Karnali Pradesh
Karnali Pradesh (Nepali: कर्णाली प्रदेश) is one of the seven federal provinces of Nepal formed by the new constitution which was adopted on 20 September 2015.[1] The total area of the province is 27,984 square kilometres (10,805 sq mi), making it the largest province in Nepal. According to the 2011 Nepal census, the population of the province was 1,570,418, making it the least populous province in Nepal. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, Gandaki Pradesh to the east, Sudurpashchim Pradesh to the west, and Province No. 5 to the south.[2] Birendranagar with a population of 47,914 is both the province's capital and largest city.[3]
Karnali Pradesh कर्णाली प्रदेश | |
|---|---|
   | |
 Seal | |
 Location of Karnali Pradesh | |
Divisions of Karnali Pradesh | |
| Country | |
| Formation | 20 September 2015 |
| Capital | Birendranagar |
| Largest city | Birendranagar |
| Districts | 10 |
| Government | |
| • Body | Government of Karnali Pradesh |
| • Governor | Govinda Prasad Kalauni |
| • Chief Minister | Mahendra Bahadur Shahi (NCP) |
| • High Court | Surkhet High Court |
| • Provincial Assembly | Unicameral (40 seats) |
| • Parliamentary constituency | Pratinidhi Sabha 12 Rastriya Sabha 8 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 27,984 km2 (10,805 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 1st |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 1,570,418 |
| • Rank | 7th |
| • Density | 56/km2 (150/sq mi) |
| • Density rank | 7th |
| Demonym(s) | Madhya Pashchimeli Nepali |
| Time zone | UTC+5:45 (NST) |
| Geocode | NP-SI |
| Official Language | Nepali |
| Other Languages |
|
| HDI | 0.469 (low) |
| Literacy | 62.77% |
| Sex ratio | 95.78 ♂ /100 ♀ (2011) |
| Website | www.karnali.gov.np |
Etymology
The province's name is derived from the Karnali River, which flows through the province. A meeting of the provincial assembly on 25 February 2018 adopted the name Karnali for the province.[4][5]
History
Karnali is an old civilization in Nepal and is connected with the Karnali River [6] Archaeological sites found in Jumla, Surkhet and Dailekh infer that the area was part of the old Khasa kingdom which was established during the 11th century. The capital of the Khas Kingdom was Sinja in present day Jumla District. The kingdom expanded to a great extent in the 13th and 14th century; expanding to Garhwal in the west, Mansarowar and Guge regions of Tibet in the north, Gorkha-Nuwakot regions in the east and Kapilvastu with large areas of Terai in the south. After the late 14th century, the Khas empire collapsed and was divided into the Baise Rajya (22 principalities) in Karnali-Bheri region.[7]
Before the unification of modern Nepal, a part of Karnali (from Karnali River to Bheri River) was in the Sanghiya Baise Rajya (22 principality confederacy). The principalities were sovereign, but intermittently allied among themselves until they were annexed during the unification of modern Nepal from 1744 to 1810.
Geography
Karnali is the largest province of Nepal with an area of 24,453 km2 (9,441 sq mi). The province is surrounded by Gandaki Pradesh in east, Province No. 5 in south-east and south, Sudurpashchim Pradesh in the west and Tibet Autonomous Region of China in north.
The province has occupied higher mountains land of north and mid-hills of Nepal. It contains Kubi Gangri, Changla and Kanjiroba mountains in north. The Shey Phoksundo National Park with Phoksundo lake is the largest national park of Nepal and Rara lake is the largest lake of Nepal which are located in Karnali Pradesh. Karnali River is the biggest river of the province which is thought to be longest river of Nepal. Seti River and Bheri River are tributaries of Karnali.
| Location | August
(°F) |
August
(°C) |
January
(°F) |
January
(°C) |
Annual
Precipitation (mm/in) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kharpunath | 48 | 8.9 | 9.5 | -12.5 | 209.5/8.2 |
| Simikot | 54.9 | 12.7 | 17.6 | -8 | 304.2/12 |
| Chandannnath | 60.8 | 16 | 29.7 | -1.3 | 728.9/28.7 |
| Narayan | 71.8 | 22.1 | 45.3 | 7.4 | 1252.3/49.3 |
| Birendranagar | 78.4 | 25.8 | 53.2 | 11.8 | 1651/65 |
Government and administration
The Governor acts as the head of the province while the Chief Minister is the head of the provincial government. The Chief Judge of the Surkhet High Court is the head of the judiciary.[9] The present Governor, Chief Minister and Chief Judge are Govindra Prasad Kaulani, Mahendra Bahadur Shahi and Hari Kumar Pokharel respectively.[10][11] The province has 40 provincial assembly constituencies,12 House of Representative constituencies and eight National Assembly seats.[12]
Karnali has a unicameral legislature, like all of the other provinces in Nepal. The term length of provincial assembly is five years. The Provincial Assembly of Karnali Pradesh is temporarily housed at the Irrigation Division Office in Birendranagar.[13]
Administrative subdivisions
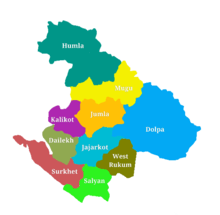
Karnali is divided into ten districts.
- Dailekh District
- Dolpa District
- Humla District
- Jajarkot District
- Jumla District
- Kalikot District
- Mugu District
- Salyan District
- Surkhet District
- Western Rukum District
A district is administrated by the head of the District Coordination Committee and the District Administration Officer. The districts are further dived to municipalities or rural municipalities which are further divided into wards. There are 25 municipalities and 54 rural municipalities in the province.[14] The capital and largest city of the province is Birendranagar. It is only city in the province with a population of over 50,000.
See also
- List of provinces of Nepal
- List of districts of Nepal
References
- "Nepal Provinces". statoids.com. Retrieved 2016-03-21.
- "Prov 6 named as Karnali, permanent capital in Birendranagar". www.myrepublica.com. 24 February 2018. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
- "Government finalises provinces' governors and temporary headquarters". nepalekhabar.com. 17 January 2018. Retrieved 19 January 2018.
- "Province 6 named Karnali; Surkhet capital". kathmandupost.ekantipur.com. Retrieved 2019-03-07.
- Times, Nepali. "Naming new provinces". Retrieved 2019-03-07.
- "कर्णाली प्रदेश एक चिनारी". www.ocmcm.karnali.gov.np. The office of chief minister and cabinet of Karnali Pradesh. Retrieved 9 July 2018.
- "Nepal in the Medieval Period". www.telegraphnepal.com. 2 February 2015. Retrieved 26 February 2018.
- "Nepal Travel Weather Averages (Weatherbase)". Weatherbase. Retrieved 2018-04-28.
- "High Courts get their chief judges". Retrieved 2018-04-27.
- "Mahendra Bahadur Shahi set to be Province 6 CM | Setopati - Nepal's Digital Newspaper". setopati.net. Retrieved 2018-04-28.
- "President administers oath of office to newly-appointed governors". The Himalayan Times. 2019-11-05. Retrieved 2019-12-19.
- "CDC creates 495 constituencies". The Himalayan Times. 2017-08-31. Retrieved 2018-04-27.
- "First Provincial Assembly meeting begins in 4 provinces". Retrieved 2018-04-27.
- "स्थानिय तह". 103.69.124.141. Archived from the original on 2018-08-31. Retrieved 2018-04-27.
