Aloe succotrina
Aloe succotrina, the Fynbos aloe, is an aloe which is endemic to Cape Town and the south-western corner of the Western Cape, South Africa.
| Aloe succotrina Fynbos aloe | |
|---|---|
| The Fynbos aloe in flower in its natural habitat. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Asphodelaceae |
| Subfamily: | Asphodeloideae |
| Genus: | Aloe |
| Species: | A. succotrina |
| Binomial name | |
| Aloe succotrina | |
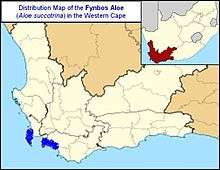 | |
| Aloe succotrina is restricted to the mountains of the Cape Peninsula, and the mountainous coast between Kogelberg and Hermanus | |
Distribution
Aloe succotrina is naturally found on the Cape Peninsula, and as far as Mossel Bay to the east. This aloe is common in Peninsula Sandstone Fynbos vegetation, and typically grows high up on cliff faces and rocky outcrops where seasonal fires do not reach it. It is one of the few Aloes that naturally occur in fynbos habitats - along with the Fan Aloe and Aloiampelos commixta of Table Mountain.
It is one of only three aloes and their relatives, with Aloiampelos commixta and Aloe maculata, that are indigenous to the city of Cape Town.
Description
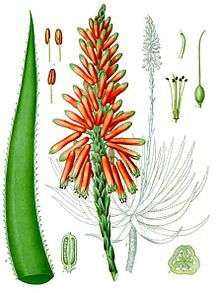
The Aloe succotrina plant forms clusters of between 1–2 metres (3.3–6.6 ft) diameter, with its leaves forming dense rosettes. In winter when it flowers (June to September) it produces a tall raceme, bearing shiny red flowers that are pollinated by sunbirds.
Taxonomically, it forms part of the Purpurascentes series of very closely related Aloe species, together with Aloe microstigma, Aloe gariepensis, Aloe khamiesensis and Aloe framesii.[1]
Cultivation and Uses
Aloe succotrina can easily be grown as an ornamental plant in Mediterranean climate gardens, rockeries, and in containers. It is particularly striking in winter, when it flowers. Western Cape gardens use it in Fynbos native plant themed natural landscaping. The plant prefers a sunny, well drained spot. Space should be provided for maturity, as it eventually grows into a large and dense cluster.
The Fynbos aloe can be propagated both by cuttings/offshoots or by seed.
This species has uses as a medicinal plant.[2]
See also
- Biodiversity of Cape Town
- Cape Floristic Region
- Index: Fynbos - habitats and species.
- Table Mountain
- Table Mountain National Park
References
- Reynolds, G.W. 1950. The aloes of Southern Africa. Balkema, Cape Town.
- Köhler, Franz Eugen (1887) Köhler's Medicinal Plants
Gallery
 Inflorescence detail.
Inflorescence detail.- Foliage detail.
- Adult Fynbos aloes on a Cape Peninsula rock face.