Ahmarian
The Ahmarian culture[1][2][3][4][5][6] was a Paleolithic archeological industry in Levant dated at 46,000-42,000 BP and thought to be related to Levantine Emiran and younger European Aurignacian cultures.
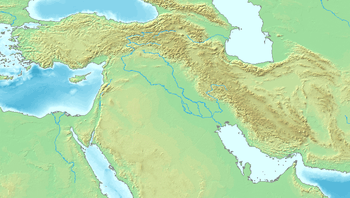 Ahmarian culture Map showing the approximate location of the Ahmarian culture | |
| Geographical range | Levant |
|---|---|
| Period | Upper Paleolithic |
| Dates | c. 46,000 – c. 42,000 BP |
| Preceded by | Aterian, Emiran, Bohunician |
| Followed by | Levantine Aurignacian Châtelperronian Aurignacian (Europe) |
| The Paleolithic |
|---|
| ↑ Pliocene (before Homo) |
|
|
|
|
Fertile Crescent:
|
| ↓ Mesolithic |
The word “Ahmarian” was adopted from the archaeological site of Erq el-Ahmar (also written Erk el Ahmar), Israel, a rockshelter in the Judean Desert in the northern Dead Sea Rift. It was explored and excavated by French Prehistorian René Neuville in 1951.[7] The "Ahmarian" category had only been recognized since the 1980s, and was previously designated as "Phase II Upper Paleolithic" or "Ksar Akil Phase B".[8][9]
Ahmarian period
The Ahmarian period together with the Emiran period, both from the Levant, are among the very first periods of the Upper Paleolithic, corresponding to the first stages of the expansion of Homo sapiens out of Africa. From this stage, the first modern humans migrated to Europe to form the beginning of the European Upper Paleolithic, including the Aurignacian culture, where they become known as the Cro-Magnons.[10]
The European Bohunician culture, probably linked to the Emiran and Ahmarian, may slightly predate the Ahmarian at 48,000 BP.[11] There is also a claim that it is roughly contemporary with the Aurignacian and the Gravettian cultures of Europe, all emerging prior to the Atlitian, which was also contemporary with the Solutrean and Magdalenian cultures of Western Europe.[12]
The technical knowledge of the Ahmarian culture, along with the other lithic industries, is considered the likely source of the abrupt and rapid takeover of the world in all directions as evidenced by the crossing of the Bering Strait towards America.[13] Ahmarian technology, which included the complex of blade/bladelet-knapping techniques is also linked to the tools used by the hunter-gatherers of southwestern Asia.[14]
Late Ahmarian is called Masraqan.[15]
Technology
Ahmarian blades are usually elongated with some curves.[7] The Levallois technique is still in use, but only sparsely, thereby making Ahmarian the first fully Upper Paleolithic period.[7]
Ahmarian assemblages can be found throughout the Levant, including Syria, Lebanon, Israel and Jordan.[7] The Lagaman industry in the Sinai can be considered as derivative to the Ahmarian culture.[7]
"Levantine Aurignacian", from the Levant, is a type of blade technology very similar to the European Aurignacian, immediately following chronologically the Emiran and Early Ahmarian in the same area of the Near East, and closely related to them.[7]
.jpg) Flint Knives, Ahmarian Culture, Nahal Boqer, 47,000-40,000 BP. Israel Museum.
Flint Knives, Ahmarian Culture, Nahal Boqer, 47,000-40,000 BP. Israel Museum..jpg) Stone core for making fine blades, Boqer Tachtit, Negev, Israel, circa 40,000 BP.
Stone core for making fine blades, Boqer Tachtit, Negev, Israel, circa 40,000 BP.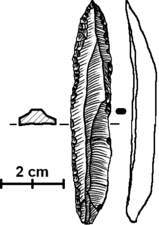
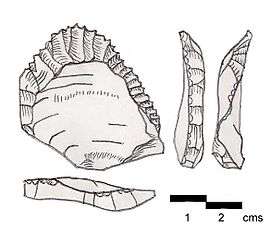 Ksar Akil flake made by Levallois technique. Found on the surface at Ksar Akil, Lebanon. Another point type typical of the Ahmarian culture (Northern Facies).[7]
Ksar Akil flake made by Levallois technique. Found on the surface at Ksar Akil, Lebanon. Another point type typical of the Ahmarian culture (Northern Facies).[7]- Entrance to el-Wad Cave, an important Ahmarian site
.jpg) Inside of el-Wad Cave.
Inside of el-Wad Cave.
Ahmarian sites
- Erq el-Ahmar (type site)
- Manot Cave
- Boker Tachtit
- Nahal Boqer
- El-Wad
- Ksar Akil (Ahmarian Northern Facies, Lebanon)
References
- "Archaeologists carbon dated a cave in Israel to reveal details about the two first modern human cultures". 28 December 2017.
- Kadowaki, Seiji; Omori, Takayuki; Nishiaki, Yoshihiro (2015). "Variability in Early Ahmarian lithic technology and its implications for the model of a Levantine origin of the Protoaurignacian". Journal of Human Evolution. 82: 67–87. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2015.02.017. PMID 25924809.
- Goring-Morris, Nigel; Belfer-Cohen, Anna (2018). "The Ahmarian in the Context of the Earlier Upper Palaeolithic in the Near East". The Middle and Upper Paleolithic Archeology of the Levant and Beyond. pp. 87–104. doi:10.1007/978-981-10-6826-3_7. ISBN 978-981-10-6825-6.
- Gilead, Isaac (1991). "The Upper Paleolithic period in the Levant". Journal of World Prehistory. 5 (2): 105–154. doi:10.1007/BF00974677.
- Akazawa, Takeru; Nishiaki, Yoshihiro; Aoki, Kenichi (16 December 2013). "Dynamics of Learning in Neanderthals and Modern Humans Volume 1: Cultural Perspectives". Springer Science & Business Media – via Google Books.
- https://books.google.com/books?id=KzZCDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA129
- Shea, John J. (2013). Stone Tools in the Paleolithic and Neolithic Near East: A Guide. Cambridge University Press. pp. 152–153. ISBN 9781107006980.
- Shea, John J. (2013). Stone Tools in the Paleolithic and Neolithic Near East: A Guide. Cambridge University Press. p. 154. ISBN 9781107006980.
- "(PDF) Selected Figures from Chapter 5. Upper Paleolithic | John Shea - Academia.edu".
- Klein, Richard G. (2009). The Human Career: Human Biological and Cultural Origins. University of Chicago Press. p. 610.
- Hoffecker, J. F (2009). "The spread of modern humans in Europe". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 106 (38): 16040–16045. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903446106. PMC 2752585. PMID 19571003.
- Avi-Yonah, Michael (2001). A History of Israel and the Holy Land. New York: Continuum. p. 20. ISBN 0826413226.
- Bachenheimer, Avi (2016). Gobekli Tepe: An Introduction to the World's Oldest Temple (Revised Edition). San Francisco, CA: Blurb, Incorporated. pp. 19–20. ISBN 9781366700940.
- De Laet, S.J.; Dani, A.H.; Lorenzo, J.L.; Nunoo, R.B. (1994). History of Humanity: Prehistory and the beginnings of civilization. London: Routledge. pp. 244. ISBN 0415093058.
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264357405_The_earlIer_Upper_Palaeolithic_a_VIew_from_The_Southern_Levant