Hungerford, Queensland
Hungerford is an outback town in the Shire of Bulloo and a locality in the Shire of Bulloo and Shire of Paroo, South West Queensland, Australia.[2][3][4] It is immediately north of the border with New South Wales and the Dingo fence. At the 2016 census, Hungerford and the surrounding area within Queensland had a population of 23.[1] The locality of Hungerford on the New South Wales side of the border had a population of 15.[5]
| Hungerford Queensland | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 The view around the Royal Mail Hotel | |||||||||||||||
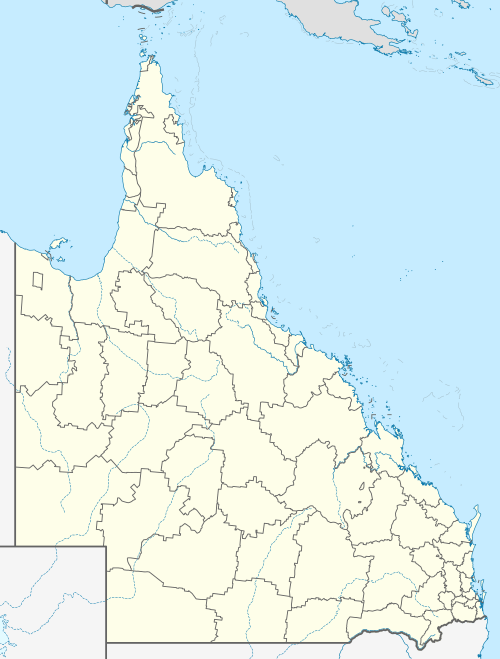 Hungerford | |||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 28.9961°S 144.4080°E | ||||||||||||||
| Population | 23 (2016 census)[1] | ||||||||||||||
| • Density | 0.00300/km2 (0.00778/sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Postcode(s) | 4493 | ||||||||||||||
| Area | 7,660.8 km2 (2,957.9 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Location |
| ||||||||||||||
| LGA(s) | |||||||||||||||
| Region | South West Queensland | ||||||||||||||
| State electorate(s) | Warrego | ||||||||||||||
| Federal Division(s) | Maranoa | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Geography
The locality is split between the Shire of Bulloo (western part) and the Shire of Paroo (eastern part).[6][7] The town is located in the Shire of Bulloo immediately north of the border between Queensland and New South Wales.[8]
Surrounding the town is the Currawinya National Park.
Hungerford Aerodrome is operated by the Bulloo Shire Council. It is to the east on the town on the Hungerford Airstrip Road (28.9965°S 144.4525°E). There is one sealed runway 1,100-metre (3,600 ft) long. It has no lighting but portable lights and flairs can be used in emergencies.[9]
History
Hungerford was in Badjiri[10] territory.
The town is named after Thomas Hungerford who once camped at the site.[11] The town developed from a border customs post on a stock route alongside the Paroo River. In 1874, the first hotel opened and the following year the town was gazetted.[11] For a number of years, before a proper survey was conducted the town was thought to be located in New South Wales.[11]
Hungerford Post Office opened on 1 October 1880, was replaced by a New South Wales office in 1881, reopened in 1886 and closed by 1907, replaced the New South Wales office in 1941 and closed by 1985.[12]
In 1892-3, Henry Lawson visited the town and wrote a short story named after it. In the story he wrote:
The town is right on the Queensland border, and an inter-provincial rabbit-proof fence -- with rabbits on both sides of it -- runs across the main street. ...
Hungerford consists of two houses and a humpy in New South Wales, and five houses in Queensland. Characteristically enough, both the pubs are in Queensland. We got a glass of sour yeast at one and paid six pence for it -- we had asked for English ale.[13]
A Cobb & Co coach service to the town was stopped in 1904.[11]
Hungerford Provisional School opened in 1892, becoming Hungerford State School in 1909. It closed in 1918, due to low attendance. It reopened in 1928, but low attendances caused it to close again in 1930. It was reopened a final time, this time located in the Bulloo Shire Hall, between 30 January and 11 December 1981.[14]
Hungerford will be the site of a total solar eclipse on 22 July 2028.[15]
Heritage listings
Hungerford has a number of heritage-listed sites, including:
- Archernar Street: Royal Mail Hotel[16]
References
- Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "Hungerford (Qld)". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- "Hungerford - town in Shire of Bulloo (entry 16466)". Queensland Place Names. Queensland Government. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- "Hungerford - locality in Shire of Bulloo (entry 42946)". Queensland Place Names. Queensland Government. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- "Hungerford - locality in Shire of Paroo (entry 42656)". Queensland Place Names. Queensland Government. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "Hungerford (NSW)". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 30 July 2017.

- "Hungerford - locality in the Shire of Bulloo (entry 50024)". Queensland Place Names. Queensland Government. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- "Hungerford - locality in the Shire of Paroo (entry 50025)". Queensland Place Names. Queensland Government. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- "Queensland Globe". State of Queensland. Retrieved 28 October 2016.
- "Aerodrome". Bulloo Shire Council. Archived from the original on 29 June 2020. Retrieved 29 June 2020.
- Tindale, Norman Barnett (1974). "Badjiri (QLD)". Aboriginal Tribes of Australia: Their Terrain, Environmental Controls, Distribution, Limits, and Proper Names - p. 164. Australian National University Press.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Environmental Protection Agency (Queensland) (2002). Heritage Trails of the Queensland Outback. State of Queensland. p. 114. ISBN 0-7345-1040-3.
- Premier Postal History. "Post Office List". Premier Postal Auctions. Retrieved 10 May 2014.
- Peter Pierce, ed. (1987). The Oxford Literary Guide to Australia. Melbourne: Oxford University Press. p. 47.
- Queensland Family History Society (2010), Queensland schools past and present (Version 1.01 ed.), Queensland Family History Society, ISBN 978-1-921171-26-0
- "Total Solar Eclipse of 2028 Jul 22". NASA. Retrieved 15 December 2018.
- "Royal Mail Hotel (entry 601390)". Queensland Heritage Register. Queensland Heritage Council. Retrieved 7 July 2013.
External links


- Town map of Hungerford, 1963