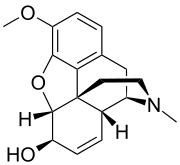
Isocodeine
Isocodeine is an opioid research chemical related to codeine. It is an epimer of codeine that can be prepared from it by a Mitsunobu reaction.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(5α,6β)-3-Methoxy-17-methyl-7,8-didehydro-4,5-epoxymorphinan-6-ol | |
| Other names
6-Isocodeine; α-Isocodeine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.366 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H21NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 299.370 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 173 to 174 °C (343 to 345 °F; 446 to 447 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H301, H302, H331 |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P301+310, P301+312, P304+340, P311, P321, P330, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dozens of derivatives and analogs of isocodeine and the related compound isomorphine have been produced.[2] One of these, dihydroisocodeine is a pharmaceutical four times stronger than dihydrocodeine and thus six times stronger than codeine which was used more extensively in the past in Continental Europe and other locales. Other isomers of codeine include allocodeine, pseudocodeine, heterocodeine and substances with intermediate qualities such as pseudoallocodeine and formylallocodeine can be prepared in the laboratory.[3]
References
- Simon, Csaba; Hosztafi, Sándor; Makleit, Sándor (1991). "Application of the Mitsunobu Reaction for the Preparation of Isomorphine and Isocodeine Derivatives". Synthetic Communications. 21 (3): 407–412. doi:10.1080/00397919108016763.
- "Report of Committee on drug addiction, 1929-1941". National Research Council (US). Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Report of the Committee On Drug Addiction 1929-1941 with Monographs, 1941, National Research Council (US) Washington DC, 1116 pages (Chapter 7)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.