Yamen
A yamen (ya-men; simplified Chinese: 衙门; traditional Chinese: 衙門; pinyin: yámén; Wade–Giles: ya2-men2; Manchu: ᠶᠠᠮᡠᠨyamun) was the administrative office or residence of a local bureaucrat or mandarin in imperial China. A yamen can also be any governmental office or body headed by a mandarin, at any level of government: the offices of one of the Six Ministries is a yamen, but so is a prefectural magistracy. The term has been widely used in China for centuries, but appeared in English during the Qing dynasty.
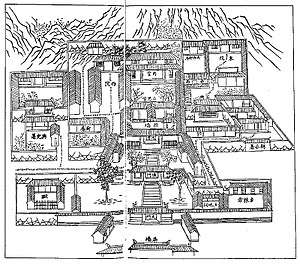
Overview
Within a local yamen, the bureaucrat administered the government business of the town or region. Typical responsibilities of the bureaucrat includes local finance, capital works, judging of civil and criminal cases, and issuing decrees and policies.
Typically, the bureaucrat and his immediate family would live in a residence attached to the yamen. This was especially so during the Qing dynasty, when imperial law forbade a person from taking government office in his native province.
Yamens varied greatly in size depending on the level of government they administered, and the seniority of the bureaucrat's office. However, a yamen at a local level typically had similar features: a front gate, a courtyard and a hall (typically serving as a court of law); offices, prison cells and store rooms; and residences for the bureaucrat, his family and his staff.

At the provincial level and above, specialisation among officials occurred to a greater extent. For example, the three chief officials of a province (simplified Chinese: 三大宪; traditional Chinese: 三大憲; pinyin: Sàn Dà Xiàn; lit.: 'the Three Great Laws') controlled the legislative and executive, the judicial, and the military affairs of the province or region. Their yamen would accordingly be specialised according to the functions of the office. The great yamens of the central government, located in the capital, are more exclusively office complexes.
The Yamen Runner in Ming Dynasty
General
Yamen Runner (Chinese: 衙役) is an occupation which served for Yamen (Chinese: 衙门), the law enforcement department in ancient China. There are three kinds of Yamen Runner, zao(皂), zhuang(壮), kuai(快). But in fact, there were more different kinds in specific. They worked as the lowest class in the government department which made them a bridge between the common people and the government.[1]
Classification
Zao usually serves around the court. Zhuang provides physical labor and Kuai is in charge of inspection, investigation, and arrest.
Zao
Zao is like the officials' bodyguards. They usually followed behind the officials. During the trial, they would stand on both sides of the court to maintain order. They also perform the duty of escorting the prisoner. Questioning the suspect and applying minor punishment are also their jobs. They have their own black uniform.[1]
Zhuang
Zhuang is like security guards today. Their main job is to guard the critical areas such as castle gates, the court, prison, and warehouse. They also patrol on the streets. Most of them are picked among strong civilians.[1]
Kuai
Kuais' job includes summoning defendants and witnesses to the court. They are usually asked to do the trips for the court, sometimes they have to travel long distance if necessary. During the tax season, they would be sent to remote areas to collect for the government. Therefore, Kuai had more chances to contact with civilians than Zao and Zhuang. They didn't have their own uniform, but they were required to hang a card on the waist belt to identify themselves.[1]
Social status
In Ming Dynasty, Yamen Runners were considered as a debased class (jianmin, Chinese: 贱民), which is even lower than good commoners (liangmin, Chinese: 良民) such as farmers. It is the lowest stratum in society.[2]
Income
The salary provided by the court for the Yamen Runner is pretty low comparing to other jobs. The average daily salary is just enough for only one meal. Obviously, the salary is not enough for a living, not to mention to raise a family. However, working for the law enforcement department gives them some power that can be taken advantage of. The Yamen Runners would charge a little amount of fee from the litigants to cover the spendings. The prefects and magistrates acquiesce such a charging system as long as the amount is in a reasonable range. The Kuai, however, couldn't contact the litigants in the lawsuit cases. They would ask for money from the other debased classes like butchers and prostitutes. Such unwritten rule is called dirty regulation (Chinese: 陋规). Therefore, the actual income of the Kuai depends on the place they are working, the Kuai in large cities can easily collect quite a lot money and the one in the rural areas can be as poor as homeless.[1]
Such corruption and extortion were rampant during Xuande Emperor reign. The prefects and magistrates just turn a deaf ear on their clerks blackmailing the lower classes. Xuande Emperor described them "licentious, greedy, and insatiably exploitative, or are degenerate and worthless."[3]
Path into the occupation
Since the social status is low and the income is unstable (usually is low). The Yamen Runners are mostly formed by vagrants, especially among Kuai. They are usually strong but uneducated.
