Biscione
The biscione (Italian pronunciation: [biʃˈʃoːne]; Milanese: bisson [bis'son], plural: "biscioni"), also less commonly known as "the vipera" ([ˈviːpera]; "viper"), is a heraldic charge showing on argent an azure serpent in the act of consuming a human (usually a child and sometimes described as a Moor or an Ottoman Turk). It is a historic symbol of the city of Milan.
.svg.png)
History
_-_Foto_Giovanni_Dall'Orto_25-Apr-2007.jpg)
The word "biscione" is a masculine augmentative of Italian feminine "biscia", "grass snake" (corrupted from "bistia", ultimately from Latin "bestia").
The charge became associated with the city after the Visconti family gained control over Milan 1277; Bonvesin da la Riva records it in his De magnalibus urbis Mediolani (On the Marvels of the City of Milan) as a Visconti symbol no later than the end of the 13th century.[1] The symbol may in turn have been derived from a bronzed serpent brought to Milan from Constantinople by Arnolf II of Arsago (Archbishop of Milan 998-1018) in the 11th century. The biscione remained associated with the Duchy of Milan even after the Visconti line died out in the 15th century.[2] The House of Sforza incorporated the symbol into their armorial after taking the duchy.
Contemporary use
As a symbol of Milan, the biscione is used by multiple organizations associated with or based in the city. Football club Inter Milan is commonly represented by a biscione, and the team's 2010–11 away shirt prominently featured the symbol. Milan-based auto manufacturer Alfa Romeo (also known as the "Casa del biscione", Italian for "House of the Biscione" or "Biscione['s] marque") includes a biscione in its logo impaled with a red cross on white (derived from the flag of Milan), as does espresso machine manufacturer Bezzera. Silvio Berlusconi, who was born and remains based in Milan, uses stylized biscione symbols in the logos for his companies Mediaset and Fininvest (with the child replaced by a flower); his residential zones Milano Due and Milano Tre and the Mediaset-owned television channel Canale 5 all also use biscione-inspired imagery.
Outside Milan, a similar design is found in the seals of the Hungarian nobleman Nicholas I Garai, palatine to the King of Hungary (1375–1385). Here the crowned snake devours a sovereign's orb, rather than a human.[3] The arms of the towns of Sanok in Poland and Pruzhany in Belarus also feature the symbol, honoring the marriage of Bona Sforza to Sigismund I of Poland while both towns were part of Poland–Lithuania.
The band Lacuna Coil used a biscione for the Black Anima album cover artwork[4] and limited edition tarot cards.
Similar symbols
Comparable to the biscione are some depictions of the Hindu deity Matsya. While his form is referred to as anthropomorphically having a humanoid upper half, and his lower half as that of a fish, some depictions show him with his upper body emerging from the mouth of a fish. In early Christian art of the catacombs, the Old Testament prophet Jonah is depicted as a man being swallowed by a serpent-like Leviathan, a sea creature of Hebrew myth.
Coats of arms, flags and symbols bearing the biscione
 The early arms of the Duchy of Milan under the House of Visconti. The coronet on the snake distinguishes this variant from the plain arms of the Visconti family.
The early arms of the Duchy of Milan under the House of Visconti. The coronet on the snake distinguishes this variant from the plain arms of the Visconti family.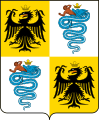 The coat of arms of the House of Sforza, featuring two biscioni and two Reichsadlers (Imperial Eagles symbolizing the German and Austrian domination over Lombardy).
The coat of arms of the House of Sforza, featuring two biscioni and two Reichsadlers (Imperial Eagles symbolizing the German and Austrian domination over Lombardy)..svg.png) The flag of the Duchy of Milan, also featuring two biscioni and two Imperial Eagles.
The flag of the Duchy of Milan, also featuring two biscioni and two Imperial Eagles. A variation of the previous: the arms of Galeazzo Maria Sforza, as inside the Sforza Castle.
A variation of the previous: the arms of Galeazzo Maria Sforza, as inside the Sforza Castle. Bona Sforza's seal, bearing similarities to the other Sforza symbols.
Bona Sforza's seal, bearing similarities to the other Sforza symbols. Coat of arms of the Sforza and Caravaggio houses, as in the German-language book Wernigeroder (Schaffhausensches) Wappenbuch.
Coat of arms of the Sforza and Caravaggio houses, as in the German-language book Wernigeroder (Schaffhausensches) Wappenbuch. The blason of the Duchy of Montbazon.
The blason of the Duchy of Montbazon.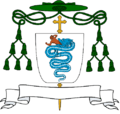 The arms of Ortensio Visconti, Bishop of Lodi.
The arms of Ortensio Visconti, Bishop of Lodi..svg.png) The coat of arms of Napoleon's Kingdom of Italy, including many symbols of Italian cities and the Imperial Eagle.
The coat of arms of Napoleon's Kingdom of Italy, including many symbols of Italian cities and the Imperial Eagle. The coat of arms of the Kingdom of Lombardy-Venetia (an Austrian crown land) quartered the Biscione with the Venetian Lion of Saint Mark.
The coat of arms of the Kingdom of Lombardy-Venetia (an Austrian crown land) quartered the Biscione with the Venetian Lion of Saint Mark. The biscione as a symbol of Milan, seen here at the Milano Centrale railway station.
The biscione as a symbol of Milan, seen here at the Milano Centrale railway station. The coat of arms (the flag is very similar) of Sanok, bearing the biscione due to Bona Sforza.
The coat of arms (the flag is very similar) of Sanok, bearing the biscione due to Bona Sforza.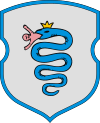 The official seal of Pruzany (also featured in its flag), also bearing the biscione due to Bona.
The official seal of Pruzany (also featured in its flag), also bearing the biscione due to Bona. Depiction of the biscione swallowing a child, the coat of arms of the House of Visconti, on the Archbishop's palace in Piazza Duomo in Milan, Italy.
Depiction of the biscione swallowing a child, the coat of arms of the House of Visconti, on the Archbishop's palace in Piazza Duomo in Milan, Italy. The city of Bellinzona in the Swiss canton of Ticino.
The city of Bellinzona in the Swiss canton of Ticino.
References
- Reina (2018), p. 68
- Fox-Davies, Arthur Charles (1909). A Complete Guide to Heraldry: Illustrated by Nine Plates and Nearly 800 Other Designs. London: T.C. & E.C. Jack. ISBN 0-517-26643-1. LCCN 09023803.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link) Page 257
- Csaba, Veress D. (2007). István, Hermann (ed.). Ugod. Száz magyar falu könyvesháza (One Hundred Hungarian Villages) (in Hungarian). Budapest.: magyar állam millenniumára. Elektronikus megjelenítés: NKÖEOK Szerkesztőség.
- Tilkin, Laureline (2019). "Interview with Lacuna Coil – "It's important to know who you are and where you come from" – Tuonela Magazine". Tuonela Magazine – Finnish Metal Magazine Based in Helsinki. Retrieved 2020-05-24.
Bibliography
- Reina, Gabriele (2018). Le imprese araldiche dei Visconti e degli Sforza (1277-1535): Storia, storia dell'arte, repertorio [The heraldic achievements of the Visconti and the Sforza (1277-1535): History, artistic change, and inventory] (PDF) (in Italian). Lausanne: Université de Lausanne, Faculté des lettres, Section d'histoire de l'art.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Coats of arms of the House of Visconti. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Coats of arms of the House of Sforza. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Coats of arms of Milan. |
.svg.png)