Azabon
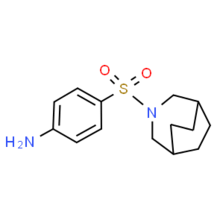
Azabon is a central nervous system stimulant[1] of the sulfonamide class[2] that is also used as a nootropic.[3] As it is a sulpha drug, care must be taken during administration, and certain individuals must avoid azabon altogether to prevent an allergic reaction. Despite being a sulfonamide, azabon has poor antibacterial potency, although this decreased activity is common among other benzenesulfonamides with two substituents on N1. Azabon is synthesized from 3-azabicyclo-[2.2.2]nonane, which is itself prepared by pyrolysis of aliphatic diamine.[4]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H20N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 280.386 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
See also
References
- Mathews SM, Jiju V, Thomas I, Panicker JT, Kuriakose LS (2015-07-28). "Sulfa drugs and the skin" (PDF). World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 4 (10): 382–390. ISSN 2277-7105.
- WO 2011089215, Vetter D, Rau H, "Dipeptide-based prodrug linkers for aromatic amine-containing drugs", published 28 July 2011, assigned to Ascendis Pharma AS
- Mao F, Ni W, Xu X, Wang H, Wang J, Ji M, Li J (January 2016). "Chemical Structure-Related Drug-Like Criteria of Global Approved Drugs". Molecules. 21 (1): 75. doi:10.3390/molecules21010075. PMC 6273477. PMID 26771590.
- Lednicer D, Mitscher LA (1980). The Organic Chemistry of Drug Synthesis (PDF). 2. Wiley Interscience. p. 115. ISBN 0-471-04392-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.