BBC Worldwide
BBC Worldwide Ltd. was the wholly owned commercial subsidiary of the BBC, formed out of a restructuring of its predecessor BBC Enterprises in January 1995. The company monetises BBC brands, selling BBC and other British programming for broadcast abroad with the aim of supplementing the income received by the BBC through the licence fee.
 Final logo from BBC Worldwide | |
Formerly | BBC Enterprises Ltd. (1979–1995) |
|---|---|
| Subsidiary | |
| Industry | Broadcasting |
| Fate | Merged into BBC Studios |
| Predecessor | BBC Enterprises |
| Successor | BBC Studios |
| Founded | 15 May 1979 |
| Founder | BBC |
| Defunct | 1 April 2018 |
| Headquarters | Television Centre, London , United Kingdom |
Area served | Worldwide |
Key people | Tony Hall (Chairman) Tim Davie (CEO) |
| Owner | BBC |
| Website | www |
The company merged with BBC Studios on 1 April 2018, to form a new licensing, production, and distribution company under the BBC Studios name.
History
Origins
In addition to broadcasting, the BBC has for much of its life also produced additional materials for sale, the profits of which would be returned to the corporation to aid in the financing of these services. The highest profile of these early products was the listings magazine Radio Times, but the net revenue gained from this in 1928 (£93,686, 10s, 1d) only equated to 10% of total BBC income.[1]
Prior to 1979, several BBC departments dealt with the exploitation and sale of BBC brands and programmes. BBC Publications, which produced magazines, books and other supplementary materials, had expanded rapidly in the late 1960s but still had difficulties with finances. In 1974, the division made a loss of £14,000.[1] This was rectified however as the economic situation eased and by 1982, BBC Publications had a trading profit of £4.7 million.[1] BBC Transcription Services licensed BBC Radio material to overseas broadcasters.
The selling of television programmes was at first handled in 1958 with the establishment of a business manager post.[1] This gradually expanded until the establishment of the Television Promotions (later renamed Television Enterprises) department in 1960 under a general manager.[1] In its first year, the department saw the sale of 550 programmes overseas with a turnover of £234,000,[1][2] with a further 1,200 programmes sold the following year.[1] Radio programmes were only exploited on the same level with the creation of the Radio Enterprises department in 1965. However, following the retirement of the Radio Enterprises general manager in 1969, the two departments were merged to form the BBC Enterprises department.
BBC Enterprises
On 15 May 1979, the department became BBC Enterprises Ltd., a subsidiary company wholly owned by the BBC.[1][2] By 1982, the division were expanding with divisions responsible for home video (under the brand BBC Video), recorded audio (under the brands BBC Records and BBC Cassettes), film and merchanding. At this point the company had a turnover of £23 million.[1] On 1 April 1986, all commercial activities of the corporation, including BBC Publications, was merged into BBC Enterprises Ltd.[3]
In 1991. BBC World Service Television became the first commercially funded BBC broadcasting operation after the Foreign Office refused to pay for it.[4] BBC Enterprises Ltd was subsequently reorganised on 1 January 1995 as BBC Worldwide Ltd.[5] A review of the BBC's commercial activities took place in 2004 and concluded that the sell off of BBC Worldwide's assets would not be as advantageous as keeping the business and driving it harder. Instead, some changes to its remit, focus, structure and governance were made, e.g. that it would only publish titles in the UK linked to BBC programmes or key genres.
