Calcium bisulfite
Calcium bisulfite (calcium bisulphite) is an inorganic compound which is the salt of a calcium cation and a bisulfite anion. It may be prepared by treating lime with an excess of sulfur dioxide and water. As a food additive it is used as a preservative under the E number E227. Calcium bisulfite is an acid salt and behaves like an acid in aqueous solution. It is used in the sulfite process for producing paper from wood chips.[1]
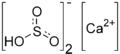 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Calcium hydrogen sulfite | |
| Other names
Calcium bisulphite E227 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.007 |
| E number | E227 (preservatives) |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ca(HSO3)2 | |
| Molar mass | 202.22 g/mol |
| Melting point | 203 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Patt, Rudolf; Kordsachia, Othar; Süttinger, Richard; Ohtani, Yoshito; Hoesch, Jochen F.; Ehrler, Peter; Eichinger, Rudolf; Holik, Herbert; Hamm (2000). "Paper and Pulp". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a18_545.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.