Battle of Parker's Cross Roads
The Battle of Parker's Cross Roads was fought on December 31, 1862, in Henderson County, Tennessee, during the American Civil War.
| Battle of Parker's Cross Roads | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of American Civil War | |||||||
 A replica cannon on the site of the battle. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Jeremiah C. Sullivan | Nathan Bedford Forrest | ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
|
50th Indiana Infantry Regiment 122nd Illinois Infantry Regiment 18th Illinois Mounted Infantry Regiment 39th Iowa Infantry Regiment 7th Wisconsin Artillery Battery 27th Ohio Infantry Regiment 39th Ohio Infantry Regiment 63rd Ohio Infantry Regiment |
8th Tennessee Cavalry 4th Alabama Cavalry 19th Tennessee Cavalry Napier's Cavalry Battalion Kentucky Battalion 4th Tennessee Cavalry 2nd Battalion Tennessee Cavalry Freeman's Battery Morton's Battery | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 3,000 | 1,800 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 237 | 500 | ||||||
Background
As Confederate Brig. Gen. Nathan Bedford Forrest's expedition into West Tennessee neared its conclusion, Union Brig. Gen. Jeremiah C. Sullivan, with the brigades of Cols. Cyrus L. Dunham and John W. Fuller, attempted to cut Forrest off from withdrawing across the Tennessee River.
Battle
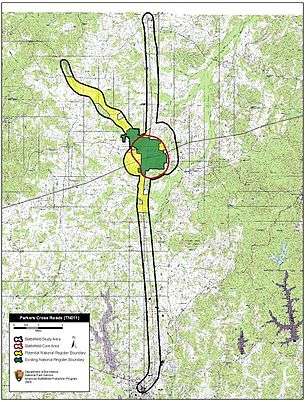
Dunham's and Forrest's march routes brought them into contact at Parker's Crossroads on December 31, 1862. Skirmishing began about 9:00 a.m., with Forrest taking an initial position along a wooded ridge northwest of Dunham at the intersection. Confederate artillery gained an early advantage. Dunham pulled his brigade back a half mile and redeployed, facing north. His Federals repelled frontal feints until attacked on both flanks and rear by Forrest's mounted and dismounted troops.
During a lull, Forrest sent Dunham a demand for an unconditional surrender. Dunham refused and was preparing for Forrest's next attack when Fuller's Union brigade arrived from the north and surprised the Confederates with an attack on their rear; Confederate security detachments had failed to warn of Fuller's approach. "Charge 'em both ways," ordered Forrest. The Confederates briefly reversed front, repelled Fuller, then rushed past Dunham's demoralized force and withdrew south to Lexington, Tennessee.
Aftermath
After the fight, Forrest was able to cross the Tennessee River. Both sides claimed this battle as a victory, but the Confederate claims appear to have more credence.
Battlefield preservation

The land upon which the Battle of Parker’s Crossroads took place is now traversed east and west by Interstate 40 and north and south by Tennessee State Route 22, located midway between Memphis and Nashville. The nearby town has grown considerably since the interstate highway opened in the late 1960s.Developers and investors are constantly looking at the battlefield area for business development, making preservation efforts particularly urgent.[1]
368 acres of the battlefield have been saved thus far, all by the Civil War Trust (a division of the American Battlefield Trust) in consort with its partners, including a local group, The Parker's Crossroads Battlefield Association.[2] In 2011, the Trust inaugurated a campaign to preserve what is called the “keystone tract,” the final unpreserved piece of land from the old battlefield. It was on this 52-acre parcel where most of the Confederate artillery was located. Many preservationists believe that if this land falls into the hands of commercial developers, the ability to interpret the battlefield in a meaningful way will be lost.[3]
References
- "Then and Now: The Battle of Parker's Crossroads," Civil War Trust, 2011
- American Battlefield Trust "Saved Land" webpage. Accessed May 25, 2018.
- "A Message From Jim Lighthizer," Civil War Trust, 2011 Archived 2012-12-23 at the Wayback Machine