S-300 missile system
The S-300 (NATO reporting name SA-10 Grumble) is a series of initially Soviet and later Russian long range surface-to-air missile systems produced by NPO Almaz, based on the initial S-300P version. The S-300 system was developed to defend against aircraft and cruise missiles for the Soviet Air Defence Forces. Subsequent variations were developed to intercept ballistic missiles. The S-300 system was first deployed by the Soviet Union in 1979, designed for the air defence of large industrial and administrative facilities, military bases and control of airspace against enemy strike aircraft. The system is fully automated, though manual observation and operation are also possible.[3][5] Components may be near the central command post, or as distant as 40 km. Each radar provides target designation for the central command post. The command post compares the data received from the targeting radars up to 80 km apart, filtering false targets, a difficult task at such great distances. The central command post features both active and passive target detection modes.[6][7]
| S-300 Family NATO reporting name: SA-10 Grumble, SA-12 Giant/Gladiator, SA-20 Gargoyle | |
|---|---|
.jpg) S-300 anti-aircraft missile system at the Victory Parade, Red Square, 9 May 2009. | |
| Type | Long-range SAM system |
| Place of origin | Soviet Union |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1978–present |
| Used by | See list of operators |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Almaz-Antey:
|
| Designed | 1967–2005[1] |
| Manufacturer | MZiK[2] |
| Produced | 1975[3]–2011 (for PS and PM)[4] V/F – free. |
| Variants | see variants |
The project-managing developer of the S-300 is Almaz-Antey. S-300 uses missiles developed by both MKB "Fakel" and NPO Novator design bureaus (separate government corporations, previously named "OKB-2" and "OKB-8").
The S-300 is regarded as one of the most potent anti-aircraft missile systems currently fielded.[8] It is mainly used in Asia and Eastern Europe, including three NATO member countries: Bulgaria, Greece and Slovakia. An evolved version of the S-300 system is the S-400 (NATO reporting name SA-21 Growler), which entered limited service in 2004.
Variations and upgrades
Serial production started in 1975.[3] The tests have been completed in 1978 (P) and 1983 (V + 1987 for anti-ballistic V).[9] Numerous versions have since emerged with different missiles, improved radars, better resistance to countermeasures, longer range and better capability against short-range ballistic missiles or targets flying at very low altitude. There are currently three main variations.
S-300 system family tree
| S-300 Family | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S-300V | S-300P | S-300F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S-300V1 | S-300V2 | S-300PT | S-300PS | Fort | Rif | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S-300VM | S-300PT-1 | S-300PM | S-300PMU | Fort-M | Rif-M | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Favorit-S | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S-300VM1 | S-300VM2 | S-300PT-1A | S-300PM1 | S-300PMU1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antey 2500 | S-300PM2 | S-300PMU2 | Domestic Version | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S-300V4 | Favorit | Export Version | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S-300VMD | S-400 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
S-300P
Land-based S-300P (SA-10)

The S-300P (transliterated from Russian С-300П, NATO reporting name SA-10 Grumble) is the original version of the S-300 system which became operational in 1978.[1] In 1987, over 80 of these sites were active, mainly in the area around Moscow. The P suffix stand for PVO-Strany (country air defence system). An S-300PT unit consists of a 36D6 (NATO reporting name TIN SHIELD) surveillance radar, a 30N6 (FLAP LID) fire control system and 5P85-1 launch vehicles. The 5P85-1 vehicle is a semi-trailer truck. Usually a 76N6 (CLAM SHELL) low altitude detection radar is also a part of the unit.[10]
This system broke substantial new ground, including the use of a passive electronically scanned array radar and multiple engagements on the same Fire-control system (FCS). Nevertheless, it had some limitations. It took over one hour to set up this semi-mobile system for firing and the hot vertical launch method employed scorched the TEL.[11]

It was originally intended to fit the Track Via Missile (TVM) guidance system onto this model. However, the TVM system had problems tracking targets below 500 m. Rather than accept the limitation, the Soviets decided that the tracking of low altitude targets was a must and decided to use a pure command-guidance system until the TVM head was ready.[11] This allowed the minimum engagement altitude to be set at 25 m.
Improvements to the S-300P have resulted in several major sub-versions for both the internal and the export market. The S-300PT-1 and S-300PT-1A (SA-10b/c) are incremental upgrades of the original S300PT system. They introduce the 5V55KD missile and the cold launch method thereafter employed. Time to readiness was reduced to 30 minutes and trajectory optimizations allowed the 5V55KD to reach a range of 75 km.[11]

The S-300PS/S-300PM (Russian С-300ПC/С-300ПМ, NATO reporting name SA-10d/e) was introduced in 1985 and is the only version thought to have been fitted with a nuclear warhead. This model saw the introduction of the modern TEL and mobile radar and command-post vehicles that were all based on the MAZ-7910 8 × 8 truck.[1] This model also featured the new 5V55R missiles which increased maximum engagement range to 90 km (56 mi) and introduced a terminal semi-active radar homing (SARH) guidance mode. The surveillance radar of these systems was designated 30N6. Also introduced with this version was the distinction between self-propelled and towed TELs. The towed TEL is designated 5P85T. Mobile TELs were the 5P85S and 5P85D. The 5P85D was a "slave" TEL, being controlled by a 5P85S "master" TEL. The "master" TEL is identifiable thanks to the large equipment container behind the cabin; in the "slave" TEL this area is not enclosed and is used for cable or spare tyre storage.
The next modernisation, called the S-300PMU (Russian С-300ПМУ, US DoD designation SA-10f) was introduced in 1992 for the export market and featured the upgraded 5V55U missile which still utilised the intermediate SARH terminal guidance method and smaller warhead of the 5V55R but increased the engagement envelope to give this missile roughly the same range and altitude capabilities as the newer 48N6 missile (max. range 150 km/93 mi). The radars were also upgraded, with the surveillance radar for the S-300PMU being designated 64N6 (BIG BIRD) and the illumination and guidance radar being designated 30N6-1 in the GRAU index.
- S-300P total produced: 3000 launchers, 28,000 missiles for the S-300P[12]
S-300PMU-1/2 (SA-20)

The S-300PMU-1 (Russian: С-300ПМУ-1, US DoD designation SA-20A, NATO reporting name SA-20 Gargoyle) was also introduced in 1993 with the new and larger 48N6 missiles for the first time in a land-based system and introduced all the same performance improvements from the S300FM version including the increased speed, range, TVM guidance and ABM capability.[13][14] The warhead is slightly smaller than the naval version at 143 kg (315 lb). This version also saw the introduction of the new and more capable 30N6E TOMB STONE radar.
The S-300PMU-1 was introduced in 1993 and for the first time introduces several different kinds of missiles in a single system. In addition to the 5V55R and 48N6E missiles the S-300PMU-1 can utilise two new missiles, the 9M96E1 and 9M96E2. Both are significantly smaller than the previous missiles at 330 and 420 kg (730 and 930 lb) respectively, and carry smaller 24 kg (53 lb) warhead. The 9M96E1 has an engagement range of 1–40 km (0.62–25 mi) and the 9M96E2 of 1–120 km (0.62–75 mi). They are still carried 4 per TEL. Rather than just relying on aerodynamic fins for manoeuvring, they use a gas-dynamic system which allows them to have an excellent probability of kill (Pk) despite the much smaller warhead. The Pk is estimated at 0.7 against a tactical ballistic missile for either missile. The S-300PMU-1 typically uses the 83M6E command and control system, although it is also compatible with the older Baikal-1E and Senezh-M1E CCS command and control systems. The 83M6E system incorporates the 64N6E (BIG BIRD) surveillance/detection radar. The fire control/illumination and guidance radar used is the 30N6E(1), optionally matched with a 76N6 low altitude detection radar and a 96L6E all altitude detection radar. The 83M6E command and control system can control up to 12 TELs, both the self-propelled 5P85SE vehicle and the 5P85TE towed launchers. Generally support vehicles are also included, such as the 40V6M tow vehicle, intended for lifting of the antenna post.
