Woollins' reagent
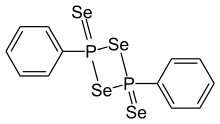
Woollins' reagent is an organic compound containing phosphorus and selenium. Analogous to Lawesson's reagent, it is used mainly as a selenation reagent. It is named after Professor John Derek Woollins, who is currently the Provost of Khalifa University, Abu Dhabi.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,4-Diphenyl-1,3,2,4- | |
| Other names
Woollins' Reagent | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.155.582 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10P2Se4 | |
| Molar mass | 532.044 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | red powder |
| Melting point | 192 to 204 °C (378 to 399 °F; 465 to 477 K) [1] |
| soluble in toluene at elevated temperatures | |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R23/25 R33 R50/53 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | (S1/2) S20/21 S28 S45 S60 S61 |
| Related compounds | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Preparation
Woollins' reagent is commercially available. It can also be conveniently prepared in the laboratory by heating a mixture of dichlorophenylphosphine and sodium selenide (Na2Se), (itself prepared from reacting elementary selenium with sodium in liquid ammonia).[2] An alternative synthesis is the reaction of the pentamer (PPh)5 with elemental selenium.[3]
Applications
The main use of Woollins' reagent is the selenation of carbonyl compounds.[4] For instance, Woollins' reagent will convert a carbonyl into a selenocarbonyl. Additionally, Woollins' reagent has been used to selenonate carboxylic acids, alkenes, alkynes, and nitriles.[5]
References
- The Merck Index. An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. 14. Auflage, 2006, S. 1731, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1.
- Ian P. Gray, Pravat Bhattacharyya, Alexandra M. Z. Slawin and J. Derek Woollins (2005). "A New Synthesis of (PhPSe2)2 (Woollins Reagent) and Its Use in the Synthesis of Novel P-Se Heterocycles". Chem. Eur. J. 11 (21): 6221–7. doi:10.1002/chem.200500291. PMID 16075451.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- M. J. Pilkington, Alexandra M. Z. Slawin and J. Derek Woollins (1990). "The preparation and characterization of binary phosphorus-selenium rings". Heteroatom Chemistry. 1 (5): 351–355. doi:10.1002/hc.520010502.
- Pravat Bhattacharyya & J. Derek Woollins (2001). "Selenocarbonyl synthesis using Woollins reagent". Tetrahedron Lett. 42 (34): 5949. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)01113-3. hdl:10023/1776.
- Guoxiong Hua & J. Derek Woollins (2009). "Formation and Reactivity of Phosphorus-Selenium Rings". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48 (8): 1368–1377. doi:10.1002/anie.200800572. PMID 19053094.