Acer micranthum
Acer micranthum, the small-leaved maple,[2] is a species of flowering plant in the family Sapindaceae in the snakebark maple group, native to Japan, on Honshū, Kyūshū and Shikoku. Its Japanese name is the Komine maple (Japanese: コミネカエデ, Hepburn: Kominekaede).[3][4][5][6][7][8][9]
| Acer micranthum | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Shoot with fruits | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Sapindaceae |
| Genus: | Acer |
| Section: | Acer sect. Macrantha |
| Species: | A. micranthum |
| Binomial name | |
| Acer micranthum | |
It is a small, sometimes shrubby tree growing 6–10 m (20–33 ft) tall, with slender, arching branches. The bark is smooth and striped at first, becoming rough and dull grey on mature trees. The shoots and winter buds are dark purple-red. The leaves are 4–10 cm long and 2–8 cm broad, palmately lobed, with five deeply toothed lobes with long acuminate tips and double-serrated margins, and with distinctive tufts of orange-red hairs in the main vein axils at the base of the leaf; the petiole is 2–5 cm long. The leaves emerge red in spring and turn shades of yellow, orange and red[2] in autumn. The flowers are produced in early summer in racemes 4–10 cm long, each flower 4 mm diameter, with five yellow to greenish-yellow sepals and petals; it is dioecious, with male and female flowers on separate trees. The fruit is a paired samara with two rounded nutlets, each with a wing 1.5–2 cm long; the two wings spreading almost horizontally from each other.[3][4][5][6][8][10][11]
It is most closely related to Acer tschonoskii, which replaces it further north and at higher altitudes in Japan; they have very similar leaf form.[8]
Acer micranthum is cultivated as an ornamental tree in European and North American gardens, and has gained the Royal Horticultural Society’s Award of Garden Merit.[2][12] Though hardy down to −20 °C (−4 °F), it requires a sheltered position in neutral or acid soil with sun or partial shade.
 Tree in cultivation, Denmark
Tree in cultivation, Denmark- Leaves, Rogów Arboretum, Poland
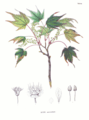 Illustration by Siebold & Zuccarini
Illustration by Siebold & Zuccarini
References
- The International Plant Names Index
- "Acer micranthum". www.rhs.org. RHS. Retrieved 26 September 2019.
- Kobe city: Acer micranthum Archived 2007-11-30 at the Wayback Machine (in Japanese; google translation)
- Kanagawa Prefecture trees and shrubs: Acer micranthum Archived 2012-03-23 at the Wayback Machine (in Japanese; google translation). Archived 2009-10-24.
- Okayama science university: Acer micranthum (in Japanese; google translation)
- Kanon tree book: Acer micranthum (in Japanese; google translation)
- Maple World: Maples of Japan Archived April 2, 2004, at the Wayback Machine
- Maple World: Komine-kaede Archived 2013-01-04 at Archive.today
- "Acer micranthum". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). Agricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- Ishikawa prefecture forestry research institute: Kominekaede Archived May 17, 2008, at the Wayback Machine (in Japanese; google translation)
- Kota's Nature Photo Gallery: Acer micranthum Archived November 20, 2007, at the Wayback Machine (in Japanese; google translation)
- "AGM Plants - Ornamental" (PDF). www.rhs.org. Royal Horticultural Society. July 2017. p. 1. Retrieved 18 February 2019.