AltaVista
AltaVista was a Web search engine established in 1995. It became one of the most-used early search engines, but lost ground to Google and was purchased by Yahoo! in 2003, which retained the brand, but based all AltaVista searches on its own search engine. On July 8, 2013, the service was shut down by Yahoo! and since then the domain has redirected to Yahoo!'s own search site.[2]
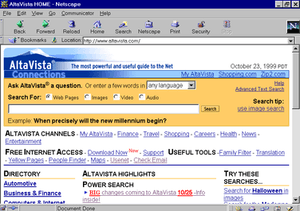 Top: 2002–2013 AltaVista logo Bottom: The AltaVista web portal in 1999 | |
Type of site | Search engine |
|---|---|
| Available in | Multilingual |
| Founded | 1995 |
| Headquarters | , |
| Key people | Paul Flaherty, Louis Monier, Michael Burrows, Jeffrey Black |
| Parent | Overture Services (2003) Yahoo! (2003–2013) Verizon Media (2017–present) |
| URL | AltaVista.com |
| Alexa rank | |
| Advertising | Yes |
| Registration | No |
| Launched | December 15, 1995 |
| Current status | Defunct (July 8, 2013)[2] |
Etymology
The word "AltaVista" is formed from the words for "high view" or "upper view" in Spanish (alta + vista); thus, it colloquially translates to "overview".[3][4]
Origins
AltaVista was created by researchers at Digital Equipment Corporation's Network Systems Laboratory and Western Research Laboratory who were trying to provide services to make finding files on the public network easier.[5] Paul Flaherty came up with the original idea,[6][7] along with Louis Monier and Michael Burrows, who wrote the Web crawler and indexer, respectively. The name "AltaVista" was chosen in relation to the surroundings of their company at Palo Alto, California. AltaVista publicly launched as an Internet search engine on December 15, 1995, at altavista.digital.com.[8][9]
At launch, the service had two innovations that put it ahead of other search engines available at the time: It used a fast, multi-threaded crawler (Scooter) that could cover many more Web pages than were believed to exist at the time, and it had an efficient back-end search, running on advanced hardware.
Popularity and technologies
AltaVista was the first searchable, full-text database on the World Wide Web with a simple interface.[10]
As of 1998, it used 20 multi-processor machines using DEC's 64-bit Alpha processor. Together, the back-end machines had 130 GB of RAM and 500 GB of hard disk drive space, and received 13 million queries every day.[11] Another distinguishing feature of AltaVista was its minimalistic interface, which was lost when it became a Web portal, but regained when it refocused its efforts on its search function. It also allowed the user to limit search results from a domain, reducing the likelihood of multiple results from the same source.
AltaVista's site was an immediate success. Traffic increased steadily from 300,000 hits on the first day to more than 80 million hits per day two years later. The ability to search the Web, and AltaVista's service in particular, became the subject of numerous articles and even some books.[5] The AltaVista site became one of the top destinations on the Web, and in 1997 it earned US$50 million in sponsorship revenue.[12] It was the 11th most visited Web site in 1998 and in 2000.[13]
AltaVista was the most favored search engine used by professional researchers at the "Internet Search-Off" study in February 1998, with 45 percent of the researchers choosing that. Second place belonged to HotBot at 20 percent.[14] At the time, AltaVista also powered Yahoo!, which was the most popular search Web site overall.[15]
By using the data collected by the crawler, employees from AltaVista, together with others from IBM and Compaq, were the first to analyze the strength of connections within the budding World Wide Web in a seminal study in 2000.[16]
In 2000, AltaVista was used by 17.7% of Internet users while Google was only used by 7% of Internet users, according to Media Metrix.[17]
Business transactions
In 1996, AltaVista became the exclusive provider of search results for Yahoo!. In 1998, Digital was sold to Compaq, and in 1999, Compaq redesigned AltaVista as a Web portal, hoping to compete with Yahoo!. Under CEO Rod Schrock, AltaVista abandoned its streamlined search page and focused on adding features such as shopping and free e-mail.[18] In June 1998, Compaq paid AltaVista Technology Incorporated ("ATI") $3.3 million for the domain name altavista.com – Jack Marshall, cofounder of ATI, had registered the name in 1994.
In June 1999, Compaq sold a majority stake in AltaVista to CMGI, an Internet investment company.[19] CMGI filed for an initial public offering (IPO) for AltaVista to take place in April 2000, but when the Internet bubble collapsed, the IPO was cancelled.[20] Meanwhile, it became clear that AltaVista's Web portal strategy was unsuccessful, and the search service began losing market share, especially to Google. After a series of layoffs and several management changes, AltaVista gradually shed its portal features and refocused on search. By 2002, AltaVista had improved the quality and freshness of its results and redesigned its user interface.[21]
In February 2003, AltaVista was bought by Overture Services, Inc. for $140 million.[22] In July 2003, Overture was taken over by Yahoo!.[23] After Yahoo! purchased Overture, AltaVista used the same search index as Yahoo! Search.[3]
In December 2010, a Yahoo! employee leaked PowerPoint slides indicating that the search engine would shut down as part of a consolidation at Yahoo!.[24]
Free services
AltaVista provided Babel Fish, a Web-based machine translation application that translated text or Web pages from one of several languages into another.[25] It was later superseded by Yahoo! Babel Fish in May 2008 and now redirects to Bing's translation service.[3][26][10] AltaVista also provided a free email service, which shut down on March 31, 2002, at 12:00 PM PST, and which had 400,000 (200,000 active) registered email accounts before shutting down.[27]
Shutdown
On June 28, 2013, Yahoo! announced on its Tumblr page that AltaVista would shut down on July 8, 2013.[28][29][30] Since the day AltaVista shut down, visits to AltaVista's home page are redirected to Yahoo!'s main page.[2]
See also
References
- "altavista.com Competitive Analysis, Marketing Mix and Traffic - Alexa". alexa.com. Retrieved May 29, 2020.