China is building its own version of the S-300PMU-1, called HQ-10.[15]

The S-300PMU-2 Favourite (Russian: С-300ПМУ-2 Фаворит – Favourite, DoD designation SA-20B), introduced in 1997 (presented ready 1996), is an upgrade to the S-300PMU-1 with range extended once again to 195 km (121 mi) with the introduction of the 48N6E2 missile. This system is apparently capable against not just short range ballistic missiles, but now also medium range ballistic missiles. It uses the 83M6E2 command and control system, consisting of the 54K6E2 command post vehicle and the 64N6E2 surveillance/detection radar. It employs the 30N6E2 fire control/illumination and guidance radar. Like the S-300PMU-1, 12 TELs can be controlled, with any mix of 5P85SE2 self-propelled and 5P85TE2 trailer launchers. Optionally it can make use of the 96L6E all altitude detection radar and 76N6 low altitude detection radar.[16] A version titledHQ-15 is currently in Chinese service.[17]
S-300F
Sea-based S-300F (SA-N-6)
The S-300F Fort (Russian С-300Ф Форт, DoD designation SA-N-6, F suffix for Flot, Russian for fleet) was introduced in 1984 as the original ship-based (naval) version of the S-300P system developed by Altair with the new 5V55RM missile with range extended to 7–90 km (4.3–56 mi; 3.8–49 nmi) and maximum target speed up to Mach 4 while engagement altitude was reduced to 25–25,000 m (82–82,021 ft). The naval version utilises the TOP SAIL or TOP STEER, TOP PAIR and 3R41 Volna (TOP DOME) radar and utilises command guidance with a terminal semi-active radar homing (SARH) mode. Its first installation and sea trials were on a Kara class cruiser and it is also installed on Slava class cruisers and Kirov class battlecruisers. It is stored in eight (Slava) or twelve (Kirov) 8-missile rotary launchers below decks. The export version of this system is known as Rif (Russian Риф – reef). The NATO name, found also in colloquial use, is "Grumble".
Sea-based S-300FM (SA-N-20)
The S-300FM Fort-M (Russian С-300ФМ, DoD designation SA-N-20) is another naval version of the system, installed only on the Kirov-class cruiser Pyotr Velikiy, and introduced the new 48N6 missile. It was introduced in 1990 and increased missile speed to approximately Mach 6 for a maximum target engagement speed of up to Mach 8.5, increased the warhead size to 150 kg (330 lb) and increased the engagement range yet again to 5–150 km (3.1–93 mi) as well as opening the altitude envelope to 10–27 km (6.2–16.8 mi). The new missiles also introduced the ultimate track-via-missile guidance method and brought with it the ability to intercept short-range ballistic missiles. This system makes use of the TOMB STONE MOD rather than TOP DOME radar. The export version is called the Rif-M. Two Rif-M systems were purchased by China in 2002 and installed on the Type 051C air-defence guided missile destroyers.
Both naval versions are believed to include a secondary infrared terminal seeker, similar to the newer US Standard missile system, probably to reduce the system's vulnerability to saturation. This also allows the missile to engage contacts over the radar horizon, such as warships or sea-skimming anti-ship missiles.
S-300V (SA-12)
In service 1984.

The 9K81 S-300V Antey-300 (Russian 9К81 С-300В Антей-300 – named after Antaeus, NATO reporting name SA-12 Gladiator/Giant) varies from the other designs in the series. This complex is not part of the C-300, including is designed by another developer.[18] It was built by Antey rather than Almaz,[19] and its 9M82 and 9M83 missiles were designed by NPO Novator. The V suffix stands for Voyska (ground forces). It was designed to form the top tier army air defence system, providing a defence against ballistic missiles, cruise missiles and aircraft, replacing the SA-4 Ganef. The "GLADIATOR" missiles have a maximum engagement range of around 75 km (47 mi) while the "GIANT" missiles can engage targets out to 100 km (62 mi) and up to altitudes of around 32 km (20 mi). In both cases the warhead is around 150 kg (330 lb).
Radar modes are different and it requires the use of all methods of jamming, while S-300V system works completely passive mode.[18]
While it was created from the same project, hence the common S-300 designation, different priorities resulted in a design quite different from the other versions. The S-300V system is carried on tracked MT-T transporters, which gives it better cross-country mobility than even the S-300Ps on 8 × 8 wheeled transporters. It is also somewhat more distributed than the S-300P's. For example, while both have mechanically-scanning radar for target acquisition (9S15 BILL BOARD A), the battery level 9S32 GRILL PAN has an autonomous search ability and SARH delegated to illumination radar on TELARs. The early 30N6 FLAP LID on the S-300P handles tracking and illumination, but is not equipped with an autonomous search capability (later upgraded). 9S15 can simultaneously carry out an active search for goals (3 coordinates) and passive (2 position).[7]
Chance to destroy a target by using single missile an interceptor (The official source)[20] Adopted in service in 1983 (1983 just using the missile 9M83), fully accepted in 1988.[7][20] [21]
9M83 /Chance/ MGM-52 Lance.......... 0,5-0,65
9M82 /Chance/ MGM-31 Pershing...... 0,4-0,6
9M83 /Chance/ aircraft........................ 0,7-0,9
9M82 /Chance/ SRAM rocket.............. 0,5-0,7

The S-300V places a greater emphasis on the ABM, with the dedicated 9M82 (SA-12B Giant) Anti-Ballistic missile. This missile is larger and only two can be held on each TELAR. It also has a dedicated ABM radar: the 9S19 HIGH SCREEN phased array radar at battalion level. A typical S-300V battalion is made up out of a target detection and designation unit, a guidance radar and up to 6 TELARs. The detection and designation unit consists of the 9S457-1 command post, a 9S15MV or 9S15MT BILL BOARD all-round surveillance radar and 9S19M2 HIGH SCREEN sector surveillance radar.[22] The S-300V uses the 9S32-1 GRILL PAN multi-channel guidance radar. Four types of missile-launcher vehicles can be used with the system:[23]
- Transporter erector and radar (TELAR) vehicles, which not only transport the missiles, but also fire and guide them (includes radar illumination and targeting as well[24]). There are two models: the 9A83-1 TELAR holding four 9M83 GLADIATOR missiles and the 9A82 TELAR holding two 9M82 GIANT missiles.[23]
- Launcher/loader vehicles (LLV), which transport the missiles and can reload the TELARs, and also fire missiles under the control of a TELAR. There are two models: the 9A84 LLV holding two 9M83 GLADIATOR missiles and the 9A85 LLV holding two 9M82 GIANT missiles.[23]
 9S15M Obzor-3 acquisition radar
9S15M Obzor-3 acquisition radar
Target detection range.[25]
- 9S15M - 10 m2 - 330 km and 3 m2 - 240 km.
- 9S19M2 - 175 km (? m2) and two passive electronically scanned array, very high resistance to interference.
- 9S32M (TELAR 9A82/9A83) range is limited to 200 km, can work independently, or target designation from the C-300B, or a variety of other target designation data systems (AWACS aircraft and various ground-based radar). The size of 0.1 square metres (of the target - warhead of a ballistic missile) at ranges up to 140 km, and not less than 120. Alogically, 9S32 detection range - MGM-52 Lance 60 km, aircraft missiles 80 km, fighter or ballistic missile MGM-31 Pershing (all of which the U.S. removed from service in 1991)140 km[26][27]
- Size of 0.05 square meters at a distance of 30 km (aiming system in the rocket (10/3 seconds before the missiles hit the target)) in addition, the guidance system inside the rocket, supplements for missile guidance systems on commands from the 9A82 / 9A83 and 9S32, and missile guidance systems to passively on the radar illumination and radiation of 9A82 / 9A83.
S-300V system may be controlled by an upper level command post system 9S52 Polyana-D4 integrating it with Buk missile system into a brigade.