Acquisitions and restructuring
In 2004, BBC Video merged with Video Collection International to form 2 Entertain, which was 60% owned by BBC Worldwide; the following year the company sold Eve magazine to Haymarket Group[6] and in 2006 the company sold a majority stake in BBC Books to publisher Random House.[7]
In 2007, BBC Worldwide purchased a 75% stake in the travel guide publisher Lonely Planet,[8] acquiring the final 25% of the company in 2011.[9] The acquisition was part of the BBC's strategy to grow its online portfolio and to increase its operations in Australia and the USA.[10]
In January 2009, it was announced that Ofcom had put forward the recommendation that Channel 4 merge with either the commercial network Five or BBC Worldwide. Channel 4's preferred option of a partnership with the latter was confirmed by chief executive Andy Duncan, who added: "We're in discussions with BBC Worldwide at the moment and they're really very exciting."[11] In the same year, the company was awarded the Queen's Award for Enterprise in recognition of the companies growth and success.[12]
In 2012, the company began to reorganise their divisions from a product based system to a location-based system, resulting in Jana Bennett leaving the company.[13]
In 2013, BBC Worldwide sold Lonely Planet to Kentucky billionaire Brad Kelley's NC2 Media for US$75 million (£51.5 million)— significantly less than the £130.2 million the BBC had paid for the company, at an £80 million loss.[14]
In 2017, under revisions to the BBC Charter and subsequent BBC Trust approval, the broadcaster formed a second commercial subsidiary known as BBC Studios, to hold most of the broadcaster's in-house production units (including Factual, Entertainment, Scripted, and Music & Events). In return for the restructuring, which also allows the BBC to produce programmes for competing broadcasters to fund its public services, the BBC agreed to allow BBC Studios and third-parties to bid on tenders to produce its in-house non-news programmes over the next 11 years.[15][16][17][18] On 29 November 2017, the BBC announced that BBC Worldwide would be merged into BBC Studios in April 2018, which gave the broadcaster an integrated division involved in both the production and sale of programming.[19][20]
BBC Worldwide profit and sales 1995–2012

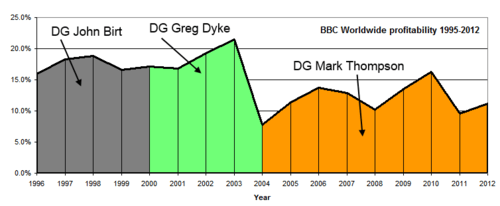
In 2013/14, BBC Worldwide generated headline profits of £157.4m and headline sales of £1,042.3m and returned £173.8m to the BBC.[21]
In 2012/13, it made a profit of £156.3m on a turnover of £1,115.8m.[22] The company had made a profit of £104m on a turnover of £1,085m in the previous financial year.[23]
BBC Worldwide's profit rate was 11.2% in 2011/2012, up slightly from 9.6% the previous year, down from a peak of 21.5% in 2002/2003, contrasting with 7.8% in 2003/2004.[24]
| Date | Headline Sales (2014) | Profit (2014) | Sales (Cash) | Profit (Cash) | Profit rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995/1996 | £527m | £84m | £332m | £53m | 15.9%[25] |
| 1996/1997 | £630m | £115m | £409m | £75m | 18.3%[24] |
| 1997/1998 | £640m | £120m | £430m | £81m | 18.8% |
| 1998/1999 | £726m | £120m | £495m | £82m | 16.5% |
| 1999/2000 | £798m | £136m | £560m | £96m | 17.1% |
| 2000/2001 | £885m | £148m | £632m | £106m | 16.7% |
| 2001/2002 | £881m | £169m | £640m | £123m | 19.2% |
| 2002/2003 | £879m | £188m | £657m | £141m | 21.4% |
| 2003/2004 | £917m | £71m | £706m | £55m | 7.7% |
| 2004/2005 | £991m | £112m | £784m | £89m | 11.3% |
| 2005/2006 | £992m | £135m | £810m | £111m | 13.7% |
| 2006/2007 | £1,076m | £138m | £916m | £118m | 12.8% |
| 2007/2008 | £1,134m | £116m | £1,004m | £103m | 10.2% |
| 2008/2009 | £1,219m | £164m | £1,074m | £145m | 13.5% |
| 2009/2010 | £1,256m | £204m | £1,158m | £188m | 16.2% |
| 2010/2011 | £1,119m | £107m | £1,085m | £104m | 9.5% |
| 2011/2012 | £1,115m | £125m | £1,115m | £125m | 11.2% |
Historical price conversion as per RPI figures from "Office for National Statistics – Dataset selector". Retrieved 24 August 2013.
Operations


In 2013, BBC Worldwide reorganised the company along geographical, rather than divisional, lines to better serve its audiences around the world and to position itself to take advantage of opportunities in high growth markets. The seven geographic markets are grouped into three regions: North America; UK, Australia and New Zealand; and Global Markets (Asia, CEMA, Latin America and Western Europe). The two global business areas – Content and Brands – set the strategic framework and parameters for activities within the regions and keep a close connection into BBC Worldwide's parent, the BBC. Digital is embedded throughout the business.[26]
BBC Worldwide was responsible for a wide range of commercial activities, primarily connected in some way with the output and public purposes of the main BBC. In the past, the business was divided into five operating businesses which covered the entire operations of the company: Channels; Content and Production; Brands, Consumers and New Ventures, Consumer Products and Sales and Distributions.