Paper Yamen Runner
Paper Yamen Runner (Chinese: 纸皂) is a piece of paper on which a Yamen Runner is drawn and the guilt of litigants or tax defaulters and a claim for them to show up in the court or pay the tax is written. The prefects and magistrates issue this to the litigants or tax defaulters in the hope that they will go to the court in time by themselves or pay tax in arrears. It’s unclear when was Paper Yamen Runner created, but literature about it and examples of the Ming and Qing Dynasties can be found.

Because Yamen Runners is easy to act jobbery, magistrates will not allow Yamen Runner to take part in but to let plaintiff to take litigants to the court first. Only if the plaintiff failed to do that, he will issue a Paper Yamen Runner. Only if both methods fail to ask the litigants to the court, a Yamen Runner is sent to arrest him. In this way, people can be less bothered by Yamen Runners.
It is usually only used to deal with cases with mild crimes. For serious crimes such as murder, theft, gambling, and fights, the magistrate will still send Yamen Runners directly for arrest.
After 1911
The institution of the yamen fell victim to the Wuchang Uprising and the Xinhai Revolution, after which warlords often wound up becoming the ultimate authorities, in spite of Sun Yat-sen's best efforts to establish a Republic of China covering all of China. Sun Yat-sen tried to establish a form of self-government, or home rule, on a regional (or local) basis, but he found that he needed bureaucracy to run a country as big as China. Hence, new bureaucratic offices arose, thus replicating the functions of the Imperial yamens in many ways.
The term yamen is still used in colloquial Chinese today, however, to denote government offices. It sometimes carries negative connotations of an arrogant or inefficient bureaucracy, much as the term "mandarin" does in English.
Notable yamens
- The Zongli Yamen acted as an office of foreign affairs in the late Qing dynasty .
- The yamen at Kowloon Walled City, Hong Kong is an important historical site.
- The Presidential Palace (Nanjing) was modified from the "yamen" of the Viceroy of Liangjiang.
- The yamen of Neixiang County, in Henan, is the best preserved county-level yamen in mainland China today.
- The yamens of the six imperial Ministries of the Qing dynasty, in Beijing, were located within what is now Tiananmen Square, and were demolished in stages in the early to mid 20th century.
- The Qing Dynasty Taiwan Provincial Administration Hall in Taipei is the sole surviving Qing Dynasty government building in Taiwan.
References
- Li, Zongya 李宗亚. Three kinds of Yamen Runner in Yamen. 衙门中的三班衙役, Chinese & Foreign Entrepreneurs, 中外企业家, Editorial E-mail, 2014(29)
- Moll-Murata, Christine. “Work Ethics and Work Valuations in a Period of Commercialization: Ming China, 1500–1644.” International Review of Social History, vol. 56, no. S19, 2011, pp. 165–195., doi:10.1017/s0020859011000514.
- Nimick, Thomas G. “The Selection of Local Officials through Recommendations in Fifteenth-Century China.” T'oung Pao, vol. 91, no. 1/3, 2005, pp. 125–182. JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/4528998.