China has built its own version of the S-300V called HQ-18.[28]
S-300VM (SA-23)
The system is available abroad (1996)
The S-300VM (Antey 2500) is an upgrade to the S-300V. It consists of a new command post vehicle, the 9S457ME and a selection of new radars. These consist of the 9S15M2, 9S15MT2E and 9S15MV2E all-round surveillance radars, and the 9S19ME sector surveillance radar. The upgraded guidance radar has the Grau index 9S32ME. The system can still employ up to six TELARs, the 9A84ME launchers (up to 4 × 9M83ME missile) and up to 6 launcher/loader vehicles assigned to each launcher (2 × 9M83ME missile each). An upgraded version, dubbed S-300V4 will be delivered to the Russian army in 2011.[29]
The Antey-2500 complex is the export version developed separately from the S-300 family and has been exported to Venezuela for an estimated export price of 1 billion dollars. The system has one type of missile in two versions, basic and amended with a sustainer stage that doubles the range (up to 200 km (120 mi), according to other data up to 250 km (160 mi)) and can simultaneously engage up to 24 aircraft or 16 ballistic targets in various combinations.
- Became the first system in the world capable of simultaneously engaging cruise missiles, aircraft and ballistic targets. It also contains a private sector radar for countering areas affected by interference.[30]
S-300V4
The S-300V4 is also called S-300VMD.[31] It is reportedly capable of targeting AWACS aircraft at very large distances.[32][33] Different versions of the NPO Novator 9M82MD[34] S-300V4 missiles have a range of 400 km at Mach 7.5 or a range of 350 km at Mach 9 and can destroy maneuvering targets even at very high altitudes.[35][36] Gladiator rockets significantly less. An export version exists, marketed as the Antey-4000.[37]
S-400 (SA-21)
The S-400 Triumf (Russian С-400 «Триумф», formerly known as the S-300PMU-3/С-300ПМУ-3, NATO reporting name SA-21 Growler) was introduced in 1999 and features a new, much larger missile. The new complex is totally different. The project has been encountering delays since its original announcement and deployment has only begun on a small scale in 2006. With an engagement range of up to 400 km (250 mi), depending on the missile variant used, and specifically designed to counter stealth, it is by far the most advanced version incorporating the ability to survive PGM threats and counter advanced jammers by using automatic frequency hopping.[38]
Specifications
An important quality of all complexes of the family of S-300 is the ability to work in various combinations within a single modification and within the same complex, between the modifications (limited), as well as through a variety of mobile superior command posts to line up in a battery of any composition, quantity, modifications, location and so on including the introduction of other air defence systems into a common battery.[39] the System for the defence of the major industrial and administrative objects, military bases and control points from the shock means of air-space attack of the enemy. Capable of hitting ballistic and aerodynamic targets. Became the first multi-channel anti-aircraft missile system, is able to accompany each system (ADMS) to 6 goals and build them up to 12 missiles. When creating funds management (FM), consisting of paragraph combat control and radar detection, solved the problem of automatic track initiation of up to one hundred goals and effective management divisions, located at a distance of 30–40 km from the (FM).
For the first time established a system with full automation of combat operation. All tasks—detection, tracking, target setting is considered, target designation, development of target designation, target acquisition, maintenance, capture, tracking and missile guidance, assessment of results of firing system capable of dealing automatically with the help of digital computing facilities. The operator functions are to control over the work of funds and implementation of the launch of rockets. In a complex environment, you can manually intervene in the course of combat operation. None of the previous systems possessed these qualities. Vertical launch missiles provided bombardment of targets flying from any direction without the reversal of the launcher in the direction of the shooting.[30][40]
Missiles are guided by the 30N6 FLAP LID or naval 3R41 Volna (TOP DOME) radar using command guidance with terminal semi-active radar homing. Later versions use the 30N6 FLAP LID B or TOMB STONE radar to guide the missiles via command guidance/seeker-aided ground guidance (SAGG). SAGG is similar to the Patriot's TVM guidance scheme. The earlier 30N6 FLAP LID A can guide up to four missiles at a time to up to four targets, and can track up to 24 targets at once. The 30N6E FLAP LID B can guide up to two missiles per target to up to six targets simultaneously. Targets flying at up to Mach 2.5 can be successfully engaged or around Mach 8.5 for later models. One missile can be launched every three seconds. The mobile control centre is able to manage up to 12 TELs simultaneously.
The original warhead weighed 100 kg (220 lb), intermediate warheads weighed 133 kg (293 lb) and the latest warhead weighs 143 kg (315 lb). All are equipped with a proximity fuse and contact fuse. The missiles themselves weigh between 1,450 and 1,800 kg (3,200 and 3,970 lb). Missiles are catapulted clear of the launching tubes before their rocket motor fires, and can accelerate at up to 100 g (1 km/s²). They launch straight upwards and then tip over towards their target, removing the need to aim the missiles before launch. The missiles are steered with a combination of control fins and through thrust vectoring vanes. The sections below give exact specifications of the radar and missiles in the different S-300 versions. Since the S-300PM most vehicles are interchangeable across variations.
Radar
The 30N6 FLAP LID A is mounted on a small trailer. The 64N6 BIG BIRD is mounted on a large trailer along with a generator and typically towed with the now familiar 8-wheeled truck. The 76N6 CLAM SHELL (5N66M[41] etc.) is mounted on a large trailer with a mast which is between 24 and 39 m (79 and 128 ft) tall. Usually is used with a mast. Target detection range of 90 km if altitude of the target of 500 meters above the ground (with a mast).[41]
The original S-300P utilises a combination of the 5N66M continuous-wave radar Doppler radar for target acquisition and the 30N6 FLAP LID A I/J-band phased array digitally steered tracking and engagement radar. Both are mounted on trailers. In addition there is a trailer-mounted command centre and up to twelve trailer-mounted erector/launchers with four missiles each. The S-300PS/PM is similar but uses an upgraded 30N6 tracking and engagement radar with the command post integrated and has truck-mounted TELs.
If employed in an anti-ballistic missile or anti-cruise missile role, the 64N6 BIG BIRD E/F-band radar would also be included with the battery. It is capable of detecting ballistic missile class targets up to 1,000 km (620 mi) away travelling at up to 10,000 km/h (6,200 mph) and cruise missile class targets up to 300 km (190 mi) away. It also employs electronic beam steering and performs a scan once every twelve seconds.
The 36D6 TIN SHIELD radar can also be used to augment the S-300 system to provide earlier target detection than the FLAP LID radar allows. It can detect a missile-sized target flying at an altitude of 60 metres (200 ft) at least 20 km (12 mi) away, at an altitude of 100 m (330 ft) at least 30 km (19 mi) away, and at high altitude up to 175 km (109 mi) away. In addition a 64N6 BIG BIRD E/F band target acquisition radar can be used which has a maximum detection range of 300 km (190 mi).
The S-300 FC Radar Flap Lid can be mounted on a standard pylon.
| GRAU index | NATO reporting name | Specialisation | Target detection range | Simultaneously detected targets | NATO frequency band | First used with | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36D6 | TIN SHIELD | – | 180–360 km (110–220 mi) | 120 | E/F | S-300P | Industrial designation: ST-68UM 350 kW to 1.23 MW power |
| 76N6 | CLAM SHELL | Low altitude detection | I | S-300P | |||
| 76N6 | CLAM SHELL | Low altitude detection | 120 km (75 mi) | 180 | I | S-300PMU | 1.4 kW FM continuous wave |
| 64N6 | BIG BIRD | Regiment radar | 300 km (190 mi) | 300 | C | S-300PMU-1 | |
| 96L6E | CHEESE BOARD | All altitude detection | 300 km | 100 | S-300PMU-1 | ||
| 9S15 | BILL BOARD | – | 250 km (160 mi) | 250 | S | S-300V | |
| 9S19 | HIGH SCREEN | Sector tracking | 16 | S-300V | |||
| MR-75[42] | TOP STEER | Naval | 300 km | D/E | S-300F | ||
| MR-800 Voskhod[42] | TOP PAIR | Naval | 200 km (120 mi) | C/D/E/F | S-300F |
| GRAU index | NATO reporting name | NATO frequency band | Target detection range | Simultaneously tracked targets | Simultaneously engaged targets | First used with | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30N6 | FLAP LID A | I/J | 4 | 4 | S-300P | ||
| 30N6E(1) | FLAP LID B | H-J | 200 km (120 mi) | 6 | 6 | S-300PMU | Phased array |
| 30N6E2 | FLAP LID B | I/J | 200 km | 6 | 6 | S-300PMU-2 | |
| 9S32-1 | GRILL PAN | Multi-band | 140–150 km (87–93 mi) | 6 | 6 | S-300V | |
| 3R41 Volna | TOP DOME | I/J | 100 km (62 mi) | S-300F |
Extrasystemic Radar (greater effectiveness)
Compared. C-300 its own listed above. Includes powerful 91N6E Anti – stealth range 150,[43] RCS 4scm 390 km, 0.4 m2 for 240 km.[44] Extrasystemic Radar multiply ability. Approximately 4-fold.
