Barka, Oman
Barka (Arabic: بركاء) is a coastal city in the region Al Bāţinah, in northern Oman. Bordered by the Sea of Oman and the Al Hajar mountains in southern Batinah, Barka is about a half-hour drive from Seeb and roughly an hours drive from Al Khuwair and Ruwi.
Barka | |
|---|---|
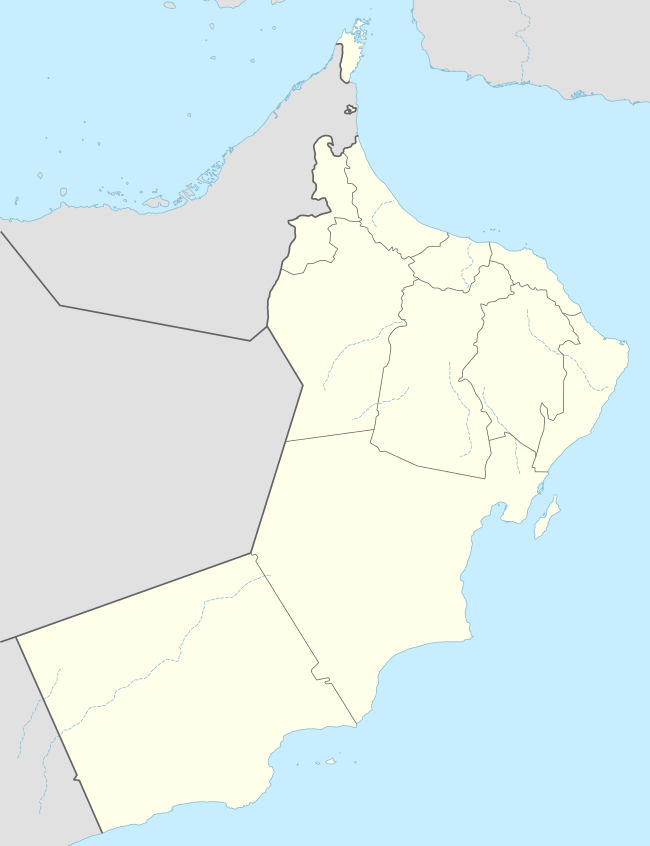 Barka Location in Oman | |
| Coordinates: 23°41′47.1″N 57°53′16.0″E | |
| Country | |
| Subdivision | Al Batinah South Governorate |
| Population (2017) | |
| • Total | 130,000 |
| Time zone | UTC+4:00 United Arab Emirates Standard Time |
History
Al Bloushi, Al-Farsi, Al Zadjali, Al Habsi, Al Ajmi (Ajam), Al Owaisi, Al Amri, Al Badri, Al Raisi tribes live here. The area is known for its agricultural beauty, fishing, and traditional pastimes like horse and camel racing, halwa making, and Omani-style bullfighting.[1]
Attractions
Nearby is Bait Na'aman (Nu'man), a four-towered fort of the 17th-century iman Bil'arab bin Sultan, renovated in 1991.[2] Barka Fort is a known tourist spot. Barka Souq, near to the beach is an economically important area.
There are two major resorts in Barka, the Al-Sawadi resort and the Al-Nahda resort.
Economy
A new quarter is now under construction in Barka, called "Blue City" (المدينة الزقاء), located in Sawadi. The development is 8 km from Sawadi beach, and many international companies are involved in Barka development projects. There is an estimated $15 billion in new construction currently taking place in Barka.
Barka is the site of several power and water plants including:
- The Barka 2 water and power plant, with generation capacity of 678 MW and desalination capacity of 26.4 million gallons of potable water per day[3]
- The Barka 3 gas turbine power plant, with generation capacity of 744 MW, sponsored by Engie, Yonden and Sojitz[4]
- A new 281,000 m³/d desalination plant is to be commissioned: Itochu, Degremont and International Power were named preferred bidders in 2015.[5]

References
- "5 Reasons To Love Barka". Times of Oman. 2016-04-24. Retrieved 2019-12-01.
- "Bait Na'aman". Al Batinah and Al Dhahirah Guide. Rough Guides.
- "Barka 2 Independent Water & Power Project". Mubadala. Retrieved 10 November 2015.
- "Commercial Operations of Sohar 2 and Barka 3 IPP Projects in Oman Start". Sojitz Corporation. Retrieved 10 November 2015.
- "Oman names preferred bidders for Sohar and Barka projects". The International Desalination & Water Reuse Quarterly. 21 October 2015. Retrieved 10 November 2015.
Further reading
- Westermann, Großer Atlas zur Weltgeschichte (in German)