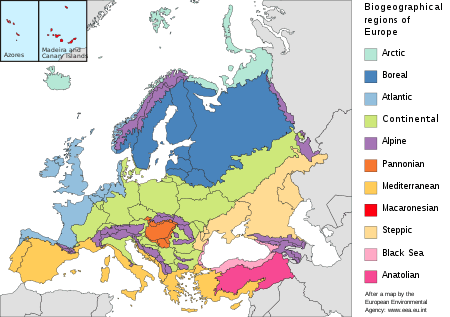
Boreal Biogeographic Region
The Boreal Biogeographic Region is the biogeographic region of Northern Europe that consists primarily of coniferous forests and wetlands.
| Boreal Biogeographic Region | |
|---|---|
Spruce-birch boreal forest in Norra Kvill National Park, South Sweden | |
 | |
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Palearctic |
| Geography | |
| Oceans or seas | Baltic Sea, Gulf of Bothnia, White Sea |
Extent
The European Commission and the Council of Europe have defined the Boreal Region for the purpose of reporting on conservation efforts and results. The Boreal Region of the European Union includes much of the Baltic sea, the Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, and most of Sweden and Finland.[1] The biogeographic region extends eastward into Russia.[2] Most of the land is below 500 metres (1,600 ft) and is fairly flat. The north of the region merges into the forest and tundra of the Arctic Biogeographic Region, while the south merges into the deciduous forests of the Continental Biogeographic Region. In the west, the land rises into the Fennoscandia mountains, which are in the Alpine Biogeographic Region.[1]
Environment
60% of the land in the European Union part of the region is covered by forest, but most of this is commercial plantings. Less than 5-10% of the forest is old growth. The typical western taiga forest contains Norway spruce (Picea abies) and Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) growing on shallow soil covered in moss, lichen and ericaceous shrubs.[1]
Petersen et al. in their 1995 review of Nordic rivers distinguish two biogeographic regions in the Fennoscandian Shield. Their Southern mixed forest rivers group in southeast Finland has short, low-gradient streams in mixed coniferous forest, connecting many clear or humic lakes, ponds, peat bogs and wetlands, which overlap the boreo-nemoral zone. The whole Neva River basin could be assigned to this region. The other region is their Boreal rivers group with "high-gradient streams in the coniferous and deciduous forests of the boreal vegetation zone."[3]
Conservation
Within the European Union, the list of Natura 2000 sites in the Boreal Region was adopted in January 2005 and has since been updated several times. As of 2009 there were 6,266 Sites of Community Importance under the Habitats Directive covering more than 111,000 square kilometres (43,000 sq mi) and 1,165 Special Protection Areas under the Birds Directive. Some sites belong to both categories. Between them they cover over 12% of the land area in the Boreal Region of the European Union.[4]
Notes
- Sundseth 2009, p. 3.
- Sundseth 2009, p. 4.
- Tockner, Uehlinger & Robinson 2009.
- Sundseth 2009, p. 6.
Sources
- Sundseth, Kerstin (2009), Natura 2000 in the Boreal Region (PDF), European Commission Environment Directorate General, doi:10.2779/84505, ISBN 978-92-79-11726-8, retrieved 2019-08-28
- Tockner, Klement; Uehlinger, Urs; Robinson, Christopher T. (31 January 2009), Rivers of Europe, Academic Press, ISBN 978-0-08-091908-9