 person is between 70 and 79, there are 12 people or 23.1% who are over 80.[10]
As of 2000, there were 33 people who were single and never married in the municipality. There were 19 married individuals, 1 widow or widower and 5 individuals who are divorced.[9]
As of 2000, there were 30 private households in the municipality, and an average of 1.9 persons per household.[8] There were 13 households that consist of only one person and 2 households with five or more people. Out of a total of 30 households that answered this question, 43.3% were households made up of just one personFALSE. Of the rest of the households, there are 8 married couples without children, 3 married couples with children There were 6 households that were made up unrelated people.[9]
In 2000 there were 185 single family homes (or 93.4% of the total) out of a total of 198 inhabited buildings. There were 5 multi-family buildings (2.5%) and 8 other use buildings (commercial or industrial) that also had some housing (4.0%). Of the single family homes 21 were built before 1919, while 1 was built between 1990 and 2000. The greatest number of single family homes (102) were built between 1919 and 1945.[11]
In 2000 there were 202 apartments in the municipality. The most common apartment size was 4 rooms of which there were 41. There were 14 single room apartments and 71 apartments with five or more rooms. Of these apartments, a total of 30 apartments (14.9% of the total) were permanently occupied, while 171 apartments (84.7%) were seasonally occupied and 1 apartment (0.5%) was empty.[11] As of 2007, the construction rate of new housing units was 17.5 new units per 1000 residents.[8] The vacancy rate for the municipality, in 2008, was 0%.[8]
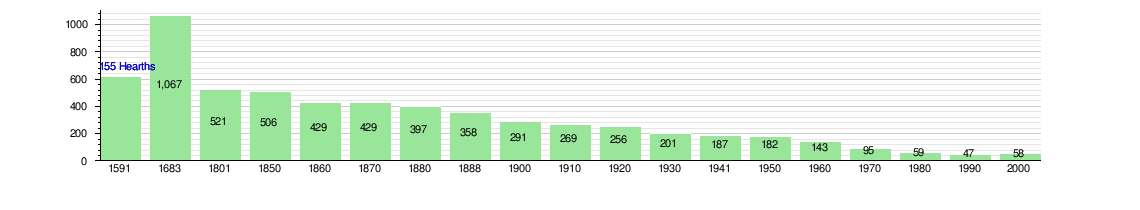
The historical population is given in the following chart:[3][12]
Heritage sites of national significance
The Case Pedrazzini and Oratory of S. Giovanni Battista and the Parish Church of S. Bernardo with Via Crucis are listed as Swiss heritage site of national significance. The entire villages of Campo and Cimalmotto are part of the Inventory of Swiss Heritage Sites.[13]
Politics
In the 2007 federal election the most popular party was the CVP which received 30.77% of the vote. The next three most popular parties were the SP (24.52%), the FDP (19.71%) and the SVP (9.62%). In the federal election, a total of 26 votes were cast, and the voter turnout was 51.0%.[14]
In the 2007 Gran Consiglio election, there were a total of 53 registered voters in Campo, of which 37 or 69.8% voted. 1 blank ballot was cast, leaving 36 valid ballots in the election. The most popular party was the PPD+GenGiova which received 11 or 30.6% of the vote. The next three most popular parties were; the SSI (with 8 or 22.2%), the PS (with 6 or 16.7%) and the PLRT (with 3 or 8.3%).[15]
In the 2007 Consiglio di Stato election, 1 blank ballot was cast, leaving 36 valid ballots in the election. The most popular party was the PPD which received 11 or 30.6% of the vote. The next three most popular parties were; the PS (with 10 or 27.8%), the SSI (with 8 or 22.2%) and the PLRT (with 3 or 8.3%).[15]
Economy
As of 2007, Campo had an unemployment rate of 1.19%. As of 2005, there were 8 people employed in the primary economic sector and about 3 businesses involved in this sector. 2 people were employed in the tertiary sector, with 1 business in this sector.[8] There were 27 residents of the municipality who were employed in some capacity, of which females made up 33.3% of the workforce.