- Anti – stealth: Protivnik-GE, Gamma-DE UHF radar 0.1 m2 for 240 km[45]
- United against all targets "Niobium" RLS (not excluding ballistic or stealth). Mobility 5 minutes. Frequency band S and UHF. Detection range of 600 km (1 sqm to 430 km), the target speed of 8000 km / h, 4791 miles, Mach 6.35. For detection, the owner of the state to transfer command of targeting items (in this application, the maximum speed grows from subordinates systems).[46][47] Stealth. Quote - However, U.S. Air Force officials were dismissive of the technique. “Just because something is technically possible doesn't make it tactically feasible,” one Air Force official with extensive stealth aircraft experience explained. All locators "Nebo" family have a double for the army air defence.[48][49]
Missiles
| GRAU index | Year | Range | Maximum velocity | Maximum target Speed | Length | Diameter | Weight | Warhead | Guidance | First used with |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5V55K[50]/ 5V55R[51] | 1978/1982[52] | 47 km (29 mi) 75 km | 1,900 m/s (4,250 mph) | 1,150 m/s (2,572 mph) | 7 m (23 ft) | 450mm | 1,450 kg (3,200 lb) | 100 kg (220 lb) | Command | |
| 5V55R/5V55KD | after 1982[51] | 75/90 km (/56mile) | 1,900 m/s (4,250 mph) | 1,150 m/s (2,572 mph) | 7 m (23 ft) | 450mm | 1,450 kg (3,200 lb) | 133 kg (293 lb) | SARH | |
| 5V55U | 1992 | 150 km (93 mi) | 2,000 m/s (4,470 mph) | 7 m (23 ft) | 450mm | 1,470 kg (3,240 lb) | 133 kg (293 lb) | SARH | ||
| 48N6 | accepted on arms 1993[53] | 150 km (93 mi) | 2,000 m/s (4,470 mph) | 2,800 m/s (6,415 mph) | 7.5 m (25 ft) | 500mm | 1,780 kg (3,920 lb) | ≈150 kg (330 lb) | Track-via-missile (TVM) | |
| 48N6P-01 | 1992 | 195 km (121 mi) | 2,000 m/s (4,470 mph) | 2,800 m/s (6,415 mph) | 7.5 m (25 ft) | 500mm | 1,800 kg (4,000 lb) | 150 kg (330 lb) | TVM | |
| 9M82 | 1984 | 13–100 km (8.1–62.1 mi) 30 km (98,000 ft) alt | 2,400 m/s (5,400 mph) | 420 kg (930 lb) | 150 kg (330 lb) | SARH by TELAR | S-300V | |||
| 9M83 | 1984 | 6–75 km (3.7–46.6 mi) 25 km (82,000 ft) alt | 1,700 m/s (3,800 mph) | 150 kg (330 lb) | SARH by TELAR | S-300V | ||||
| 9M83ME | 1990 | 200 km (120 mi) | SARH by TELAR | S-300VM | ||||||
| 9M96E1 | 1999 | 40 km (25 mi) | 900 m/s[54] (2,010 mph) | 4,800–5,000 m/s (10,737–11,185 mph) | 330 kg (730 lb) | 24 kg (53 lb) | Active radar homing | S-400 | ||
| 9M96E2 | 1999 | 120 km (75 mi) | 1,000 m/s[54] (2,240 mph) | 4,800–5,000 m/s (10,737–11,185 mph) | 420 kg (930 lb) | 24 kg (53 lb) | Active Radar Homing | S-400 | ||
| 40N6 | 2000 | 400 km (250 mi) | Active Radar Homing | S-400 |
Means of camouflage and protection
- Masking components of S-300 systems are used in full-scale inflatable layouts, equipped with additional devices to simulate electromagnetic radiation in the infrared, optical and radar.[55]
Additional means of masking are used, such as camouflage nets and placement of components of the C-300 in trenches that considerably complicates detection from long range. Station interference with radar enemy, SPN-30, Veil-1.[39]
- Protection. Additional elements of protection are the placement of components of C-300 in the trenches (practiced as placing on the hills for a better view and more rapid care of the horizon, and in the trenches for stealth and protection against fragments of explosions).
Composite element to counter the radar missile program is for S-300 system Paperboy-E,[39][56] the likelihood of intercepting missiles PIS type of HARM is 0.85 for missiles with active radar-guided, heat or body-managed system pointing the probability of interception of 0.85–0.99. Under the interception perceived inability of the object to cause harm because of his hit miss the target.
Comparison with other systems
| Official designation of unit | S-300PMU[57] | S-300PMU1[58] | S-300PMU2 [39] | S-300VM[39]/S-300V4[59] | Patriot PAC-2 [60] | Patriot PAC-3[61] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range of, km |
aerodynamic target | 5–90 | 5–150 | 3–200 | 200 (400)[62] | 3–160 | 15, at most 20[63] / 0.3-20[64] |
| ballistic targets | at most 35 | at most 40 | 5–40 | 40 | 20 | 15–45[65] (20)[66] possible max 50[64] | |
| Height defeat, km |
aerodynamic target | 0.025–27 | 0.01–27 | 0.01–27 | 0.025–30 /?-37 | 0.06–24 | 15[66] |
| ballistic targets | (?) | (?) | 2–25 | 1–30 | 3–12[67] | 15(?).[66] 15, possible max 20.[63] | |
| Maximum target speed, m/s | 1,150, at most 1,300 (for the escort 3000)[67] | at most 2,800 (for the escort 10000)[58][67] | at most 2,800 | 4,500 of ballistic targets[39] | at most 2,200[67] | at most 1,600[66] | |
| Maximum speed of the rocket complex, m/s | at most 2,000[57] | 2000[58] | 1,900 | 2,600 and 1,700[66]/7.5M or 9M (more 3000) and (?) | 1,700[68] | (?) approximately 1,500[64] | |
| Number of simultaneously guided anti-aircraft missiles by one unit | at most 12 | at most 12 | at most 72[69] | at most 48[31] | at most 9 | ||
| Number of simultaneously engaged targets by one unit | at most 6 | at most 6 | at most 36[69] | at most 24[70] | at most 9 | at most 9 | |
| Mass of a rocket, kg | 1,400–1,600 | (?) | 330–1,900 | (?) | 900 | 312 | |
| Warhead weight, kg | 150 | (?) | 180[71] | (?) | 91 | 74 | |
| Minimum time between missile launches, seconds | 3–5 | 3–5 | 3 (0 at start from different
CARRIERS MISSILES) |
1.5 (0 at start from different
CARRIERS MISSILES) |
3–4 (1[68] at start from different
CARRIERS MISSILES) |
(?) | |
| The set up time and clotting time of starting
complex, mins |
5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 15/30[67] | 15/30(?) | |
| Means of transportation | Wheeled | Wheeled | Wheeled | tracked | semi trailer | semi trailer | |
Operational history
The system has put in strong performances in real-world exercises.[72] In 1991, 1992 and 1993, various versions of the S-300 had successfully destroyed ballistic missiles and other objects in exercises, with a high success rate (90% or more if 1 missile interceptor is used).[72][73][74][75] In 1995, it was the first system in the world to successfully destroy a R-17 Elbrus Scud missile in the air.[75] China is to test the S-300PMU2 effectiveness in destroying targets in real exercises. This UAV (4.6 km) and simulator a strategic bomber aircraft (186 km), tactical missile (range of the system to the point of interception 34 km and a height of 17.7 km) and also against pinpoint missile. Although none of the S-300 versions have fired a missile in a conflict, it is considered a very capable SAM system that poses a significant hazard even to the most advanced aircraft or other airborne targets. In April 2005, NATO had a combat exercise in France and Germany called Trial Hammer 05 to practice Suppression of Enemy Air Defenses missions.[76][77][78] Participating countries were pleased that the Slovak Air Force brought an S-300PMU along, providing a unique opportunity for NATO to become familiar with the system.
