Bay of Pigs
The Bay of Pigs (Spanish: Bahía de Cochinos) is an inlet of the Gulf of Cazones located on the southern coast of Cuba. By 1910, it was included in Santa Clara Province, and then instead to Las Villas Province by 1961, but in 1976, it was reassigned to Matanzas Province, when the original six provinces of Cuba were re-organized into 14 new Provinces of Cuba.
| Bay of Pigs | |
|---|---|
 Bay of Pigs from Cueva de los Peces | |
 Bay of Pigs Location of the Bay of Pigs in Cuba | |
 Geographical location of the Bay of Pigs | |
| Location | Matanzas, Cuba |
| Coordinates | 22°13′N 81°10′W |
| Type | Bay |
| Native name | Bahía de Cochinos (Spanish) |
| Etymology | Cochino meaning both "pig" and "triggerfish" |
| Part of | Gulf of Cazones |
| Ocean/sea sources | Caribbean Sea |
| Max. length | max. 27 km (17 mi) |
| Max. width | max. 10 km (6.2 mi) |
| Surface area | 200 km2 (77 sq mi) |
| Shore length1 | 87 km (54 mi) |
| Max. temperature | 29 °C (84 °F) |
| Min. temperature | 22 °C (72 °F) |
| Frozen | Never |
| Islands | Cayo Piedra |
| Settlements | Playa Girón, Playa Larga |
| References | [1][2] |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
The bay is historically important for the failed Bay of Pigs Invasion of 1961. The area is a site known for its diving, with an abundance of marine fauna, e.g. 30 species of sponges belonging to 19 families and 21 genera,[3] to be found in the bay.[4]
Etymology
In Cuban Spanish, cochinos may also mean the queen triggerfish (Balistes vetula), which inhabit coral reefs in Bahía de Cochinos, not swine (Sus scrofa).[5][6]
Geography

This bay is approximately 30 kilometres (19 mi) south of Jagüey Grande, 70 kilometres (43 mi) west of the city of Cienfuegos, and 150 kilometres (93 mi) southeast from the capital city Havana. On the western side of the bay, coral reefs border the main Zapata Swamp, part of the Zapata Peninsula. On the eastern side, beaches border margins of firm ground with mangroves and extensive areas of swampland to the north and east. At the north end of the bay, the village of Buena Ventura is adjacent to Playa Larga (Long Beach). 35 kilometres (22 mi) southeast of that, Playa Girón (Giron Beach) at the village of Girón, named after the notorious French pirate Gilberto Giron (c. 1604).[7]
History
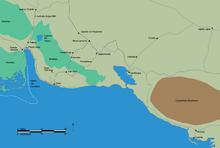
Playa Girón and Playa Larga were the landing sites for seaborne forces of armed Cuban exiles in the Bay of Pigs Invasion, an American CIA-sponsored attempt to overthrow the new government of Cuban Prime Minister Fidel Castro in April 1961.
According to Fidel Castro's former bodyguard, the late Juan Reinaldo Sánchez, Castro lived in great luxury and had a private island called Cayo Piedra in the Bay of Pigs, replete with "mansions, guest houses, a heliport, dolphinarium, turtle lagoon, his luxury yacht Aquarama – a gift from Leonid Brezhnev – and deep-sea fishing speedboat".[8]
Diving

The Bay of Pigs is a relatively quiet site for diving. Dive centers exist in Playa Larga, Playa Girón and Caleta Buena. Twelve dive sites in the bay display excellent visibility of 20 to 40 metres (66 to 131 ft), an average water temperature of 22 °C (72 °F) in December and 29 °C (84 °F) in July. Walls of coral, caverns and a variety of fish (including the barracuda, lionfish and groupers, among others), coral and sponges can be found in the Bay of Pigs.[4]
The Cueva de los Peces, with 72 metres (236 ft) depth the deepest cenote of Cuba, is located at 18 kilometres (11 mi) south of Playa Larga.[9]
Biodiversity
Surrounding the Bay of Pigs, the endemic wormlizards Amphisbaena barbouri and A. cubana have been noted.[10] The following marine species have been registered along the eastern coast of the Bay of Pigs:
| Group | Common name | Scientific name | Image | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish | blue chromis | Chromis cyanea |  | |
| blue tang | Acanthurus coeruleus |  | ||
| bluehead wrasse | Thalassoma bifasciatum |  | ||
| striped parrotfish | Scarus iserti |  | ||
| beau gregory | Stegastes leucostictus | |||
| bicolor damselfish | Stegastes partitus | |||
| boga | Inermia vittata | |||
| Colon goby | Coryphopterus dicrus | |||
| creole wrasse | Clepticus parrae | |||
| longfin damselfish | Stegastes diencaeus | |||
| masked goby | Coryphopterus personatus | |||
| threespot damselfish | Stegastes planifrons | |||
| yellowhead wrasse | Halichoeres garnoti | |||
| French grunt | Haemulon flavolineatum |  | ||
| ocean surgeon | Acanthurus bahianus |  | ||
| sergeant major | Abudefduf saxatilis |  | ||
| slippery dick | Halichoeres bivittatus |  | ||