In 2008 the total number of full-time equivalent jobs was 6. The number of jobs in the primary sector was 5, all of which were in agriculture. There were no jobs in the secondary sector. The number of jobs in the tertiary sector was 1 in a hotel or restaurant.[16]
In 2000, there were 8 workers who commuted away from the municipality.[17] Of the working population, 0% used public transportation to get to work, and 33.3% used a private car.[8]
As of 2009, there was one hotel in Campo.[18]
Religion
From the 2000 census, 47 or 81.0% were Roman Catholic, while 5 or 8.6% belonged to the Swiss Reformed Church. There were 3 (or about 5.17% of the population) belonged to no church, are agnostic or atheist, and 3 individuals (or about 5.17% of the population) did not answer the question.[9]
Education
In Campo about 14 or (24.1%) of the population have completed non-mandatory upper secondary education, and 7 or (12.1%) have completed additional higher education (either university or a Fachhochschule). Of the 7 who completed tertiary schooling, 71.4% were Swiss men, 14.3% were Swiss women.[9]
In Campo there were a total of 2 students (as of 2009). The Ticino education system provides up to three years of non-mandatory kindergarten but in Campo there were no children in kindergarten, primary school or the lower secondary school system.
The upper secondary school includes several options, but at the end of the upper secondary program, a student will be prepared to enter a trade or to continue on to a university or college. In Ticino, vocational students may either attend school while working on their internship or apprenticeship (which takes three or four years) or may attend school followed by an internship or apprenticeship (which takes one year as a full-time student or one and a half to two years as a part-time student).[19] There were no vocational students who were attending school full-time and 1 who attend part-time.
The professional program lasts three years and prepares a student for a job in engineering, nursing, computer science, business, tourism and similar fields. There was 1 student in the professional program.[20]
As of 2000, there was 1 student from Campo who attended a school outside the municipality.[17]
References
- "Arealstatistik Standard - Gemeinden nach 4 Hauptbereichen". Federal Statistical Office. Retrieved 13 January 2019.
- "Bilanz der ständigen Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Staatsangehörigkeit (Kategorie), Geschlecht und demographischen Komponenten". Federal Statistical Office. Retrieved 12 January 2019.
- Campo (Vallemaggia) in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Altitudine, superficie, secondo il genere di utilizzazione, rilevazione 1992/1997, e densità della popolazione, nel 2000 (in Italian) accessed 25 October 2010
- Flags of the World.com accessed 14-February-2011
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office - STAT-TAB, online database – Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Geburtsort und Staatsangehörigkeit (in German) accessed 23 September 2019
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Superweb database - Gemeinde Statistics 1981-2008 Archived June 28, 2010, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 19 June 2010
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office Archived January 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine accessed 14-February-2011
- STAT-TAB Datenwürfel für Thema 40.3 - 2000 Archived April 9, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 2 February 2011
- 01.02.03 Popolazione residente permanente Archived July 7, 2011, at the Wayback Machine (in Italian) accessed 23 November 2010
- Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB - Datenwürfel für Thema 09.2 - Gebäude und Wohnungen Archived January 21, 2015, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 28 January 2011
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB Bevölkerungsentwicklung nach Region, 1850-2000 Archived September 30, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 29 January 2011
- "Kantonsliste A-Objekte:Ticino" (PDF). KGS Inventar (in German). Federal Office of Civil Protection. 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 12 July 2010.
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office, Nationalratswahlen 2007: Stärke der Parteien und Wahlbeteiligung, nach Gemeinden/Bezirk/Canton Archived May 14, 2015, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 28 May 2010
- Elezioni cantonali: Gran Consiglio, Consiglio di Stato Archived July 7, 2011, at the Wayback Machine (in Italian) accessed 23 November 2010
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB Betriebszählung: Arbeitsstätten nach Gemeinde und NOGA 2008 (Abschnitte), Sektoren 1-3 Archived December 25, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 28 January 2011
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Statweb (in German) accessed 24 June 2010
- Settori alberghiero e paralberghiero Archived July 7, 2011, at the Wayback Machine (in Italian) accessed 23 November 2010
- EDK/CDIP/IDES (2010). KANTONALE SCHULSTRUKTUREN IN DER SCHWEIZ UND IM FÜRSTENTUM LIECHTENSTEIN / STRUCTURES SCOLAIRES CANTONALES EN SUISSE ET DANS LA PRINCIPAUTÉ DU LIECHTENSTEIN (PDF) (Report). Retrieved 24 June 2010.
- Allievi e studenti, secondo il genere di scuola, anno scolastico 2009/2010 Archived July 7, 2011, at the Wayback Machine (in Italian) accessed 23 November 2010
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Campo (Vallemaggia). |
- Official website (in Italian)
- Campo in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.