Apical foramen
In anatomy the apical foramen is the opening at the apex of the root of a tooth, through which the nerve and blood vessels that supply the dental pulp pass. Thus it represents the junction of the pulp and the periodontal tissue.[1]
| Apical foramen | |
|---|---|
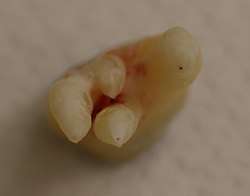 Apical foramina on a wisdom tooth | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | foramen apicis dentis |
| TA | A05.1.03.050 |
| FMA | 57159 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
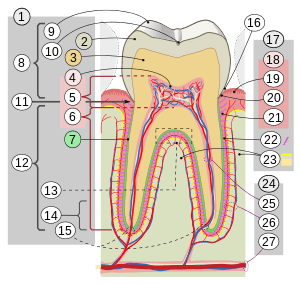
17. Periodontium
:18. Gingiva: ::19. free or interdental ::20. marginal ::21. alveolar :22. Periodontal ligament :23. Alveolar bone 24. Vessels and nerves: :25. dental :26. periodontal :27. alveolar through channel
Characteristics
The average size of the orifice is 0.3 to 0.4 mm in diameter. There can be two or more foramina separated by a portion of dentin and cementum or by cementum only. If more than one foramen is present on each root, the largest one is designated as the apical foramen and the rest are considered accessory foramina.[1]
Apical delta
Apical delta refers to the branching pattern of small accessory canals and minor foramina seen at the tip or apex of some tooth roots. The pattern is said to be reminiscent of a river delta when sectioned and viewed using a microscope. Because the anatomy of this area is very small and complex with several portals of entry to the root canal i.e. more than one apical foramen.[1]
Endodontic treatment
It is a point of interest in endodontics, as it is considered necessary to thoroughly chemomechanically debride the pulp space to remove all necrotic tissue and minimise bacterial load in the pulp space. Ideally this debridement would terminate exactly at the apical foramen. In reality determining the exact position of the apical foramen is problematic, requiring radiography and/or use of an electronic apex locator to produce a refined estimate. A tooth may have multiple small accessory canals in the root apex area forming an apical delta which can complicate the endodontic problem.[1]
The presence of an apical delta may make successful endodontic treatment less likely. The root tip is removed during apicoectomy to eliminate the apical delta and maximise the chance of successful healing.[1]
An apical constriction is often present. In immature teeth the root is not fully formed leading to an open apex. This is also seen in some pathological teeth.[1]
References
- Color Atlas and Textbook of Oral Anatomy, Histology, and Embryology by B. K. Berkovitz, G. R. Holland, B. J. Moxham Hardcover, Mosby, ISBN 0-8151-0697-1 (0-8151-0697-1)