Mount Judi
Mount Judi (Arabic: ٱلْجُوْدِيّ[1] al-Ǧūdiyy, Kurdish: Cûdî, Turkish: Cudi), also known as Qardū (Aramaic: קרדו, Classical Syriac: ܩܪܕܘ),[2] is Noah's apobaterion or "Place of Descent", the location where the Ark came to rest after the Great Flood, according to very Early Christian and Islamic tradition (based on the Qur'an, 11:44).[1]
| Jūdī, Cudi, Cûdî, Qardū | |
|---|---|
 The mountain range, seen from Şırnak. | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 2,089 m (6,854 ft) |
| Coordinates | 37°22′10″N 42°20′39″E |
| Geography | |
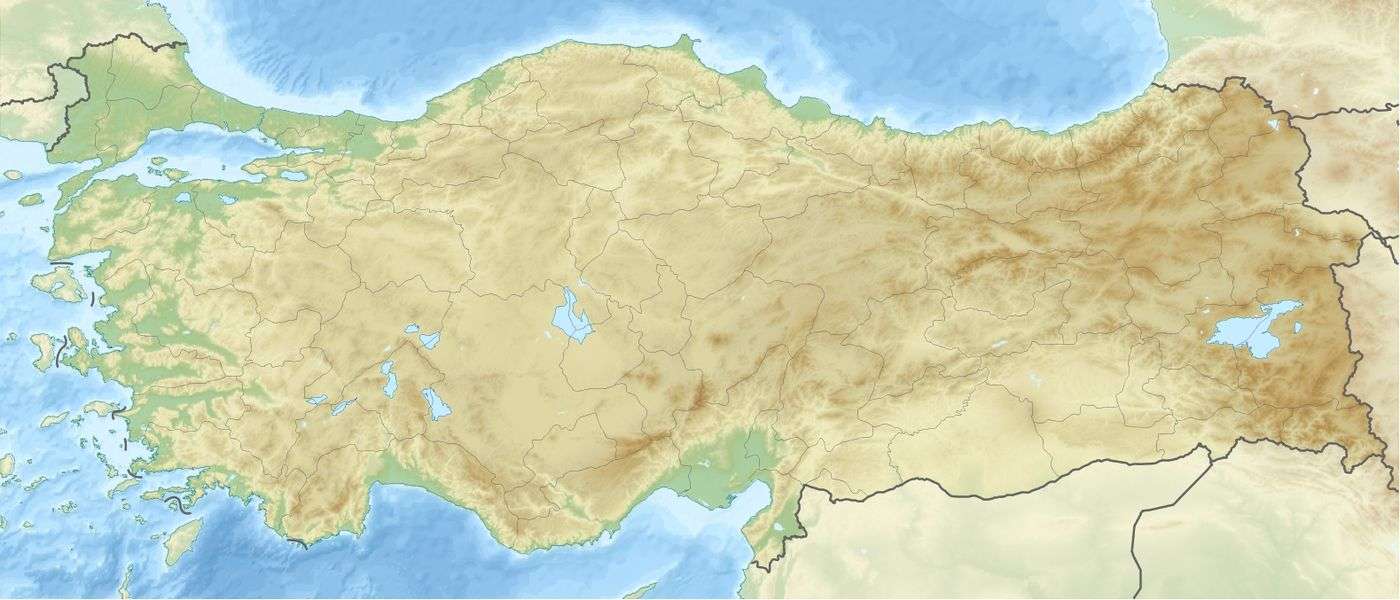 Jūdī, Cudi, Cûdî, Qardū  Jūdī, Cudi, Cûdî, Qardū Jūdī, Cudi, Cûdî, Qardū (Asia) .svg.png) Jūdī, Cudi, Cûdî, Qardū Jūdī, Cudi, Cûdî, Qardū (Earth) | |
| Parent range | Zagros |
The Quranic tradition is similar to the Judeo-Christian legend. The identification of Mount Judi as the landing site of the ark persisted in Syriac and Armenian tradition throughout Late Antiquity but was abandoned for the tradition equating the biblical location with the highest mountain of the region, Mount Ararat.
Jewish Babylonian, Syriac, and Islamic traditions identify Mount Judi or Qardu as a peak near the town of Jazirat ibn Umar (modern Cizre), at the headwaters of the Tigris, near the modern Syrian–Turkish border. Arab historian Al-Masudi[3] (d. 956), reported that the spot where the ark came to rest could be seen in his time. Al-Mas'udi locates Jabal Judi at 80 parasangs from the Tigris. Mount Judi was historically located in the province of Corduene, south of Lake Van. The mountains of this region, where Syria, Turkey, Iraq and Iran meet, are referred to as the 'Zagros'.[4]
Name
The relation of some of the spellings is clear. The origin of Judi is less clear. It is usually interpreted as a corrupted version of the same name, via al-gurdi (Reynolds 2004). The proposal that the two names are ultimately the same was first advanced by the English Orientalist George Sale in his translation of the Qur'an published in 1734. Sale's footnote reads:
This mountain [al-Judi] is one of those that divide Armenia on the south, from Mesopotamia, and that part of Assyria which is inhabited by the Kurds, from whom the mountains took the name Cardu, or Gardu, by the Greeks turned into Gordyae, and other names. ... Mount Al-Judi (which seems to be a corruption, though it be constantly so written by the Arabs, for Jordi, or Giordi) is also called Thamanin ..., probably from a town at the foot of it.
