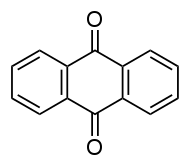
Anthraquinone
Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene, is an aromatic organic compound with formula C
14H
8O
2. Isomers include various quinone derivatives. The term anthraquinone, however refers to the isomer, 9,10-anthraquinone (IUPAC: 9,10-dioxoanthracene) wherein the keto groups are located on the central ring. It is a building block of many dyes and is used in bleaching pulp for papermaking. It is a yellow, highly crystalline solid, poorly soluble in water but soluble in hot organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble in ethanol near room temperature but 2.25 g will dissolve in 100 g of boiling ethanol.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Anthraquinone | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 390030 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.408 |
| 102870 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3143 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 208.216 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
| Density | 1.308 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 286 °C (547 °F; 559 K) |
| Boiling point | 379.8 °C (715.6 °F; 653.0 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H350 |
| P201, P202, P281, P308+313, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 185 °C (365 °F; 458 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
quinone, anthracene |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis
There are several current industrial methods to produce 9,10-Anthraquinone:
- The oxidation of anthracene, a reaction that is localized at the central ring. Chromium(VI) is the typical oxidant.
- The Friedel-Crafts reaction of benzene and phthalic anhydride in presence of AlCl3 producing o-benzoylbenzoic acid which then undergoes cyclization, forming anthraquinone. This reaction is useful for producing substituted anthraquinones.
- The Diels-Alder reaction of naphthoquinone and butadiene followed by oxidative dehydrogenation
- The acid-catalyzed dimerization of styrene to give a 1,3-diphenylbutene, which then can be transformed to the anthraquinone.[1] This process was pioneered by BASF.
It also arises via the Rickert-Alder reaction, a retro-Diels-Alder reaction.
Reactions
Hydrogenation gives dihydroanthraquinone (anthrahydroquinone). Reduction with copper gives anthrone.[2] Sulfonation with sulfuric acid gives anthroquinone-1-sulfonic acid,[3], which reacts with sodium chlorate to give 1-chloroanthaquinone.[4]
Applications
Digester additive in papermaking
9,10-Anthraquinone is used as a digester additive in production of paper pulp by alkaline processes, like the Kraft, the alkaline sulfite or the Soda-AQ processes. The anthraquinone is a redox catalyst. The reaction mechanism may involve single electron transfer (SET).[5] The anthraquinone is oxidizing the reducing end of polysaccharides in the pulp, i.e., cellulose and hemicellulose, and thereby protecting it from alkaline degradation (peeling). The anthraquinone is reduced to 9,10-dihydroxyanthracene which then can react with lignin. The lignin is degraded and becomes more watersoluble and thereby more easy to wash away from the pulp, while the antraquinone is regenerated. This process gives an increase in yield of pulp, typically 1-3% and a reduction in kappa number.[6]
Other isomers
Several other isomers of anthraquinone are possible, including the 1,2-, 1,4-, and 2,6-anthraquinones. They are of comparatively minor importance. The term is also used in the more general sense of any compound that can be viewed as an anthraquinone with some hydrogen atoms replaced by other atoms or functional groups. These derivatives include substances that are technically useful or play important roles in living beings.
Recently, a class of anthraquinone derivates were shown to have self-healing properties when doped in PMMA matrix.[9]
Safety
Anthraquinone has no recorded LD50, probably because it is so insoluble in water. Many drugs are derivatives of anthroquinone.[1]
In terms of metabolism of substituted anthraquinones, the enzyme encoded by the gene UGT1A8 has glucuronidase activity with many substrates including anthraquinones.[10]
See also
References
- Vogel, A. "Anthraquinone". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_347.
- Macleod, L. C.; Allen, C. F. H. (1934). "Benzanthrone". Organic Syntheses. 14: 4. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.014.0004.
- Scott, W. J.; Allen, C. F. H. (1938). "Potassium Anthraquinone-α-Sulfonate". Organic Syntheses. 18: 72. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.018.0072.
- Scott, W. J.; Allen, C. F. H. (1938). "α-Chloroanthraquinone". Organic Syntheses. 18: 15. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.018.0015.
- Samp, J. C. (2008). A comprehensive mechanism for anthraquinone mass transfer in alkaline pulping (Thesis). Georgia Institute of Technology. p. 30. hdl:1853/24767.
- Sturgeoff, L. G.; Pitl, Y. (1997) [1993]. "Low Kappa Pulping without Capital Investment". In Goyal, G. C. (ed.). Antraquinone Pulping. TAPPI Press. pp. 3–9. ISBN 0-89852-340-0.
- "www.americanheritage.com". Archived from the original on 2009-06-09. Retrieved 2009-09-22.
- Dudding, Adam (29 July 2012). "How to solve a problem like a kea". Sunday Star Times. New Zealand. Retrieved 11 November 2014.
- Ramini, Shiva K.; Kuzyk, Mark G. (2012-08-07). "A self healing model based on polymer-mediated chromophore correlations". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 137 (5): 054705. arXiv:1205.0481. Bibcode:2012JChPh.137e4705R. doi:10.1063/1.4739295. ISSN 0021-9606. PMID 22894369.
- Ritter, J. K.; Chen, F.; Sheen, Y. Y.; Tran, H. M.; Kimura, S.; Yeatman, M. T.; Owens, I. S. (1992). "A Novel Complex Locus UGT1 Encodes Human Bilirubin, Phenol, and other UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase Isozymes with Identical Carboxyl Termini" (PDF). Journal of Biological Chemistry. 267 (5): 3257–3261. PMID 1339448.