- Rossiter, Jay (June 28, 2013). "Keeping our Focus on What's Next". yahoo.tumblr.com. Retrieved June 16, 2019.
- "Search engine rankings on Alta Vista: a brief history of the AltaVista search engine". websearchworkshop.co.uk. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
- Sherman, Chris (October 8, 2003). "What's In A (Search Engine's) Name?". Search Engine Watch. Retrieved September 3, 2019.
- Ray, Eric J.; Ray, Deborah S.; Selzer, Richard (May 1, 1998). The AltaVista Search Revolution (2nd ed.). Osborne/McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0078824357.
- Alleman, Andrew (June 1, 2011). "Viking Office Products Tries to Take Sentimental Domain Name from Altavista Inventor's Widow". Domain Name Wire.
- Daniel B. Banks, Jr. (May 31, 2011). "National Arbitration Forum Decision Claim Number: FA1104001383534". ADR Forum. Archived from the original on June 22, 2012. Retrieved January 28, 2012.
- Lewis, Peter H. (December 18, 1995). "Digital Equipment Offers Web Browsers Its 'Super Spider'". The New York Times.
- Digital Press and Analysts News (December 15, 1995). "Digital Develops Internet's First 'Super Spider'". Newsgroup: biz.digital.announce. Retrieved February 26, 2007.
- "Short History of Early Search Engines". The History of SEO. Retrieved February 5, 2019.
- Baeza-Yates, Ricardo; Ribeiro-Neto, Berthier (2010). Modern Information Retrieval: The Concepts and Technology behind Search. Addison-Wesley/ACM Press. pp. 374, 390. ISBN 978-0321416919.
- Battelle, John (September 14, 2006). The Search: How Google and Its Rivals Rewrote the Rules of Business and Transformed Our Culture. Portfolio publishing. ISBN 978-1857883626.
- Barba, Ronald (December 26, 2014). "The Top 20 Most Popular Websites: 1996 to the Present [INFOGRAPHIC]". tech.co.
- Feldman, Susan. "The Internet Search-Off". Information Today. Archived from the original on December 5, 1998.
- "Considered ... Staying ahead in existing markets?". webculture.co.uk. Archived from the original on June 15, 2009.
- Broder, Andrei; Kumar, Ravi; Maghoul, Farzin; Raghavan, Prabhakar; Rajagopalan, Sridhar; Stata, Raymie; Tomkins, Andrew; Wiener, Janet. "Graph structure in the web (paper presented to the 9th International WWW Conference, Amsterdam, May 2000)". Computer Networks.
- Patsuris, Penelope (October 20, 2000). "Don't Count AltaVista Out Yet". Forbes.
- Kopytoff, Verne (March 27, 2000). "AltaVista Switches Web Portal Into High Gear / Revamped site adds new services". San Francisco Chronicle.
- Afzali, Cyrus (June 29, 1999). "CMGI Acquires 83 Percent of AltaVista for $2.3 Billion". internet.com.
- Barnes, Cecily (January 10, 2001). "AltaVista cancels proposed IPO". news.com. Archived from the original on January 4, 2013.
- Glasner, Joanna (November 13, 2002). "AltaVista Makeover: A Better View". Wired.
- Hansell, Saul (February 19, 2003). "Overture Services to Buy AltaVista for $140 Million". The New York Times.
- "YAHOO! TO ACQUIRE OVERTURE (press release)". Yahoo! Media Relations. July 14, 2003. Archived from the original on July 8, 2007.
- "RIP AltaVista, Yahoo Buzz, Delicious, MyBlogLog". Silicon Tap. December 16, 2010.
- "Babelfish: English". infotektur.com. May 27, 1999. Archived from the original on April 27, 1999.
- "Welcoming Yahoo! Babel Fish users!". Microsoft Translator Blog. May 30, 2012.
- Richardson, Tim (February 20, 2002). "AltaVista cans Web mail service". The Register.
- Lepitak, Stephen (July 2, 2013). "Yahoo! announces closure of AltaVista". The Drum. Retrieved September 4, 2019.
- "Yahoo shuts down internet relic AltaVista". CBC News. July 8, 2013.
- "Yahoo sends search engine relic AltaVista to Internet graveyard". National Post. July 8, 2013.