Altheimer, Arkansas
Altheimer is a city in Plum Bayou Township, Jefferson County, Arkansas. It is situated on the Union Pacific Railway, 11 miles (18 km) northeast of Pine Bluff. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 984,[4] down from 1,192 at the 2000 census. As of 2018 the estimated population was 829.[5]
Altheimer, Arkansas | |
|---|---|
| City of Altheimer | |
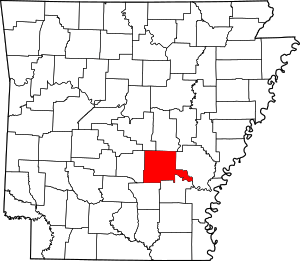
 Location of Altheimer in Jefferson County, Arkansas. | |
 Altheimer Location of Altheimer in the US | |
| Coordinates: 34°19′09.3″N 91°50′50.5″W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | Jefferson |
| Township | Plum Bayou |
| Incorporated | June 9, 1919 |
| Named for | Joseph and Louis Altheimer |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–Council |
| • Mayor | Zola Hudson (I) |
| • Council | Members
|
| Area | |
| • City | 2.12 sq mi (5.49 km2) |
| • Land | 2.05 sq mi (5.31 km2) |
| • Water | 0.07 sq mi (0.18 km2) |
| Elevation | 207 ft (63 m) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • City | 984 |
| • Estimate (2019)[3] | 811 |
| • Density | 395.61/sq mi (152.78/km2) |
| • Metro | 100,258 |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (Central (CST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (CDT) |
| ZIP code | 72004 |
| Area code | 870 |
| FIPS code | 05-01150 |
| GNIS feature ID | 45849 |
| Major airport | LIT |
Geography
Altheimer is part of the Timberlands Region, an area rich in natural resources that was discovered by pioneers from the eastern states in the early 19th century. Deer hunting, bass fishing, timber and oil are plentiful in this area.[6]
Altheimer is in northeastern Jefferson County, 14 miles (23 km) northeast of Pine Bluff, the county seat. U.S. Route 63/79 runs along the northwestern edge of the city, leading southwest to Pine Bluff and northeast 11 miles (18 km) to Humphrey. Little Rock, the state capital, is 50 miles (80 km) to the northwest by road.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Altheimer has a total area of 2.2 square miles (5.6 km2), of which 2.1 square miles (5.4 km2) are land and 0.1 square miles (0.2 km2), or 3.22%, are water.[4] Flat Bayou winds through the center of the city, flowing north toward Wabbaseka Bayou, which in turn flows southeast via a succession of names to the Arkansas River.
History
The city was named for brothers Joseph and Louis Altheimer, two Pine Bluff merchants.[7] Louis, who was born in Eberstadt in 1850, read stories by German adventurer Frederick Gerstacker telling of the rich natural resources in Arkansas, and left for America as a teenager, eventually settling in Pine Bluff.[8][9] Louis brought his brother Joseph with him to the land that would eventually bear their name. Joseph's son, Benjamin, became a successful attorney, establishing the prominent Chicago law firm of Altheimer, Mayer, Woods, and Smith (later known as Altheimer & Gray), and serving twice as president of Chicago's Iroquois Club, the city's oldest Democratic Party political club.[10] Benjamin owned 15,000 acres (61 km2) of land in Arkansas. His foundation, the Ben J. Altheimer Foundation, provided scholarships and funding for projects throughout the state and continues today as the Ben J. Altheimer Charitable Foundation, Inc.[11]
Altheimer is home to many restored pioneer-era log cabins, Victorian era plantation houses and museums. One of the most prominent locations is The Elms, a former plantation house on the Collier Estate built in 1886, renovated by Ben Altheimer in the 1930s. Listed on the National Register of Historic Places, The Elms is open to the public for retreats, family reunions and tours.[11] Also located on the property are the Elms Duck Lodges, which provides hunting and fishing in the private lake and pond.[6] Roselawn, also known as the Collier-Barnett House, was built in 1875 and added to National Register of Historic Places in 1978.[12] Lake Dick is an oxbow lake located four miles (6 km) south of Altheimer.[13] This area formerly held farmsteads of eighty Caucasian families who were moved into the area in 1936 as part of the Farm Security Administration. Lake Dick was added to the register in 1975.[13]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1920 | 450 | — | |
| 1930 | 475 | 5.6% | |
| 1940 | 494 | 4.0% | |
| 1950 | 680 | 37.7% | |
| 1960 | 979 | 44.0% | |
| 1970 | 1,037 | 5.9% | |
| 1980 | 1,231 | 18.7% | |
| 1990 | 972 | −21.0% | |
| 2000 | 1,192 | 22.6% | |
| 2010 | 984 | −17.4% | |
| Est. 2019 | 811 | [3] | −17.6% |
| Encyclopedia of Arkansas History and Culture | |||
As of the census of 2010, there were 984 people, 361 households, and 248 families residing in the city. The racial makeup of the city was 10% White, 88.1% Black or African American, 1% Asian, 0.6% from other races, and 0.3% from two or more races. 1.4% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 361 households, out of which 25.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 37.1% were married couples living together, 24.1% had a female householder with no husband present, and 31.3% were non-families. 27.1% of all households were made up of individuals, and 2.2% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.73 and the average family size was 3.29.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 29.3% under the age of 18, 7.4% from 15 to 19, 7.0% from 40 to 44, 5.3% from 60 to 64, and 13.7% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 36.9 years.
The median income for a household in the city was $32,500, and the median income for a family was $34,153. About 30.9% of families and 35.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including 60.4% of those under age 18 and 3.9% of those age 65 or over.[14]
Education
Primary and secondary schools
Altheimer is served by the Dollarway School District.[15] Students are zoned to James Matthews Elementary School, Robert F. Morehead Middle School, and Dollarway High School, all in Pine Bluff.
