Bernard 70
The Bernard 70 was a 1920s design for a French single-seat monoplane fighter aircraft by the Société des Avions Bernard. It was not built but was developed into a racing monoplane designated the Bernard S-72, (later Bernard S-73). It was further developed into single-seat fighters, the Bernard 74-01 and Bernard 74-02, although only two of the fighters were built.
| Bernard 70 Series | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Bernard 74 | |
| Role | Racing and Fighter monoplanes |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Bernard |
| First flight | 1930 (Bernard 72) |
| Number built | 3 |
Design and development
The Bernard S-72 was a wooden stressed skin constructed cantilever low-wing monoplane powered by a Gnome-Rhône 5Bc[1] radial engine and had a fixed tailskid landing gear.[2] Flown by Paillard, the Bernard S-72 participated in the 1930 Coupe Michelin race. On 29 June, he took off from Le Bourget, landed successively in Reims, Nancy, Strasbourg, Dijon and Clermont-Ferrand, but unfortunately had to retire near Lyon as a result of engine failure.[1] The S-72 was re-engined with a Gnome-Rhône 7Kb[3] and re-designated the Bernard S-73. The S-73 was then developed into the Bernard 74 single-seat fighter and retained the Titan-Major engine.[2] Two prototypes were built with the first flying in February 1931, powered by a 280 hp (kw) Gnome-Rhône 7Kbs radial engine,[4] the second was fitted with a 268 kW (360 hp) Gnome-Rhône 7Kd engine and first flew in October 1931.[1] The first prototype 74 was re-engined with a Gnome-Rhône 9Kbrs radial engine and re-designated the Bernard 75 it was later used as a pilot-trainer.[2] No further aircraft were built.
Variants

- Bernard 70
- Unbuilt design for a single-seat fighter.[2]
- Bernard S-72
- Single-seater racing monoplane powered by a 179 kW (240 hp) Gnome-Rhône 5Bc radial engine, first flight in May 1930 Later converted to the Bernard S-73.[1][2]
- Bernard S-73[3]
- The Bernard 72 re-engined with a 224 kW (300 hp) Gnome-Rhône 7Kb radial engine, first flown in May 1930.[2][3]
- Bernard 74-01
- Single-seat fighter variant, powered by a 209 kW (280 hp) Gnome-Rhône 7Kbs radial engine, later converted to the Bernard 75.[2][4]
- Bernard 74-02
- A second prototype powered by a 268 kW (360 hp) Gnome-Rhône 7Kd, first flown on 21 October 1931[1]
- Bernard 75
- Prototype Bernard 74-01 fighter re-engined with a 373 kW (500 hp) Gnome-Rhône 9Kbrs radial engine and later used as a pilot-trainer.[2][5]
Specifications (Bernard 74.01)
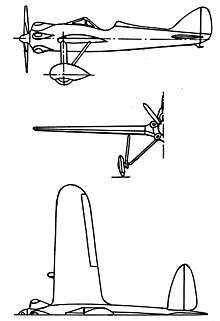
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 6.72 m (22 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 9.20 m (30 ft 2 in)
- Height: 2.50 m (8 ft 3 in)
- Wing area: 13.45 m2 (145 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 825 kg (1,819 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 1,106 kg (2,438 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Gnome-Rhône 7Kbs radial piston engine, 209 kW (280 hp)
- Propellers: 2-bladed
Performance
- Maximum speed: 310 km/h (193 mph, 104 kn)
- Service ceiling: 8,000 m (26,247 ft)
Armament
- Guns: Two fixed 7.7mm (0.303in) synchronised Vickers machine-guns
References
Notes
- http://www.aviafrance.com/aviafrance1.php?ID=9538&ID_CONSTRUCTEUR=202&ANNEE=0&ID_MISSION=0&MOTCLEF=
- Orbis 1985, p. 638
- http://www.aviafrance.com/aviafrance1.php?ID=9539&ID_CONSTRUCTEUR=202&ANNEE=0&ID_MISSION=0&MOTCLEF=
- http://www.aviafrance.com/aviafrance1.php?ID=9540&ID_CONSTRUCTEUR=202&ANNEE=0&ID_MISSION=0&MOTCLEF=
- http://www.aviafrance.com/aviafrance1.php?ID=9541&ID_CONSTRUCTEUR=202&ANNEE=0&ID_MISSION=0&MOTCLEF=
Bibliography
- The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft (Part Work 1982-1985). Orbis Publishing.