Buffer zone
A buffer zone is generally a zonal area that lies between two or more areas (often, but not necessarily, countries), but depending on the type of buffer zone, it may serve to separate regions or conjoin them. Common types of buffer zones are demilitarized zones, border zones and certain restrictive easement zones and green belts. Such zones may be, but not necessarily, comprised by a sovereign state, forming a buffer state.
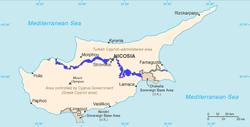

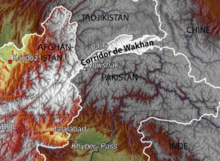
Buffer zones have various purposes, political or otherwise. They can be set up to prevent violence, protect the environment, shield residential and commercial zones from industrial accidents or natural disasters, or isolate prisons, and have uses in several other scenarios. Buffer zones often result in large uninhabited regions that are themselves noteworthy in many increasingly developed or crowded parts of the world.
Conservation
implementing For use in nature conservation, a buffer zone is often created to enhance the protection of areas under management for their biodiversity importance. The buffer zone of a protected area may be situated around the periphery of the region or may be a connecting zone within it which links two or more protected areas, therefore increasing their dynamics and conservation productivity. A buffer zone can also be one of the protected area categories (e.g. category V or VI of IUCN Protected Area) or a classification scheme (e.g. NATURA 2000) depending on the conservation objective.[1] The term 'buffer zone' initially gained prominence in the conservation of natural and cultural heritage through its usage in the establishment of UNESCO's World Heritage Convention, and the term was intended to be used as follows:
A buffer zone serves to provide an additional layer of protection to a World Heritage property. The concept of a buffer zone was first included in the Operational Guidelines for the implementation of the World Heritage Convention in 1977. In the most current version of the Operational Guidelines of 2005 the inclusion of a buffer zone into a nomination of a site to the World Heritage List is strongly recommended but not mandatory.
—World Heritage Convention[2]
The buffer zone is one of the Best Management Practices (BMPs). A buffer zone is intended to avert the effect of negative environmental or human influences, whether or not it embodies great/good natural or cultural value itself.[3] The importance and function of a buffer zone and the necessary protective measures derived thereof is a relatively new concept in conservation science and can differ greatly for each site.[4]
Ecological functions (conservation)
Improve water quality
It shows that the quality of surface water in many countries is getting worse because humans do not use land properly.[5] Although the buffer zone occupies a small area, it greatly improves the quality of water in the agricultural watershed due to its filtering effect on nutrients in the underground water and surface water.
Because farmland is sprayed with large amounts of pesticides, some of which can seep into surface water. It will have a negative impact on fish and other aquatic life, which can lead to environmental damage. Vegetation buffer has been proved to be an effective filter for sediment, especially for sediment-bound pesticides.[6] When pesticides are sprayed in excess, a vegetation buffer can be built to reduce the penetration of pesticides into surface water. The buffer zone also prevents heavy metals or toxins from spreading to protected areas.[7]
Stabilize the riverbanks
When the riverbanks are low, due to the plant root can enter the interior of the riverbank vertically, the sediment of riverbank is affected by the action of plant root, and the ability to resist erosion is higher than that without plant root. But when the riverbanks are higher, the roots of the plants do not penetrate deeply into the soil, and the lakeshore soil is not very strong. Herbaceous plants can play a role to some extent, but in the long term, vegetation buffer zone can effectively solve the problem of water level rise and water erosion.
The adsorption capacity of buffer zone can reduce the speed of surface runoff and increase the effective water content of soil. Through increasing soil organic matter content and improving soil structure, it has a positive effect on soil water storage performance. In addition, plant roots make the soil stronger, withstand waves and rainstorm, mitigate the erosion of riverbanks by floods, and effectively control the erosion of the beach.
Provide food and habitat to wildlife
The riparian buffer zones have been used in many areas to protect the habitats of many animals which are being devastated by increased human activity. The areas around the buffer zone can form the habitat of many animals, the woody parts and leaves of plants can become food for small aquatic animals. The buffer zone itself can also support the life activities of various amphibians and birds. Plants and animals can migrate or spread in response to these buffer zones and then increasing the biodiversity in the area.
A study shows that the species and number of animals and plants in riparian zones are higher than in other ecosystems.[8] Because of their ability to provide abundant water, soft soil and stable climate, small animals such as Myotis and Martes prefer to live along riverbanks rather than in hilly areas.[9] The buffer zone can also provide a good environment for upland habitat, which is in line with the living conditions of freshwater turtles, making them more dependent on the wetland environment.[10] The protection level of the buffer zones will affect the habitat range of amphibians and reptiles, and the environmental management of the wetland habitat around buffer zone is extremely important.