Sale goes on to say that there was once a famous Christian monastery on the mountain, but that this was destroyed by lightning in the year 776 AD, following which
the credit of this tradition hath declined, and given place to another, which obtains at present, and according to which the ark rested on Mount Masis, in Armenia, called by the Turks Agri Dagh.
Religious traditions

Christianity
The Syrians of the east Tigris had a legend of the ark resting on the Djûdi mountain in the land of Kard. This legend may in origin have been independent of the Genesis account of Noah's flood, rooted in the more general Near Eastern flood legends, but following Christianization of the Syrians, from about the 2nd century AD, it became associated with the Mountains of Ararat where Noah landed according to Genesis, and from Syria also this legend also spread to the Armenians. The Armenians did not traditionally associate Noah's landing site with Mount Ararat, known natively as Masis, but until the 11th century continued to associate Noah's ark with Mount Judi.[5]
Mount Judi is traditionally believed to be situated to the north-east of the Jazirat of Ibn 'Umar in south-east Turkey, close to the Iraqi and Syrian borders.
The biblical Ararat is thought be a variation of Urartu, an ancient term for the region north of ancient Assyria which encompasses the Armenian plateau. According to Josephus, the Armenians in the 1st century showed the remains of Noah's ark at a place called αποβατηριον "Place of Descent" (Armenian: Նախիջեւան, Nakhichevan, Ptolemy's Ναξουανα), about 60 miles southeast of the summit of Mount Ararat (ca. 39.07°N 45.08°E).[6] The "mountains of Ararat" in Genesis have become identified in later (medieval) Christian tradition with the peak now known as Mount Ararat itself, a volcanic massif in Turkey and known in Turkish as "Agri Dagh" (Ağrı Dağı).
Islam
The Quranic account of the Flood and Noah's Ark agrees with that given in Genesis, with a few variations. One of these concerns the final resting place of the Ark: according to Genesis, the Ark grounded on the "mountains of Ararat". According to the Qur'an (11:44),[1] the final resting place of the vessel was called "Judi", without the word "mountain". However, the use of Arabic definite letter "Al" in front of word Judi in the Quran signifies that it is pointing to a definite place (or mountain, in this case). Had it been referring to a general height, it would have been just "Judi", not "Al-Judi".[7]
And the word was spoken: "O earth! swallow up thy waters! And, O sky, cease [thy rain]!" And the water sank into the earth, and the will [of God] was done, and the ark came to rest on Al-Judi. And the word was spoken: "Away with these evil doing folk!"
— Quran, 11:44[1]
The 9th century Arab geographer Ibn Khordadbeh identified the location of mount Judi as being in the land of Assyria (Al-Akrad), and the Abbasid historian Al-Mas'udi (c. 896-956) recorded that the spot where it came to rest could be seen in his time. Al-Mas'udi also said that the Ark began its voyage at Kufa in central Iraq, and sailed to Mecca, where it circled the Kaaba, before finally travelling to Judi. Yaqut al-Hamawi, also known as Al-Rumi, placed the mountain "above Jazirat ibn Umar, to the east of the Tigris," and mentioned a mosque built by Noah that could be seen in his day, and the traveller Ibn Battuta passed by the mountain in the 14th century.[3]
Searches for the mountain

In the 1980s, adventurer and self-styled archaeologist Ron Wyatt and his colleague David Fasold claimed to have discovered Noah's Ark at Durupınar, some twenty miles from Mt. Ararat near a mountain locals called Cudi Dağı.[8] Fasold later vacillated on the claim.[9][10][11][12]
The description of medieval geographer Yaqut al-Hamawi matches a 2,089 m (6,854 ft) peak north of Silopi, that is now called Jabal Judi or Judi Dagh by Muslims and Gardu by Christians and Jews.
See also
- Mount Alvand, another location considered for the ark
References
- Quran 11:44 (Translated by Yusuf Ali)
- McAuliffe, Jane Dammen (2001). Encyclopaedia Of The Quran. 1. Brill. pp. 146–147. ISBN 978-90-04-11465-4.
- Lewis, J. P. (December 1984), Noah and the Flood: In Jewish, Christian, and Muslim Tradition, The Biblical Archaeologist, p. 237
- "Zagros Mountains". Britannica. Retrieved 17 August 2017.
- Frederick Cornwallis Conybeare, review of Friedrich Murat, Ararat und Masis, Studien zur armenischen Altertumskunde und Litteratur, Heidelberg, 1900.
- Conybeare (1901)
- Arabic definite article
- Fasold, David (1988). The Ark of Noah. New York: Wynwood. pp. 92–93. ISBN 0-922066-10-8.
- Clifton, Brad (9 April 1997). "Doubts sank faith in Ark". The Daily Telegraph (Sydney).
- Thomson, Kirstyn (9 April 1997). "Witness Tells How Ark Faith Sank". The West Australian.
- Deal, David Allen (2005). Noah's Ark: The Evidence. Muscogee, Oklahoma: Artisan. ISBN 0-933677-02-2.
- Dawes, June (2000). Noah's Ark: Adrift in Dark Waters. Belrose, New South Wales: Noahide. p. 184. ISBN 0-646-40228-5.