Afzelechin
Afzelechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in Bergenia ligulata (a.k.a. Paashaanbhed in Ayurveda traditional Indian medicine).[1] It exists as at least 2 major epimers (afzelechin and epi-afzelechin).
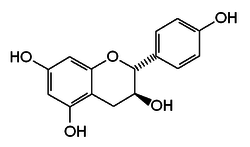 Chemical structure of Afzelechin (2R,3S) | |
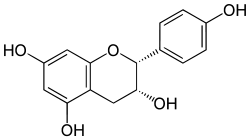 Chemical structure of Epiafzelechin (2R,3R) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Afzelechin - (2R,3S)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromene-3,5,7-triol Epiafzelechin - (2R,3R)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromene-3,5,7-triol | |
| Other names
3,5,7,4'-Tetrahydroxyflavan 3,4',5,7-Flavantetrol | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H14O5 | |
| Molar mass | 274.26 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Metabolism
(2R,3S)-catechin:NADP+ 4-oxidoreductase transforms cis-3,4-leucopelargonidin into afzelechin.[2]
Glycosides
Arthromerin A (afzelechin-3-O-β-D-xylopyranoside) and arthromerin B (afzelechin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside) are afzelechin glycosides isolated from the roots of the fern Arthromeris mairei.[3] (+)-afzelechin-O-β-4'-D-glucopyranoside can be isolated from the rhizomes of the fern Selliguea feei.[4]
Proanthocyanidins
- dimers
Afzelechin-(4alpha→8)-afzelechin (molecular formula : C30H26O10, molar mass : 546.52 g/mol, exact mass : 546.152597, CAS number : 101339-37-1, Pubchem CID : 12395) is a B type proanthocyanidin.
Ent-epiafzelechin-3-O-p-hydroxybenzoate-(4α→8,2α→O→7)-epiafzelechin) is an A-type proanthocyanidin found in apricots (Prunus armeniaca).[5]
- Trimers
Selligueain A (epiafzelechin-(4β-8,2β-0-7)-epiafzelechin-(4β-8)-afzelechin) is an A type proanthocyanidin.
References
- High pressure liquid chromatographic determination of bergenin and (+) -afzelechin from different parts of Paashaanbhed (Bergenia ligulata yeo). Umashankar D. Chandra Reddy, Amrik S. Chawla, Mundkinajeddu Deepak, Deepa Singh , Sukhdev S. Handa, 1997
- (2R,3S)-catechin:NADP+ 4-oxidoreductase on nashua.case.edu
- Two afzelechin glycosides from Arthromeris mairei. Yu Wen-Sheng, Li Hong, Chen Xin-Min and Yang Lei, Phytochemistry, December 1992, Volume 31, Issue 12, pages 4385–4386, doi:10.1016/0031-9422(92)80488-Z, INIST:4682275
- Flavonoids and a proanthrocyanidin from rhizomes of Selliguea feei. Baek Nam-In, Kennelly E.J, Kardono L.B.S, Tsauri S, Padmawinata K, Soejarto D.D and Kinghorn A.D, Phytochemistry, 1994, vol. 36, no 2, pages 513-518, INIST:3300075
- Prasad, D; Joshi, RK; Pant, G; Rawat, MS; Inoue, K; Shingu, T; He, ZD (1998). "An A-type proanthocyanidin from Prunus armeniaca". Journal of Natural Products. 61 (9): 1123–5. doi:10.1021/np970383n. PMID 9748379.