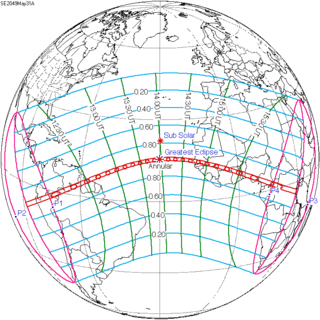
Solar eclipse of May 31, 2068
A total solar eclipse will occur on May 31, 2068. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
| Solar eclipse of May 31, 2068 | |
|---|---|
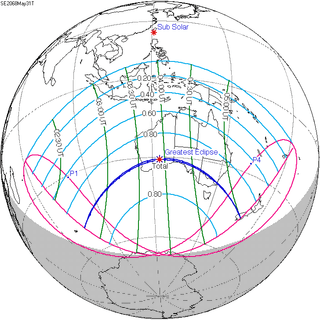 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | -0.797 |
| Magnitude | 1.011 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 66 sec (1 m 6 s) |
| Coordinates | 31°S 123.2°E |
| Max. width of band | 63 km (39 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 3:56:39 |
| References | |
| Saros | 148 (24 of 75) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9660 |
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 2065–2069
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
| 118 | July 3, 2065 Partial |
123 | December 27, 2065 Partial |
| 128 | June 22, 2066 Annular |
133 | December 17, 2066 Total |
| 138 | June 11, 2067 Annular |
143 | December 6, 2067 Hybrid |
| 148 | May 31, 2068 Total |
153 | November 24, 2068 Partial |
| 158 | May 20, 2069 Partial |
Saros 148
Solar saros 148, repeating every about 18 years and 11 days, contains 75 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on September 21, 1653. It has annular eclipses on April 29, 2014, and May 9, 2032, and a hybrid eclipse on May 20, 2050. It has total eclipses from May 31, 2068, to August 3, 2771. The series ends at member 75 as a partial eclipse on December 12, 2987. The longest total eclipse will be on April 26, 2609, at 5 minutes and 23 seconds.[2]
| Series members 15–25 occur between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 15 | 16 | 17 |
 February 23, 1906 |
 March 5, 1924 |
 March 16, 1942 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 |
 March 27, 1960 |
 April 7, 1978 |
 April 17, 1996 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 |
 April 29, 2014 |
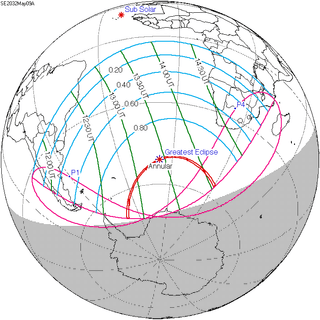 May 9, 2032 |
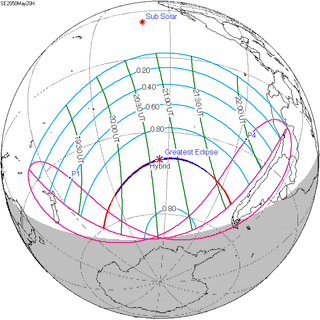 May 20, 2050 |
| 24 | 25 | |
 May 31, 2068 |
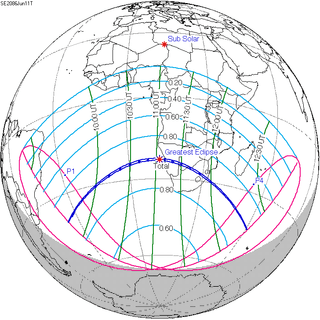 June 11, 2086 | |
Tritos series
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1901 and 2100 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