In the racial segregation era Altheimer Training School served as the high school for African-Americans, while Altheimer High School served as the high school for white students.[16] Altheimer was formerly served by the Altheimer-Sherrill School District until September 1, 1993, when it consolidated into the Altheimer Unified School District;[17] Altheimer Unified operated two schools: Martin Elementary School and Altheimer-Sherrill High School.[18] The Altheimer Unified School District consolidated into the Dollarway School District on July 10, 2006.[17]
Altheimer-Martin Elementary School, a Dollarway School District elementary school, occupied the former high school facility. The 30,000-square-foot (2,800 m2) building was built in 1987; it included a gymnasium. Up to 2013 the school's enrollment declined, and in 2013 the Dollarway superintendent decided that the school should be closed in light of the declining attendance. Since 2013 some property had been taken from the school building, and a lack of maintenance occurred. Altheimer mayor Zola Hudson stated a desire for the city government to repurpose the building.[19]
Public libraries
The Pine Bluff-Jefferson County Library System operates the Altheimer Branch, an about 3,500 square feet (330 m2) building identical to that of the Redfield Library,[20] located on a 1-acre (0.40 ha) tract in Altheimer. The library was built on land sold by Altheimer Unified to the county government for $3,784.[21] The library was constructed in October 2001.[20]
Notable people
- Gloria Long Anderson[16][22]
- Tail Dragger Jones (born James Yancey Jones, 1940), American singer
- James McDonnell (1899-1980), American aerospace engineer
See also
References
- "Altheimer". Arkansas Municipal League. Retrieved January 4, 2017.
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 30, 2020.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". United States Census Bureau. May 24, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- "Geographic Identifiers: 2010 Census Summary File 1 (G001): Altheimer city, Arkansas". American Factfinder. U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved April 17, 2018.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved February 20, 2020.
- "Your New Hometown: The Timberlands." Archived March 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine Arkansas.com. Retrieved January 15, 2016.
- Biographical and Historical Memoirs of Pulaski, Jefferson, Lonoke, Faulkner, Grant, Saline, Perry, Garland and Hot Spring Counties, Arkansas. Chicago, Nashville and St. Louis: Goodspeed Publishing Co. 1889. p. 149. LCCN 01001243. OL 24190554M – via Internet Archive.
- "Louis Altheimer". Arkansasties.com. Archived from the original on October 2, 2013. Retrieved June 7, 2013.
- Teske, Steven (January 5, 2012). "Altheimer (Jefferson County)". Encyclopedia of Arkansas History and Culture. Butler Center for Arkansas Studies at the Central Arkansas Library System. Retrieved March 29, 2014.
- Andreas, Thomas Alfred. History of Chicago. Google Books. 3. Chicago: A.T. Andreas, 1884-1886. pp. 398–407. ISBN 1236331788. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- LeMaster, Carolyn Gray. "Benjamin Joseph Altheimer Jr." Encyclopedia of Arkansas History and Culture. Retrieved June 10, 2013.
- "Arkansas-Jefferson County". National Register of Historic Places. Retrieved June 10, 2013.
- Norman, Bill. "Lake Dick." Encyclopedia of Arkansas History and Culture. Retrieved June 10, 2013.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 28, 2013.
- "SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP (2010 CENSUS): Jefferson County, AR." U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved on July 31, 2017. Note that, while the Altheimer Unified School District's boundaries are indicated, the district had already consolidated into Dollarway School District at the time the map was made.
- Brown, Jeannette E. (August 21, 2009). Gloria L. Anderson, Transcript of Interview Conducted by Jeannette E. Brown at Morris Brown College Atlanta, Georgia on 21 August 2009 (PDF). Philadelphia, PA: Chemical Heritage Foundation.
Her high school was called Altheimer Training School; the one for white students was called Altheimer High School.
- "ConsolidationAnnex_from_1983.xls." Arkansas Department of Education. Retrieved on July 31, 2017.
- "2002-2003 Arkansas Education Directory." Arkansas Department of Education. Retrieved on July 31, 2017. Page 65 (PDF p. 71/157).
- Hardy, Benjamin (July 28, 2016). "School's out forever". Arkansas Times. Retrieved July 31, 2017.
- "Altheimer Public Library." Pine Bluff-Jefferson County Library System. Retrieved on August 2, 2017.
- "Altheimer Unified School District No. 22 Jefferson County, Arkansas General Purpose Financial Statements and Other Reports June 30, 2001." Legislative Joint Auditing Committee, Arkansas Legislature. Retrieved on August 2, 2017. page 3 (PDF p. 5/22).
- Center for Oral History. "Gloria L. Anderson". Science History Institute.
Further reading
- Leslie, James W. (1981). Pine Bluff and Jefferson County: A Pictorial History. Norfolk, Va.: Donning Co. ISBN 978-0898651485. OCLC 7462693.
- Moneyhon, Carl H. (1997). West, Elliott (ed.). Arkansas and the New South 1874-1929. Histories of Arkansas. Fayetteville: University of Arkansas Press. ISBN 1-55728-490-3. OCLC 37269309.
- Rand, McNally & Co.'s New Business Atlas Map of Arkansas (Map). 1:900,000. Rand, McNally & Co. 1898. LCCN 98688447. Retrieved July 4, 2017 – via Library of Congress.
External links
- Government
- Altheimer at Jefferson County, Arkansas (jeffersoncounty.arkansas.gov)
- General information
- Altheimer Public Library at Pine Bluff and Jefferson County Library System (pineblufflibrary.org)