The Channels division was formed in 2005[27] and is the company's largest generator of revenue and growth. It operates the broadcasting of several international channels and domestic networks:[27]
- BBC America – 50.1% with AMC Networks owning 49.99%
- BBC Canada – 20% with Corus Entertainment owning 80%
- BBC Entertainment
- BBC First
- BBC Brit
- BBC Earth
- BBC HD
- BBC Kids – 20% with Knowledge Network Corporation owning 80%
- BBC Knowledge
- BBC Lifestyle
- CBeebies
- CBBC
- British UKTV network of 10 channels – 50% with Discovery, Inc. owning the other 50%
- BBC UKTV in Australia and New Zealand
The Content and Production division was formed in 2006 and invests the company's money into new productions by both the BBC and other independent productions.[28] It also exploits the formats of BBC programmes and alters them to be suitable for an international audience – an example is the exploitation of the Strictly Come Dancing brand to become Dancing with the Stars – maximising revenues by receiving a production fee from the local broadcaster as well as a sum from selling the initial re-versioning rights.[28] The division works alongside the Sales and Distribution division, which sells the broadcasting rights to completed programmes made by the BBC and other producers – an example being the Red Production Company drama Mine All Mine for the ITV network in 2004. It includes the selling of individual clips through the BBC Motion Gallery to other broadcasters. In the financial year 2010/11, this division sold the rights to over 74,000 hours worth of television content.[29]
The other two divisions of the company deal with the individual programme brands: Global Brands focuses on the international recognition of the brands[30] while the Consumer Products division produces a variety of goods based around these brands. The work of the former includes expanding the brands into new areas – the Top Gear Live tour is a key example of this.[30] The latter creates and sells a variety of consumer products, occasionally as a stake or partnership in another company, including VHS and DVD releases, spoken word and music audio products, CD-ROMs, videogames, books and magazines.[31]
Assets and brands
- Owned video publishing company 2 Entertain with products dual branded 2 Entertain and BBC.
- Owned Demon Music Group.
- The BBC Shops closed in 2016, although Worldwide still retains Doctor Who and Top Gear branded online shops.
- Operated the BBC Motion Gallery.
- Operated the BBC Store until its closure in November 2017.
- 12.2% stake in production company Left Bank Pictures.[32]
- held 25% stake in Cliffhanger Productions, an independent production company.[33]
- held 25% stake in BBC Children's Books, an imprint of Penguin Group who hold a 75% stake.[34]
- Licensed the publishing of magazine titles to the Immediate Media Company. The titles were formerly published in-house by BBC Magazines.
- Licensed audio content to Penguin Random House UK for global sales and distribution.[35][36] Titles were previously published in-house by BBC Radio Collection and BBC Audiobooks and later by AudioGO, in which BBC Worldwide held a 15% stake.[37][38]
- Held minority share in BBC Books, with Random House Group taking majority share.[7] Books published using BBC Books brand.
- Held minority stake in BBC Active, with Pearson PLC taking the majority share.[39] The brand publishes educational material.
- In partnership with ITV, launched a US SVOD service, BritBox, launching in March 2017.[40][41]
These commercial activities allow BBC Worldwide to return profits and dividends to the BBC to re-invest in its broadcasting operations. In 2007/08 BBC Worldwide invested £75.1m in in-house and independent programmes commissioned by the BBC. However, the BBC has often been criticised for the amount of money it makes from BBC Worldwide. Some commercial rivals protest at the advantage the company has from being associated with and being able to exploit the programme catalogue and resources of the BBC to provide its goods and services.[42]
References
- Cain, John (1992). The BBC: 70 years of broadcasting. London: British Broadcasting Corporation. pp. 116–119. ISBN 0-563-36750-4.
- "1970s" (PDF). The BBC Story. BBC. Retrieved 5 June 2012.
- Cain, John (1992). The BBC: 70 years of broadcasting. London: British Broadcasting Corporation. p. 150. ISBN 0-563-36750-4.
- Crisell, Andrew (1997). An Introductory History of British Broadcasting. Routledge. p. 24. ISBN 0-415-12802-1.
- Webmaster. "British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) – Public Opinions International". pubopinions.org. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 10 October 2017.