Israel's purchase of F-35 Lightning II fighters was allegedly motivated in part to nullify the threat of S-300 missiles that were, at the time the fighters were initially sought, subject to a potential arms sale to Iran.[79][80]
The system can destroy ground targets at a range of 120 km (19,000 fragments or 36,000 according to various missiles). If the S-300 missiles are launched against ballistic missile launched, the range reaches up to 400 km.[9][81]
In 2010, Russia announced that its military had deployed the S-300 systems in breakaway Abkhazia in 2008, leading to condemnation from the government of Georgia.[82]
After a Russian Sukhoi Su-24 was shot down over Syria in November 2015, Russia deployed S-300 and S-400 to the region - some to the Khmeimim Air Base, some with the Russian cruiser Moskva.[83]
On 28 September 2018, a Russian-supplied Syrian S-200 systems downed a Russian military plane, killing 15 Russian service members. Moscow accused Israel of indirectly causing this incident, and announced that to keep its troops safe, it started to supply Syria with modern S-300 anti-missile rocket systems.[84][85] Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu objected to the move in a telephone call with Russian president Vladimir Putin, stating that the delivery of S-300 anti-missile rocket systems to "irresponsible players" would be dangerous for the region.[86]
In 2020, Syrian military criticized the Russian S-300 missile defence system, saying that it was largely ineffective against Israeli air strikes. Syrian military sources talking to the Russian outlet Avia.pro said that the radar used on the S-300 and the Pantsir-S systems had proven to be incapable of detecting and hitting Israeli cruise missiles on numerous occasions.[87]
Operators and other versions
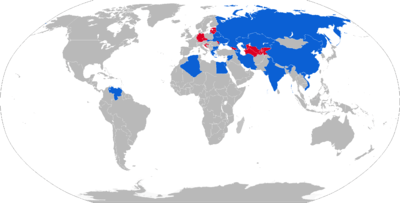


.jpg)
The S-300 is mainly used in Eastern Europe and Asia although sources are inconsistent about which countries possess the system.[88]












Modernization of all units of the version S-300P to the version S-300PM1 was to end in 2014. Resource of each taken increased by 5 years. PM 1 continued to version PM 2. By 2015 S-300V4 was to have been delivered. Modernization of all S-300V to the version S-300V4 was to end in 2012.[120][121]

- Following the Syrian military's downing of Russian Il-20 aircraft in Syria in September 2018 using a Russian-made S-200 system (for which Russia held Israel responsible) Russian defense minister Sergey Shoygu on 24 September said that within two weeks, the Syrian Army will receive S-300 systems. Though the variant was not specified, the stated range of the system is to be 250 km.[128][129][130][131][132] On 2 October 2018, Sergey Shoygu told president Vladimir Putin during a meeting broadcast that the delivery of the S-300 system to Syria had been completed a day prior.[133][134] On 8 October 2018, Russian news agency TASS reported that three S-300PM battalions had been given to Syria free of charge, citing "On 1 October three battalion sets of S-300PM systems of eight launchers each were delivered to Syria,". According to the source, the deliveries also included more than 100 surface-to-air missiles for each battalion.[135] It is operated by the Syrian Air Defense Force.



Former operators

Evaluation-only operators

Related
- Bavar 373[147]
See also
Notes
- Russian President Vladimir Putin ordered the acceleration of highly advanced Russian weapons supplies to Syria. Referring to S-300 anti-air systems and the nuclear-capable 9K720 Iskander (NATO named SS-26 Stone) surface missiles. Since Syrian Air Defense Force teams have already trained in the Russian Federation on the handling of the S-300 interceptor batteries, they can go into service as soon as they are landed by one of Russia's daily airlifts to Syria. Russian air defence officials will supervise their deployment and prepare them for operation.[124] According to President Vladimir Putin, components of the S-300 have been delivered to Syria but the delivery has not been completed.[125] 2 SA-20B (4 batalions), contract 2010, fully prepared in 2012. Centre for Analysis of World Arms Trade (armstrade.org/english.shtml) SA-20B actually received in 2013[126]
References
- "Almaz/Antei Concern of Air Defence S-300P (NATO SA-10 'Grumble') family of low to high-altitude surface-to-air missile systems". Jane's. 16 January 2008. Retrieved 4 August 2008.
- "Big Russian flotilla led by Admiral Kuznetsov carrier heads for Syrian port". DEBKAfile. 21 August 2008. Archived from the original on 23 August 2008. Retrieved 22 August 2008.
- "Кремль опроверг информацию о готовности РФ поставить Ирану С-300". KM.RU Новости – новости дня, новости России, последние новости и комментарии. Archived from the original on 8 September 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "ЦАМТО / Новости / Прекращение производства ЗРС С-300 касается систем С-300ПС и С-300ПМ". armstrade.org. 23 August 2011. Archived from the original on 8 April 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- Редактор. "Комплекс С-300В впервые поразил мишени-имитаторы ОТБР". army-news.ru. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- "Зенитно ракетный комплекс С-300 ПМУ-1". kapyar.ru. Archived from the original on 25 August 2011. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "Зенитно-ракетная система С-300В (СССР/Россия)". modernarmy.ru. Archived from the original on 8 October 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- "International Assessment and Strategy Center > Research > Almaz S-300 – China's "Offensive" Air Defense". Strategycenter.net. 25 February 2006. Archived from the original on 28 September 2011. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- "Система С-300П". soldiering.ru. Archived from the original on 14 September 2013. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "Encyclopedia Astronautica – "S-300"". Archived from the original on 30 April 2010. Retrieved 5 September 2008.
- German: http://www.dtig.org/docs/sa-10.pdf
- "Anti-Aircraft Missiles & Systems, ракеты и системы ПВО России". Inbsite.com. Archived from the original on 23 December 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- "S-300/Favorit (SA-10 'Grumble'/SA-20 'Gargoyle')". Jane's. 8 February 2008. Retrieved 4 August 2008.
- S-300 PMU2 SA-20B Gargoyle B Surface-to-Air missile Archived 22 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- "MissileThreat – "Hongqi-10 (HQ-10)"". Archived from the original on 5 April 2013. Retrieved 5 September 2008.
- "Almaz Scientific Industrial Corporation – "FAVORIT S-300 PMU2 SURFACE-TO-AIR MISSILE SYSTEM"". Archived from the original on 27 January 2006. Retrieved 23 June 2006.
- "HQ-15 – Missile Defense Advocacy Alliance". Archived from the original on 10 November 2018. Retrieved 10 November 2018.
- "Зенитно-ракетная система С-300В (СССР/Россия)". www.modernarmy.ru. Archived from the original on 8 October 2015. Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- "S-300V/Antey 2500 (SA-12 'Gladiator/Giant')". Jane's. 13 February 2008. Retrieved 4 August 2008.
