2-Naphthol
2-Naphthol, or β-naphthol, is a fluorescent colorless (or occasionally yellow) crystalline solid with the formula C10H7OH. It is an isomer of 1-naphthol, differing by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol, but more reactive. Both isomers are soluble in simple alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. 2-Naphthol is a widely used intermediate for the production of dyes and other compounds.
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Naphthalen-2-ol | |
| Other names
2-Hydroxynaphthalene; 2-Naphthalenol; beta-Naphthol; Naphth-2-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.712 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H8O | |
| Molar mass | 144.173 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.280 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 121 to 123 °C (250 to 253 °F; 394 to 396 K) |
| Boiling point | 285 °C (545 °F; 558 K) |
| 0.74 g/L | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.51 |
| -98.25·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful when inhaled or swallowed; dangerous to environment, esp. aquatic organisms.[1] |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R20 R22 R50 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S24 S25 S61 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 161 °C (322 °F)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production
Traditionally, 2-naphthol is produced by a two-step process that begins with the sulfonation of naphthalene in sulfuric acid:[2]
- C10H8 + H2SO4 → C10H7SO3H + H2O
The sulfonic acid group is then cleaved in molten sodium hydroxide:
- C10H7(SO3H) + 3 NaOH → C10H7ONa + Na2SO3 + 2 H2O
Neutralization of the product with acid gives 2-naphthol.
2-Naphthol can also be produced by a method analogous to the cumene process.[2]
2-Naphthol-derived dyes
The Sudan dyes are popular dyes noted for being soluble in organic solvents. Several of the Sudan dyes are derived from 2-naphthol by coupling with diazonium salts.[3] Sudan dyes I -IV and Sudan Red G consist of arylazo-substituted naphthols.
- Selected 2-Naphthol-derived dyes
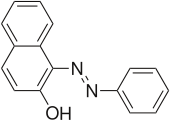
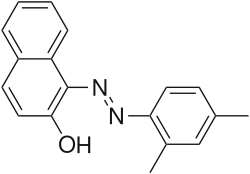
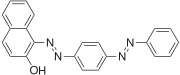
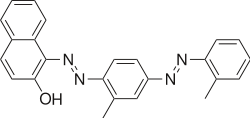
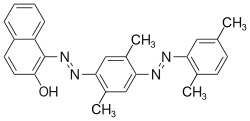
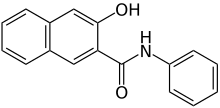
Reactions
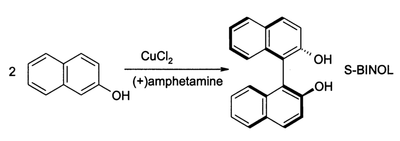
2-Naphthol reacts to form BINOL, a C2-symmetric ligand popularized for use in asymmetric catalysis.
2-Naphthol converts to 2-naphthalenethiol via reaction with dimethylthiocarbamoyl chloride via the Newman-Kwart rearrangement.[4]
Safety
Naphthols (both 1 and 2 isomers) are used as biomarkers for livestock and humans exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.[5]
References
- Safety data for 2-naphthol
- Gerald Booth (2005). "Naphthalene Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_009..
- Booth, Gerald (2000). "Dyes, General Survey". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a09_073. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- Melvin S. Newman; Frederick W. Hetzel (1971). "Thiophenols from Phenols: 2-Naphthalenethiol". Org. Synth. 51: 139. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.051.0139.
- Sreekanth, R.; Prasanthkumar, Kavanal P.; Sunil Paul, M. M.; Aravind, Usha K.; Aravindakumar, C. T. (7 November 2013). "Oxidation Reactions of 1- and 2-Naphthols: An Experimental and Theoretical Study". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 117 (44): 11261–11270. doi:10.1021/jp4081355. PMID 24093754.
