Alpine states
The term Alpine states or Alpine countries refers to the territory of eight countries associated with the Alpine region, as defined by the Alpine Convention of 1991: Austria, France, Germany, Italy, Liechtenstein, Monaco, Slovenia, and Switzerland.[1] This territory includes 83 NUTS 3-level local administrative divisions and about 6,200 municipalities.
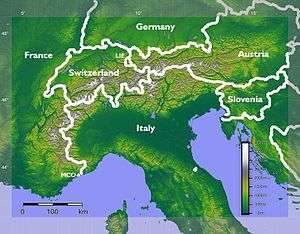
In a narrow sense, the term "Alpine states" could be applied to Austria (28.7% of the total area), Italy (27.2%), and France (21.4%), which represent more than 77% of the Alpine territory and more than three quarters of the Alpine population. However, the Alpine share of the larger Italian and French state territories only amounts to 17% and 7% respectively. From a strictly national point of view, and with the exception of microstates Liechtenstein and Monaco, the Alps are dominant in only two countries: Austria (65.5% of its territory) and Switzerland (65%).
See also
- Association of the Alpine States (on state level)
- Andean states
- Himalayan states
References
- "The contracting Parties of the Alpine Convention". Archived from the original on 2011-02-13. Retrieved 2011-01-21.