- "Ракетный комплекс С-300В4 пополнит ВС России". Российская газета. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- "C- 300В". guns.ru. Archived from the original on 20 January 2016. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- "Federation of American Scientists – "S-300V SA-12A Gladiator and SA-12B Giant – Russia/Soviet Nuclear Forces"". Archived from the original on 7 September 2008. Retrieved 5 September 2008.
- "S-300V, SA-12A GLADIATOR and SA-12B GIANT, HQ-18". Archived from the original on 15 August 2015. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- "C- 300В - Пусковая установка 9А83 и 9А82". guns.ru. Archived from the original on 1 August 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- Евгений Даманцев. "Перевес стратегического баланса сил на Ближнем Востоке снова стремится к России". army-news.ru. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- "C- 300В - Многоканальная станция наведения ракет 9С32". guns.ru. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- Василий Н.Я., Гуринович А.Л., Зенитные ракетные комплексы, стр. 271
- "S-300V SA-12A GLADIATOR and SA-12B GIANT HQ-18". FAS.org. 30 June 2000. Archived from the original on 15 August 2015. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- "Russian army to receive advanced weaponry in 2011 | Defense | RIA Novosti". En.rian.ru. 28 February 2011. Archived from the original on 16 November 2011. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- "Зенитно-ракетная система С-300В / С-300ВМ Антей-2500". Archived from the original on 7 October 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- Administrator. "S-300VM Antey-2500 SA-23 Gladiator Giant data pictures video - Russia Russian missile system vehicle UK - Russia Russian army military equipment vehicles UK". www.armyrecognition.com. Archived from the original on 16 December 2017. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- "Модернизация до уровня ЗРС С-300В4 ПВО сухопутных войск полностью завершится в 2012 году". Archived from the original on 12 November 2016. Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- "С-300 обновили до С-400". Российская газета. Archived from the original on 31 October 2016. Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- Plopsky, Guy (19 January 2017). "Are Russia's Lethal S-400 SAMs Equipped with the Latest Long-Range Missiles?". Archived from the original on 7 November 2017. Retrieved 31 October 2017.
- "Задача трудная, но решаемая - Журнал "Воздушно-космическая оборона"". vko.ru. Archived from the original on 13 December 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- "МО РФ: ЗРС С300В4 подтвердила способность поражать цели до 400 км". РИА Новости. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- "Создана новая зенитная система "Антей-4000"". Российская газета. Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- Kopp, Dr. Carlo (May 2009). "Almaz-Antey 40R6 / S-400 Triumf Self Propelled Air Defence System / SA-21 Самоходный Зенитный Ракетный Комплекс 40Р6 / С-400 "Триумф"". AusAirPower. Carlo Kopp Updated February 2010 Updated May, June 2011 Updated April 2012. Archived from the original on 25 June 2015. Retrieved 13 July 2015.
- "- -". Archived from the original on 26 September 2011. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- "Antiaircraft missile system series S-300П | the History of air and MISSILE defense". Archived from the original on 6 May 2013.
- THE S-300V – first mobile universal system of missile and anti-aircraft defense.
- Dr Carlo Kopp, PEng. "76N6 Clam Shell Low Altitude Acquisition Radar / 5N66/5N66M/76N6/76N6E/40V6M/MD Clam Shell". ausairpower.net. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- Not a GRAU index. GRAU indices only apply to land-based versions.
- "С-400 vs Patriot: в чем американцы уступают нашим ЗРС". 28 April 2015. Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- сборник, БАСТИОН: военно-технический. "НЕВСКИЙ БАСТИОН, ВОЕННО-ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ СБОРНИК, ВООРУЖЕНИЯ, ВОЕННАЯ ТЕХНИКА, ВОЕННО-ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ СБОРНИК, СОВРЕМЕННОЕ СОСТОЯНИЕ, ИСТОРИЯ РАЗВИТИЯ ОПК, БАСТИОН ВТС, НЕВСКИЙ БАСТИОН, ЖУРНАЛ, СБОРНИК, ВПК, АРМИИ, ВЫСТАВКИ, САЛОНЫ, ВОЕННО-ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЕ, НОВОСТИ, ПОСЛЕДНИЕ НОВОСТИ, ВОЕННЫЕ НОВОСТИ, СОБЫТИЯ ФАКТЫ ВПК, НОВОСТИ ОПК, ОБОРОННАЯ ПРОМЫШЛЕННОСТЬ, МИНИСТРЕСТВО ОБОРОНЫ, СИЛОВЫХ СТРУКТУР, КРАСНАЯ АРМИЯ, СОВЕТСКАЯ АРМИЯ, РУССКАЯ АРМИЯ, ЗАРУБЕЖНЫЕ ВОЕННЫЕ НОВОСТИ, ВиВТ, ПВН". nevskii-bastion.ru. Archived from the original on 18 July 2017. Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- "Гамма-ДЕ - Алмаз-Антей". www.almaz-antey.ru. Archived from the original on 20 May 2017. Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 October 2015. Retrieved 27 January 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- сборник, БАСТИОН: военно-технический. "ВООРУЖЕНИЯ, ВОЕННАЯ ТЕХНИКА, ВОЕННО-ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ СБОРНИК, СОВРЕМЕННОЕ СОСТОЯНИЕ, ИСТОРИЯ РАЗВИТИЯ ОПК, БАСТИОН ВТС, НЕВСКИЙ БАСТИОН, ЖУРНАЛ, СБОРНИК, ВПК, АРМИИ, ВЫСТАВКИ, САЛОНЫ, ВОЕННО-ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЕ, НОВОСТИ, ПОСЛЕДНИЕ НОВОСТИ, ВОЕННЫЕ НОВОСТИ, СОБЫТИЯ ФАКТЫ ВПК, НОВОСТИ ОПК, ОБОРОННАЯ ПРОМЫШЛЕННОСТЬ, МИНИСТРЕСТВО ОБОРОНЫ, СИЛОВЫХ СТРУКТУР, КРАСНАЯ АРМИЯ, СОВЕТСКАЯ АРМИЯ, РУССКАЯ АРМИЯ, ЗАРУБЕЖНЫЕ ВОЕННЫЕ НОВОСТИ, ВиВТ, ПВН". bastion-karpenko.ru. Archived from the original on 20 July 2017. Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- "RusArmy.com - Радиолокационная станция "Оборона-14"". www.rusarmy.com. Archived from the original on 12 August 2017. Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- "RusArmy.com - Радиолокационная станция "Небо"". www.rusarmy.com. Archived from the original on 20 July 2017. Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- "Вестник ПВО :: С-300ПТ". guns.ru. Archived from the original on 24 April 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "Вестник ПВО :: ЗРС С-300П". guns.ru. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "Зенитно-ракетная система C-300ПС (C-300ПМУ )". new-factoria.ru. Archived from the original on 9 May 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "Сильные и слабые стороны самого опасного для противников Асада зенитно-ракетного комплекса". rusplt.ru. Archived from the original on 3 April 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- German: http://www.dtig.org/docs/sa-21.pdf
- Редактор. "Надувные макеты на службе армии". army-news.ru. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- "Военный парад" №34, 1999
- "Зенитно-ракетная система C-300ПС (C-300ПМУ )". Archived from the original on 9 May 2015. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- "Зенитно-ракетная система C-300 ПМУ-1". Archived from the original on 7 October 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- "МО РФ: ЗРС С300В4 подтвердила способность поражать цели до 400 км". РИА Новости. 10 January 2015. Archived from the original on 19 April 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "Patriot TMD". Archived from the original on 25 December 2018. Retrieved 19 March 2019.
- "Patriot TMD". GlobalSecurity. Archived from the original on 15 September 2010. Retrieved 17 August 2010.
- "Main defense product range - "Almaz – Antey" Corp". Archived from the original on 24 April 2013. Retrieved 22 August 2018.
- "Зенитный ракетный комплекс Patriot PAC-3". Archived from the original on 8 October 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- "11.04.12 c -3 -3". Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- John Pike. "Patriot TMD". Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- "Lockheed Martin Patriot PAC-3". Archived from the original on 12 April 2015. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- "-300 -1". Archived from the original on 13 October 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- "/". Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ARG. "S-300PMU-2 Favorit Long-Range Air Defense Missile System - Military-Today.com". www.military-today.com. Archived from the original on 2 May 2018. Retrieved 20 April 2018.