- "BBC Worldwide announces sale of eve magazine to Haymarket". BBC Press Office. 11 January 2005. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- "The Random House Group acquires majority shareholding in BBC Books". BBC Press Office. 22 June 2006. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- "BBC buys Lonely Planet". The Age. 1 October 2007. Retrieved 1 October 2007.
- "BBC takes last slice of Planet". The Sydney Morning Herald. 20 February 2011. Retrieved 5 March 2011.
- "BBC Worldwide acquires Lonely Planet". BBC Worldwide Press Release. BBC Press Office. 1 October 2007. Retrieved 19 March 2013.
- "Channel 4 'must form partnership'". BBC News. 21 January 2009. Retrieved 29 March 2009.
Channel 4 should become part of a bigger organisation through a merger or partnerships, Ofcom has recommended.
- Shearman, Sarah (21 April 2009). "BBC Worldwide wins Queen's Enterprise award". MediaWeek. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- "Jana Bennett to leave BBC Worldwide". BBC News. 22 June 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- "BBC Worldwide sells Lonely Planet business at £80m loss". BBC News. 19 March 2013. Retrieved 19 March 2013.
- "BBC to begin making programmes for other broadcasters". Radio Times. Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- Williams, Christopher (20 December 2016). "BBC Studios wins go-ahead for commercial production push". The Daily Telegraph.
- "BBC Studios approved to launch commercially". Realscreen. Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- Gannagé-Stewart, Hannah (7 January 2016). "BBC Studios takes shape". Broadcast.
- Chu, Henry (29 November 2017). "BBC Worldwide, BBC Studios to Merge into Single Operation". Variety. Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- White, Peter (29 November 2017). "BBC To Merge BBC Worldwide & BBC Studios Into $1.9B Company". Deadline Hollywood. Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- "BBC Worldwide – Annual Review 2013/14 – Annual Review 2014". Archived from the original on 14 August 2014. Retrieved 14 August 2014.
- "BBC Worldwide – Annual Review 2012/13 – Annual Review 2013". Archived from the original on 7 July 2014. Retrieved 14 August 2014.
- "BBC Worldwide – Annual Review 2011/12 – Annual Review 2012". Archived from the original on 5 September 2013. Retrieved 6 September 2013.
- "Annual Review". Archived from the original on 14 September 2013. Retrieved 6 September 2013.
- "BBC Worldwide Annual Report and Accounts". Archived from the original on 18 August 2000. Retrieved 6 September 2013.
- "About Us". BBC Worldwide. Retrieved 14 August 2014.
- "Channels". BBC Worldwide. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- "Content & Production". BBC Worldwide. Archived from the original on 4 July 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- "Sales & Distribution". BBC Worldwide. Archived from the original on 4 July 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- "Global Brands". BBC Worldwide. Archived from the original on 3 October 2012. Retrieved 11 October 2012.
- "Consumer Products". BBC Worldwide. Archived from the original on 9 June 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- "The Telegraph" Sony takes stake in Left Bank The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 7 September 2012
- "BBC Worldwide buys into Cliffhanger". BBC Press Office. 22 November 2007. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- "Penguin Books and BBC Worldwide form new venture for BBC Children's Books". BBC Press Office. 30 April 2004. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- "BBC Worldwide partners with Random House Audio for new publishing and distribution deal". BBC Media Centre. 20 December 2013. Retrieved 31 March 2014.
- "Penguin Random House UK extends relationship with BBC Worldwide to become the global publisher and distributor of BBC Audio content" (Press release). The Random House Group. 20 May 2015. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- "BBC Worldwide announces sale of majority shareholding in BBC Audiobooks". BBC Press Office. 14 July 2010. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- Sweney, Mark (14 July 2010). "BBC Audiobooks sold". The Guardian. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- "BBC Active signals new partnership for BBC Worldwide and Pearson Education". BBC Press Office. 13 October 2005. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- "BBC – BBC Worldwide and ITV partner to bring new SVOD service BRITBOX to the US – Media Centre". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 2 April 2017.
- "BBC, ITV launch BritBox video streaming service in U.S." Reuters. 7 March 2017. Retrieved 2 April 2017.
- "About BBC Worldwide". BBC Worldwide. 2008/09. Archived from the original on 6 October 2009. Retrieved 10 September 2009. Check date values in:
|year=(help)
External links
- Official website
- BBC Worldwide's channel on YouTube
- BBC Studios Distribution (formerly BBC Worldwide) at Companies House