Provide aesthetic value
As an important part of riparian zone, the vegetation buffer zones form a variety of landscape, and the landscape pattern of combining land and water improves the aesthetic value of river basin landscape. The riparian buffer is rich in plant resources, and the wetland, grassland and forest ecosystem make the landscape more beautiful. In addition, some recreational facilities can be built in the buffer zone to provide better living conditions for residents or tourists and improve people's quality of life.
In the buffer zone, those trees up to 6 meters tall greatly enhance the aesthetic value of the landscape.[11] These tall trees have luxuriant branches and leaves, especially their upright posture, making them of higher ornamental value. Some colorful landscape tree species can be planted on both sides of rivers with tourism and sightseeing value to improve the aesthetic value of the place. The establishment of vegetation buffer zone can increase green land, improve forest coverage, beautify environment and visual effect, improve people's living environment, enrich humanistic landscape and enhance aesthetic value. we need to call on people to pay attention to the importance of the buffer zone, encourage local residents to participate in the protection and management of the buffer zone, and set up checkpoints around the buffer zone to make it more secure and effective.
See also
References
- A-Z of Areas of Biodiversity Importance: Buffer Zones
- "International Expert meeting on World Heritage and buffer zones". UNESCO World Heritage Convention. Retrieved 24 Nov 2010.
Background and contents
- Martin, Oliver, and Piatti, Giovanna (ed.) World Heritage and Buffer Zones, International Expert Meeting on World Heritage and Buffer Zones Davos, Switzerland 11 – 14 March 2008 (Paris: UNESCO, 2009)
- Ebregt, Arthur and de Greve, Pol, Buffer Zones and their Management: Policy and Best Practices for Terrestrial Ecosystems in Developing Countries (Wageningen: Netherlands Ministry of Foreign Affairs, 2000)
- Carpenter, S. R.; Caraco, N. F.; Correll, D. L.; Howarth, R. W.; Sharpley, A. N.; Smith, V. H. (August 1998). "Nonpoint Pollution of Surface Waters with Phosphorus and Nitrogen" (PDF). Ecological Applications. 8 (3): 559. doi:10.2307/2641247. hdl:1813/60811. ISSN 1051-0761. JSTOR 2641247.
- Syversen, Nina; Bechmann, Marianne (May 2004). "Vegetative buffer zones as pesticide filters for simulated surface runoff". Ecological Engineering. 22 (3): 175–184. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2004.05.002. ISSN 0925-8574.
- Deroanne-Bauvin, J; Delcarte, E; Impens, R (January 1987). "Monitoring of lead deposition near highway: A ten years study". Science of the Total Environment. 59: 257–266. Bibcode:1987ScTEn..59..257D. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(87)90447-5. ISSN 0048-9697.
- Sturtevant, Brian R (October 1998). "A model of wetland vegetation dynamics in simulated beaver impoundments". Ecological Modelling. 112 (2–3): 195–225. doi:10.1016/s0304-3800(98)00079-9. ISSN 0304-3800.
- Doyle, A. T. (1990-02-20). "Use of Riparian and Upland Habitats by Small Mammals". Journal of Mammalogy. 71 (1): 14–23. doi:10.2307/1381312. ISSN 1545-1542. JSTOR 1381312.
- Burke, Vincent J.; Gibbons, J. Whitfield (December 1995). "Terrestrial Buffer Zones and Wetland Conservation: A Case Study of Freshwater Turtles in a Carolina Bay". Conservation Biology. 9 (6): 1365–1369. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.1995.09061365.x. ISSN 0888-8892.
- Borin, Maurizio; Passoni, Matteo; Thiene, Mara; Tempesta, Tiziano (January 2010). "Multiple functions of buffer strips in farming areas". European Journal of Agronomy. 32 (1): 103–111. doi:10.1016/j.eja.2009.05.003. ISSN 1161-0301.
External links
- "The World Heritage Convention and the Buffer Zone". ICOMOS Symposium. Kyushu University Graduate School of Law - Programs in English. November 28–29, 2006. Archived from the original on 2011-06-04. Retrieved 24 Nov 2010.
- "World Heritage and Buffer Zones Patrimoine mondial et zones tampons" (PDF/Adobe Acrobat 3.76 MB). International Expert Meeting on World Heritage and Buffer Zones, Davos, Switzerland 11–14 March 2008. World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 24 Nov 2010.
Buffer zones are an important tool for conservation of properties inscribed on the World Heritage List. All along the history of implementation of the World Heritage Convention, the protection of the “surroundings” of the inscribed properties was considered an essential component of the conservation strategy, for cultural and natural sites alike.