- ARG. "S-300V Long-Range Air Defense Missile System - Military-Today.com". www.military-today.com. Archived from the original on 21 April 2018. Retrieved 20 April 2018.
- "Зенитно-ракетная система C-300 ПМУ-2 'Фаворит'". Archived from the original on 20 October 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- "С-300 (SA-10, Grumble), зенитная ракетная система и ее модификации". arms-expo.ru. Archived from the original on 25 February 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "20 лет назад Вооруженные силы России потрясли мировое сообщество". Российская газета. Archived from the original on 6 November 2014. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- "Зенитно-ракетная система С-300В / С-300ВМ Антей-2500". new-factoria.ru. Archived from the original on 18 April 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "Зенитная ракетная система С-400 "Триумф" в 3 раза эффективнее аналогов". Росбалт. Archived from the original on 25 February 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
-
Gyürösi, Miroslav (11 March 2005). "Exclusive – NATO Aircraft Will 'Hunt' Russian Missile Systems During Defence-suppression Exercise". Jane's Information Group. The Internet Archive Wayback Machine. Archived from the original on 10 June 2007. Retrieved 9 December 2010.
...the participants of Trial Hammer ‘05, particularly France, Germany, the UK and the US, were keen to have the Slovak Air Force S-300PMU system take part in the exercise...
- Miroslav Gyürösi. (11 March 2005). "the Slovak SA-10 radar set to participate in NATO exercise". Jane's Missiles and Rockets. ISSN 1365-4187. Archived from the original on 10 June 2007. Retrieved 19 July 2006.
- "Slovak radar missile systems s-300PMU will take part in NATO exercises". Archived from the original on 29 October 2012. Retrieved 12 August 2008.
- "Israel 'close to deal on F-35'". Upi.com. 24 June 2009. Archived from the original on 2 November 2011. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- "Israel orders U.S. stealth planes to counter Iran, Syria threat". En.rian.ru. Archived from the original on 2 November 2011. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- "С-300 способны бить по наземным целям. Но белорусы их этому не учили". naviny.by. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "U.S.: 'Russia has had S-300 in Abkhazia for Past 2 Years'". Civil Georgia. 12 August 2010. Retrieved 7 October 2017.
- "Turkey Takes Action Against Russia's Syrian Air War". Aviation International News. 26 November 2015. Archived from the original on 26 November 2015. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- "Russia Begins Missile System Delivery to Syria, Warns West on Peace Talks". Reuters via VOA. 28 September 2018. Archived from the original on 29 September 2018. Retrieved 29 September 2018.
- Irish, John; Nichols, Michelle (28 September 2018). "Russia begins missile system delivery to Syria, warns West on peace..." Reuters. Archived from the original on 3 October 2018. Retrieved 29 September 2018.
- Nikolskaya, Polina; Gabrielle, Tétrault-Farber (25 September 2018). "Russia to give Syria S-300 air defense after accusations against..." Reuters. Archived from the original on 26 September 2018. Retrieved 26 September 2018.
- "Syria says Russian missile defence system 'ineffective'". Middle East Monitor. 1 May 2020. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- Barletta, Michael; Jorgensen, Erik; Saracino, Peter (July 1998). "The Russian S-300PMU-1 TMD System". James Martin Center for Nonproliferation Studies. Archived from the original on 10 November 2010.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 28 September 2018. Retrieved 25 September 2018.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "missilethreat.com". missilethreat.com. Archived from the original on 11 November 2011. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- "News from Armenia, Events in Armenia, Travel and Entertainment | Armenia Confirms Possession of Sophisticated Missiles". ArmeniaDiaspora.com. 20 December 2010. Archived from the original on 7 July 2011. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- SIPRI Armstrade Register Archived 14 April 2010 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 27 October 2013.
- "Russia completes S-300PS deliveries to Belarus". articles.janes.com. 14 June 2006. Archived from the original on 3 May 2012. Retrieved 7 August 2011.
- Russia will deliver four divisions of S-300 ground-to-air defense missile systems to Belarus Archived 16 March 2018 at the Wayback Machine - Armyrecognition.com, 24 April 2013
- "Balkananalysis.com – "Balkan Defence Overview: Developments and Prospects "". Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 5 September 2008.
- "Sino Defence Today – "S-300 (SA-10) Surface-to-Air Missile"". Archived from the original on 10 September 2008. Retrieved 5 September 2008.
- S-300 (missile)
- defensenews http://www.defensenews.com/story/defense/2015/11/24/egypt-russia-negotiating-missile-sale/76330914/. Retrieved 24 November 2015. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ""Рособоронэкспорт" поставит в Египет зенитные системы С-300ВМ". Рамблер-Новости. Archived from the original on 23 December 2014. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "ТАСС: Армия и ОПК – Источник: Россия поставит Египту полк систем ПВО "Антей-2500" до конца 2016 года". ТАСС. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "В вооружениях не стесняться". kommersant. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- "According sources, Russia would start deliveries of Antey-2500 missile systems to Egypt". 6 March 2015. Archived from the original on 19 December 2016. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
- Kommersant. "Те, кто сегодня критикует Иран, будут бороться за него". Archived from the original on 8 March 2018. Retrieved 7 February 2018.
- "Russia in talks with Turkey and Egypt for the sale of the S-400". newsru.com. Archived from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- "Hellenic Air Force Weapons - S-300 PMU1". Archived from the original on 23 November 2013. Retrieved 21 May 2013.
- "SIPRI Military Expenditure Database - SIPRI". www.sipri.org. Archived from the original on 11 July 2011. Retrieved 9 February 2018.
- Russian-made S-300 air defence missile system test-fired for the first time by Army of Greece Archived 14 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine - Armyrecognition.com, 14 December 2013
- "Ballistic Missile Defence for India". www.bharat-rakshak.com. BHARAT RAKSHAK. Archived from the original on 2 August 2012. Retrieved 27 July 2016.
- "India's Missile Defense: Is the Game Worth the Candle?". thediplomat.com. THE DIPLOMAT. 2 August 2013. Archived from the original on 23 July 2016. Retrieved 27 July 2016.
- Behnam Ben Taleblu. "Understanding Iran's Deployment of the S-300 System". defenddemocracy.org. Archived from the original on 9 August 2017. Retrieved 14 July 2017.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 31 August 2017. Retrieved 31 August 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ваше имя. "Политика. Казахстан получит бесплатно до десяти комплексов С-300". Vesti.kz. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- "Казахстан и РФ подписали контракт на поставку дивизионов С-300". РИА Новости. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- "Россия безвозмездно поставит Казахстану пять дивизионов ЗРС С-300". Interfax.ru. 31 January 2014. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- "ТАСС: Армия и ОПК - Минобороны РФ безвозмездно передало Казахстану пять зенитно-ракетных комплексов". ТАСС. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 5 January 2019. Retrieved 22 February 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- The Military Balance 2010. p.222,223
- Eugene Yanko, Copyright 1997 – warfare.ru (10 August 1995). "SA-20 GARGOYLE / S300PMU/2/3 | Russian Arms, Military Technology, Analysis of Russia's Military Forces". Warfare.ru. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- "Новости NEWSru.com :: Россия прекращает выпуск ракетных комплексов С-300 и готовится участвовать в евроПРО с новейшими С-500". Newsru.com. Archived from the original on 19 March 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- "Модернизация до уровня ЗРС С-300В4 ПВО сухопутных войск полностью завершится в 2012 году — ОРУЖИЕ РОССИИ, Информационное агентство". Arms-expo.ru. Archived from the original on 29 March 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- "Минобороны РФ подписало трехлетний контракт на поставку ЗРС С-300В4 – Военный Обозреватель". Warsonline.info. Archived from the original on 23 October 2013. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 August 2017. Retrieved 29 July 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "В Дамаске будут следить за переговорами Путина и Кэмерона". vesti.ru. 10 May 2013. Archived from the original on 3 October 2018. Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- Walker, Shaun; McDonald-Gibson, Charlotte; Morris, Nigel (29 May 2013). "Russia stokes fears of an arms race with threat to deliver anti-aircraft missiles to Syria's Assad regime". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 29 May 2013. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "Russia Does Not Rule Out Backing Military Action in Syria – Putin / Sputnik international". Archived from the original on 1 August 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- "ЦАМТО: Сирийские ЗРС С-300 достигнут боеготовности не ранее конца 2014 года". vz.ru. Archived from the original on 25 September 2018. Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- "Russian S-300 Supplies to Syria to Boost Political Stability - Syrian Lawmaker". 20 April 2018. Archived from the original on 13 October 2018. Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- Syria to get Russia's S-300 air-defense missile system within two weeks Archived 24 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine TASS, 24 September 2018.