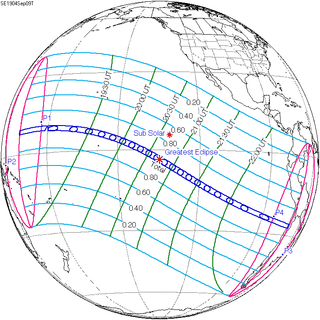 September 9, 1904 (Saros 133) |
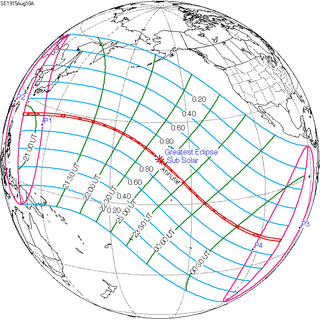 August 10, 1915 (Saros 134) |
 July 9, 1926 (Saros 135) | |
 June 8, 1937 (Saros 136) |
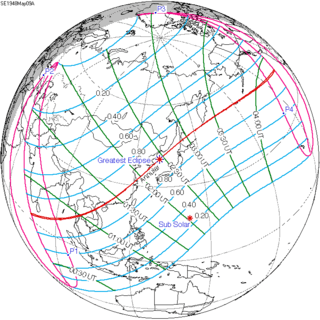 May 9, 1948 (Saros 137) |
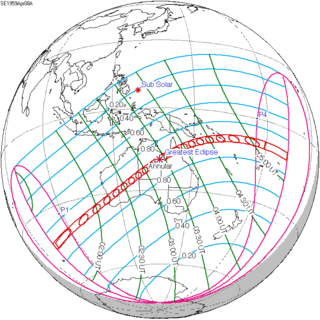 April 8, 1959 (Saros 138) | |
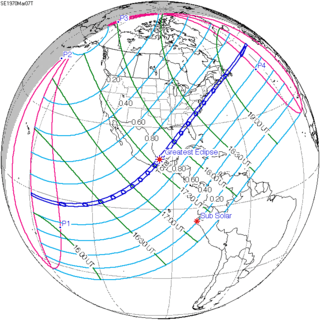 March 7, 1970 (Saros 139) |
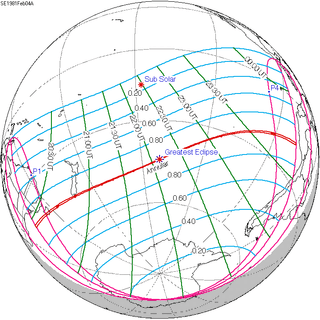 February 4, 1981 (Saros 140) |
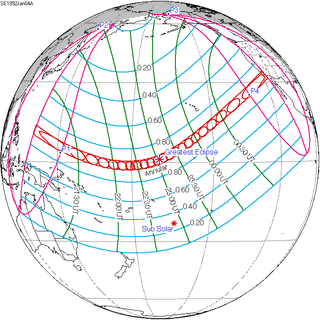 January 4, 1992 (Saros 141) | |
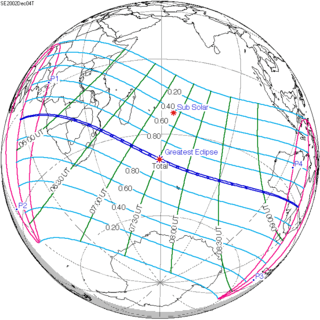 December 4, 2002 (Saros 142) |
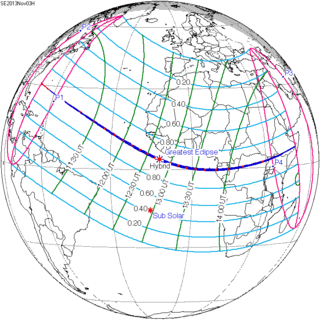 November 3, 2013 (Saros 143) |
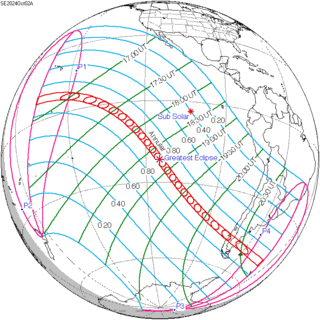 October 2, 2024 (Saros 144) | |
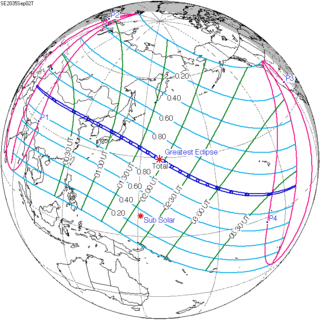 September 2, 2035 (Saros 145) |
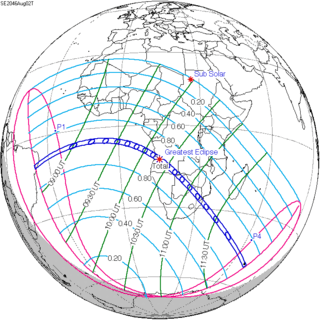 August 2, 2046 (Saros 146) |
 July 1, 2057 (Saros 147) | |
 May 31, 2068 (Saros 148) |
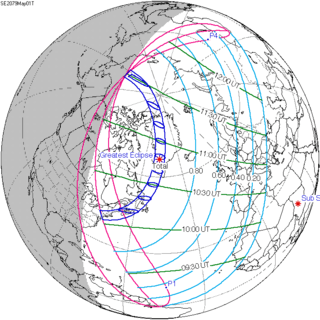 May 1, 2079 (Saros 149) |
 March 31, 2090 (Saros 150) | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 21 eclipse events between June 1, 2011 and June 1, 2087 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| May 31 – June 1 | March 19–20 | January 5–6 | October 24–25 | August 12–13 |
| 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 | 126 |
 June 1, 2011 |
 March 20, 2015 |
 January 6, 2019 |
 October 25, 2022 |
 August 12, 2026 |
| 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 | 136 |
 June 1, 2030 |
 March 20, 2034 |
 January 5, 2038 |
 October 25, 2041 |
 August 12, 2045 |
| 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 | 146 |
 May 31, 2049 |
 March 20, 2053 |
 January 5, 2057 |
 October 24, 2060 |
 August 12, 2064 |
| 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 | 156 |
 May 31, 2068 |
 March 19, 2072 |
 January 6, 2076 |
 October 24, 2079 |
 August 13, 2083 |
| 158 | 160 | 162 | 164 | 166 |
 June 1, 2087 |
 October 24, 2098 |
|||
Notes
- van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- Saros Series Catalog of Solar Eclipses NASA Eclipse Web Site.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
.jpg)
