Borane carbonyl
Borane carbonyl is the inorganic compound with the formula H3BCO. This colorless gas is the adduct of borane and carbon monoxide. It is usually prepared by combining borane-ether complexes and CO. The compound is mainly of theoretical and pedagogical interest.[2] It reacts with aqueous base to give boranocarbonate H3BCO22−.[3] Bond distances are B−C, 1.529; C−O, 1.140; 1.194 Å. The H−B−H angle is 113.7°. The CO vibrational band is at 2165 cm−1, 22 cm−1 higher than that of free CO.[4]
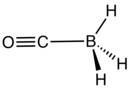 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Carbonyltrihydroboron | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Properties | |
| CH3BO | |
| Molar mass | 41.84 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless gas |
| Density | 1.71 g/L[1] |
| Melting point | −137[1] °C (−215 °F; 136 K) |
| Boiling point | −64[1] °C (−83 °F; 209 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- www.chemicalbook.com https://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB72358168.htm. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Alberto, R.; Ortner, K.; Wheatley, N.; Schibli, R.; Schubiger, A. P. (2001). "Synthesis and Properties of Boranocarbonate: A Convenient in Situ CO Source for the Aqueous Preparation of [99mTc(OH2)3(CO)3]+". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123: 3135–3136. doi:10.1021/ja003932b. PMID 11457025.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Jacobsen, H.; Berke, H.; Doering, S.; Kehr, G.; Erker, G.; Froehlich, R.; Meyer, O. (1999). "Lewis Acid Properties of Tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane. Structure and Bonding in L-B(C6F5)3 Complexes". Organometallics. 18: 1724–1735. doi:10.1021/OM981033E.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.