Danish Gold Coast
The Danish Gold Coast (Danish: Danske Guldkyst or Dansk Guinea) comprised the colonies that Denmark–Norway controlled in Africa as a part of the Gold Coast (roughly present-day southeast Ghana), which is on the Gulf of Guinea. It was colonized by the Dano-Norwegian fleet, first under indirect rule by the Danish West India Company (a chartered company), later as a crown colony of the kingdom of Denmark-Norway.
Danish Gold Coast Danish Guinea Danske Guldkyst Dansk Guinea | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1658–1850 | |||||||||
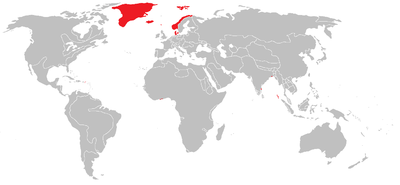 Denmark-Norway and its overseas territories | |||||||||
Danish Gold Coast (Ghana) Map of the Danish Gold Coast | |||||||||
| Status | Denmark–Norway crown colony (1658–1814) Denmark territory (1814–1850) | ||||||||
| Capital | Osu (Christiansborg) (1658–1850) | ||||||||
| Common languages | Danish, German (official) Ga, Dangme, Ewe, Akan | ||||||||
| King of Denmark | |||||||||
• 1658–1670 | Frederick III of Denmark (first) | ||||||||
• 1848–1863 | Frederick VII of Denmark (last) | ||||||||
| Governor-General | |||||||||
• 1658–1659 | Hendrik Carloff | ||||||||
• 1847–1850 | Rasmus Eric Schmidt | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| 1658 | |||||||||
| 1660 | |||||||||
• Disestablished | March 30 1850 | ||||||||
| Currency | Danish rigsdaler | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||
| Gold Coast |
|---|
.svg.png) |
|

The five Danish Gold Coast Territorial Settlements and forts of the Kingdom of Denmark were sold to the United Kingdom and were incorporated into the British Gold Coast in 1850.
History
On April 20, 1663, the Danish seizure of Fort Christiansborg and Carlsborg completed the annexation of the Swedish Gold Coast settlements. From 1674 to 1755 the settlements were administered by the Danish West India-Guinea Company. From December 1680 to 29 August 1682, the Portuguese occupied Fort Christiansborg. In 1750 it was made a Danish crown colony. From 1782 to 1785 it was under British occupation. On 30 March 1850 all of Denmark's Danish Gold Coast Territorial Settlements and forts of the Kingdom of Denmark were sold to Britain and incorporated into the British Gold Coast.[1]
The title of its chief colonial administrator was Opperhoved (singular; sometimes rendered in English as Station Chief) since 1658, only in 1766 upgraded to Governor.
Danish slave trade
The Danes were involved in the slave trade from the mid-17th century until the early 19th century. The Danish navy and its "mercantile marine" were recorded as the fourth largest in Europe in this period. With the establishment of the Gold Coast colony in the 1660s, "commodities such as gold and ivory dominated" at first, but by "the turn of the 18th century, slaves were the most important commodity in the Danish trade." Those who commanded the "large slave ships were often instructed to convert their cabin into a kind of moveable showroom upon arrival on the African coast." While throughout the 18th century, "Danish exports of enslaved Africans accounted for about 5 percent of the total exports from the Gold Coast," by the 1780s, this was up to 10 percent.
In 1672, the Danish West India and Guinea Company also began establishing colonies in the Caribbean at Saint Thomas, Saint John in 1718, and Saint Croix in 1733. While these possessions were rather small, at only 350 square kilometers collectively, they became "of utmost importance in the transatlantic slave trade under the Danish flag because of their intensive and highly profitable sugar production which depended on slave labor." As a result, and "because mortality rates were higher than fertility rates among slaves in the Danish West Indies," it became "necessary to import slaves every year." Most of these enslaved human beings came "directly from Africa" while others came from "foreign Caribbean islands."
After the slave trade was abolished in 1803, Danish colonizers attempted to establish "cotton, coffee, and sugar plantations on the Gold Coast instead," yet these were largely unsuccessful. By 1817, "almost all of the Danish posts on the Coast were abandoned, with the exception of Fort Christiansborg," which was, along with the other posts, sold to the British in 1850.[1] Throughout the transatlantic slave trade, it is estimated that about 12.5 million Africans were taken captive and 10.7 million of them were transported to the Americas. The Danish slave trade constituted about 1 percent of this trade, with "about 100,000 Africans embarked." Denmark was reportedly the first European colonial empire to ban its slave trade in 1792, although this law did not come into effect until 1803, and illegal trading continued into the nineteenth century.[2]
Forts and settlements
Main forts
The following forts were in the possession of Denmark until all forts were sold to the United Kingdom in 1850.
| Place in Ghana | Fort name | Founded/ Occupied |
Ceded | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accra | Fort Christiansborg | 1658 | 1850 | First captured from the Swedes in 1658. Occupied between 1680 and 1682 by the Portuguese. Sold to the United Kingdom in 1850. |
| Old Ningo | Fort Fredensborg | 1734 | 1850 | Sold to the United Kingdom in 1850. |
| Keta | Fort Prinsensten | 1784 | 1850 | Sold to the United Kingdom in 1850. |
| Ada | Fort Kongensten | 1784 | 1850 | Sold to the United Kingdom in 1850. |
| Teshie | Fort Augustaborg | 1787 | 1850 | Sold to the United Kingdom in 1850. |
Temporarily held forts and trading posts
Apart from these main forts, several forts and trading posts were temporarily held by the Danes.
| Place in Ghana | Fort name | Founded/ Occupied |
Ceded | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cape Coast | Fort Carlsborg | 1658 | 1664 | Captured from the Swedes in 1658. Captured by the British in 1664. |
| Amanful | Fort Frederiksborg | 1659 | 1685 | |
| Cong | Cong Heights | 1659 | 1661 |
See also
- Colonial Heads of Danish Gold Coast the office-holders of the Danish Gold Coast
- Dane gun
- Danish Africa Company
References
- Gobel, Erik (2016). The Danish Slave Trade and Its Abolition. Brill Academic Pub. pp. 3–7. ISBN 9789004330276.
- Erik, Gobel (2016). The Danish Slave Trade and Its Abolition. Brill Academic Pub. pp. 182–183. ISBN 9789004330276.
Further reading
- Closing the Books: Governor Edward Carstensen on Danish Guinea, 1842-50. Translated from the Danish by Tove Storsveen. Accra, Ghana: Sub-Saharan Publishers, 2010.
.svg.png)
.svg.png)