- Гутенев: реакция Израиля на инцидент с Ил-20 вынудила РФ на поставки С-300 в Сирию: Председатель комиссии Госдумы по правовому обеспечению развития ОПК отметил, что теперь израильские летчики не смогут прятаться за российскими самолетами Archived 24 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine TASS, 24 September 2018.
- Россия передаст Сирии С-300 в течение двух недель Archived 24 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine Kommersant, 24 September 2018.
- Путин обсудил с Асадом поставки российских комплексов С-300 в Сирию: В Кремле отметили, что президент сообщил сирийскому лидеру о дополнительных мерах по обеспечению безопасности военных РФ в республике Archived 24 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine TASS, 24 September 2018.
- Израиль может попытаться помешать поставке С-300 в Сирию, считает эксперт Archived 24 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine RIA Novosti, 24 September 2018.
- Devitt, Polina (2 October 2018). "Russia completes delivery of S-300 system to Syria". Reuters. Moscow. Archived from the original on 6 October 2018. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- Binnie, Jeremy; Ripley, Tim (5 October 2018). "Russia announces Syrian S-300 delivery". IHS Jane's 360. London. Archived from the original on 6 October 2018. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- "Three Russian S-300PM battalion sets delivered to Syria free of charge — source". 8 October 2018. Archived from the original on 13 October 2018. Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- John Pike. "Ukraine – Air Force Equipment". Globalsecurity.org. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- "Украинская рулетка: 20-летние С-300 попадают в цель один раз из четырех | Ракетная техника". Rbase.new-factoria.ru. Archived from the original on 22 October 2013. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- Ukrainian Air Force received refurbished anti-aircraft S-300PS missile system Archived 7 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine, UNIAN (6 September 2016)
- "Путин рассказал про украинские С-300 в Крыму. Что с ними стало?". Archived from the original on 2 August 2016. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
- Kroth, Olivia. "Venezuela's partnership with Russia: An emblematic step." Archived 25 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine Pravda, 23 June 2012.
- Indigo Guevara Venezuela receives ITS First S-300VM / / Jane's Defence Weekly (10 April 2013) C 6
- "Asia Times – "Russian missiles to guard sky over Vietnam"". Archived from the original on 30 June 2012. Retrieved 5 September 2008.
- "96Л6-1 / 96Л6Е Всевысотный обнаружитель". militaryrussia.ru. Archived from the original on 1 December 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- Diplomat, Franz-Stefan Gady, The. "Vietnam Deploys Precision-Guided Rocket Artillery in South China Sea". Archived from the original on 27 August 2017. Retrieved 27 August 2017.
- "Продажа комплекса С-300: расследование". 9 March 1995. Archived from the original on 22 August 2018. Retrieved 22 August 2018.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 22 October 2013. Retrieved 2015-08-18.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Three Iranian long range air defense systems". Mashregh News Agancy. Archived from the original on 20 November 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to S-300. |
- S-300 | CSIS Missile Threat
- S-300 and various other system (in English language) in the Russia (official developer site).
- Australian Air Power: Part 1 and Part 2
- www.dtig.org detailed overview of the S-300P & S-300V family.
- S-300 PMU2 SA-20B Gargoyle B Surface-to-Air missile(Army recognition)
- Almaz S-300 – China's "Offensive" Air Defence
- Soviet/Russian Missile Designations
- S-300PMU2 Favorit EnemyForces.com
- Almaz S-300P/PT/PS/PMU/PMU-1/PMU-2
- 76N6 Clam Shell Acquisition Radar
- "Antey 9K81 S-300V – SA-12A/B Gladiator/Giant". ausairpower.net: 1. 23 December 2006.
- Matching of the Patriot (1/2/3) against the S-300 (v/ Antey 2500). In English. Used 8 parameters. Admonition. This test is are not officially authenticated but not refuted.
- Aviation Week S-300 Surface-To-Air Missile System
Gallery
 S-300V with 9M83 rockets.
S-300V with 9M83 rockets. 5P85-1 launcher for the S-300PT.
5P85-1 launcher for the S-300PT. S-300 launcher on parade in Sofia.
S-300 launcher on parade in Sofia. S-300PS surface-to-air missile launcher.
S-300PS surface-to-air missile launcher. A U.S. military photo of the S-300P (SA-10).
A U.S. military photo of the S-300P (SA-10). S-300 at the 2009 Victory Day parade in Moscow.
S-300 at the 2009 Victory Day parade in Moscow. S-300 system operated by the Bulgarian military.
S-300 system operated by the Bulgarian military. KrAZ-260 tractor-trailer of an S-300PMU2 SAM system.
KrAZ-260 tractor-trailer of an S-300PMU2 SAM system.
 The 5P85TE2 of an S-300PMU2 SAM on parade in Baku in 2011.
The 5P85TE2 of an S-300PMU2 SAM on parade in Baku in 2011. S-300PS displayed in a Ukrainian Air Force museum in Vinnitsa.
S-300PS displayed in a Ukrainian Air Force museum in Vinnitsa. Transport-launch container with a 5V55 surface-to-air missile for the S-300P.
Transport-launch container with a 5V55 surface-to-air missile for the S-300P. A 64N6E2 reconnaissance radar, which forms part of the 83M6E2 command post of this S-300PMU-2 system.
A 64N6E2 reconnaissance radar, which forms part of the 83M6E2 command post of this S-300PMU-2 system. Three S-300PMU missile launchers in firing position. Displayed by the Slovak military in Piešťany.
Three S-300PMU missile launchers in firing position. Displayed by the Slovak military in Piešťany. The 5P85-1 launcher for S-300PT displayed at the Air Defense History Museum in Zarya, Moscow Oblast.
The 5P85-1 launcher for S-300PT displayed at the Air Defense History Museum in Zarya, Moscow Oblast. From left to right: the 64N6E2 radar, 54K6E2 command post, 5P85 missile launch vehicle, and the 9M96E2 missiles.
From left to right: the 64N6E2 radar, 54K6E2 command post, 5P85 missile launch vehicle, and the 9M96E2 missiles. A view of the deck area housing the S-300F vertical missile launchers on the Slava Class Guided Missile Cruiser Marshal Ustinov.
A view of the deck area housing the S-300F vertical missile launchers on the Slava Class Guided Missile Cruiser Marshal Ustinov. Installing inflatable decoys of the S-300 during a Russian army exercise by the Guards Engineer Brigade and the Engineer Camouflage Regiment.
Installing inflatable decoys of the S-300 during a Russian army exercise by the Guards Engineer Brigade and the Engineer Camouflage Regiment.
.jpg) 9A83 TELAR.
9A83 TELAR. S-300V air defense system.
S-300V air defense system..jpg) 9S19M2 Imbir acquisition radar.
9S19M2 Imbir acquisition radar..jpg) 9S15M Obzor-3 round sight acquisition radar.
9S15M Obzor-3 round sight acquisition radar..jpg) 9S457 self-propelled command post.
9S457 self-propelled command post..jpg) 9S32 multichannel missile engagement guidance radar.
9S32 multichannel missile engagement guidance radar.
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)