| yellowtail snapper | Ocyurus chrysurus |  | ||
| bar jack | Caranx ruber | |||
| barred hamlet | Hypoplectrus puella | |||
| brown chromis | Chromis multilineata | |||
| foureye butterflyfish | Chaetodon capistratus | |||
| graysby | Epinephelus cruentatus | |||
| longjaw squirrelfish | Holocentrus marianus | |||
| redband parrotfish | Sparisoma aurofrenatum | |||
| royal gramma | Gramma loreto | |||
| stoplight parrotfish | Sparisoma viride | |||
| tomtate grunt | Haemulon aurolineatum | |||
| white grunt | Haemulon plumierii | |||
| porgies | Calamus sp. | |||
| banded butterflyfish | Chaetodon striatus |  | ||
| buffalo trunkfish | Lactophrys trigonus |  | ||
| flat needlefish | Ablennes hians |  | ||
| glasseye | Heteropriacanthus cruentatus |  | ||
| longspine squirrelfish | Holocentrus rufus |  | ||
| plate fish | Bothus lunatus |  | ||
| red lionfish (invasive) | Pterois volitans |  | ||
| spotfin butterflyfish | Chaetodon ocellatus |  | ||
| trumpetfish | Aulostomus maculatus |  | ||
| Sponges | azure vase sponge | Callyspongia plicifera |  | |
| yellow tube sponge | Aplysina fistularis |  | ||
| green finger sponge | Iotrochota birotulata | |||
| orange icing sponge | Mycale laevis | |||
| pink vase sponge | Niphates digitalis | |||
| row pore rope sponge | Aplysina cauliformis | |||
| touch-me-not sponge | Neofibularia nolitangere | |||
| demosponges | Cliona sp. | |||
| Cliona aprica | ||||
| Cliona delitrix | ||||
| Cliona varians | ||||
| Aiolochroia crassa | ||||
| Ectyoplasia ferox | ||||
| Ircinia felix | ||||
| Mycale laxissima | ||||
| Plakortis angulospiculatus | ||||
| Scopalina ruetzleri | ||||
| Smenospongia aurea | ||||
| Spirastrella coccinea | ||||
| Corals | boulder brain coral | Colpophyllia natans |  | |
| Caribbean sea whip | Plexaura homomalla |  | ||
| elkhorn coral | Acropora palmata |  | ||
| great star coral | Montastraea cavernosa |  | ||
| maze coral | Meandrina meandrites |  | ||
| purple sea fan | Gorgonia ventalina |  | ||
| sea ginger | Millepora alcicornis |  | ||
| Crustaceans | Caribbean spiny lobster | Panulirus argus |  | |
| Echinoderms | donkey dung sea cucumber | Holothuria mexicana |  | |
| Mollusks | queen conch | Lobatus gigas |  | |
See also
References
Citations
- Area Calculator
- Distance Calculator
- Caballero et al., 2009, p.95
- (in Spanish) Bucear en Playa Girón - Bahía de Cochinos
- Claro, Rodolfo; García-Arteaga, Juan P.; Gobert, Bertrand; Cantelar Ramos, Karel (13 May 2003). "Tabla 2. Pesos y tallas mínimos legales en Cuba y proporción de peces con tallas inferiores en las capturas con chinchorros y nasas de la empresa pesquera de Caibarién" (pdf). Situación actual de los recursos pesqueros del Archipiélago Sabana-Camagüey, Cuba. Invemar. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- "Common Names List - Balistes vetula". Fishbase.org. Retrieved 2015-04-17.
- Rodríguez Cruz, 1999, p.115
- (in Spanish) Cerca de 20 mansiones, tres yates y un helipuerto son algunas de las posesiones de Fidel Castro
- (in Spanish) La Cueva de los Peces, el cenote más profundo y bello de Cuba
- Rodríguez Schettino et al., 2013, pp.9–10
- Chevalier & Cárdenas, 2005, p.60
- Chevalier & Cárdenas, 2005, p.61
- Chaetodon striatus
- Lactophrys trigonus
- Ablennes hians
- Heteropriacanthus cruentatus
- Holocentrus rufus
- Bothus lunatus
- Pterois volitans
- Chaetodon ocellatus
- Aulostomus maculatus
- Callyspongia plicifera
- Caballero et al., 2009, p.101
- Colpophyllia natans
- Plexaura homomalla
- Acropora palmata
- Montastraea cavernosa
- Meandrina meandrites
- Gorgonia ventalina
- Millepora alcicornis
- Panulirus argus
- Holothuria mexicana
- Lobatus gigas
Sources
- Caballero, Hansel; Linnet Busutil; Yanel García, and Pedro M. Alcolado. 2009. Variación espacial en comunidades de esponjas de la costa oriental de Bahía de Cochinos, Cuba. Rev. Invest. Cost. I. 95–109. Accessed 2018-08-01.
- Chevalier, Pedro P., and Antonio L. Cárdenas. 2005. Variación espacial y temporal de las asociaciones de peces en arrecifes costeros de la costa oriental de la Bahía de Cochinos - II: Análisis multidimensional. Rev. Invest. Mar. 26. 59–66. Accessed 2018-08-01.
- Rodríguez Cruz, Juan Carlos. 1999. Bay of Pigs and the CIA, 1–212. Ocean Press, Melbourne. Accessed 2018-08-01.
- Rodríguez Schettino, Lourdes; Carlos A. Mancina, and Vilma Rivalta González. 2013. Reptiles of Cuba: Checklist and Geographic Distributions. Smithsonian Herpetological Information Service 144. 1–96. Accessed 2018-08-01.
Further reading
- Wyden, Peter. 1979. Bay of Pigs – The Untold Story. Simon and Schuster. New York. ISBN 0-671-24006-4 ISBN 0224017543 ISBN 978-0-671-24006-6
External links
