White & Thompson No. 1 Seaplane
The White & Thompson No. 1 Seaplane (also No. 1 Flying boat) was the first British built twin-engined biplane flying boat,[1] assembled just prior to the outbreak of the First World War to compete in an air-race around the UK. It was unsuccessful, only the single prototype being built.
| No. 1 Seaplane | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Circuit of Britain No.1 Seaplane, summer 1914. | |
| Role | Flying boat |
| National origin | United Kingdom |
| Manufacturer | White & Thompson |
| Designer | Norman Thompson |
| First flight | October 1914 |
| Status | Prototype |
| Number built | 1 |
Design and development
In 1914, the White and Thompson Company Limited, of Bognor Regis, England, who had become exclusive licence holders for Curtiss flying boats for Great Britain the previous year, decided to build two different flying boats, designed by Norman Thompson, co-owner and the driving force behind White & Thompson, to compete in the Daily Mail £5,000 Circuit of Britain race for seaplanes, scheduled to start on 10 August that year. Thompson's designs were a single-engined flying boat, similar to the Curtiss Model F flying boat which Thompson had a licence for, and a larger twin-engined aircraft.[2][3]
The twin-engined aircraft, the White & Thompson No. 1 Seaplane, was a biplane powered by two pusher Curtiss OX water-cooled V-8 engines driving three-bladed propellers with adjustable pitch.[4][5] It was of wooden construction, with the fuselage built of elm and spruce planked with mahogony. The crew of two sat side-by side in a cockpit fitted with dual-controls just ahead of the wings. Its tail assembly had a large fin which was supplemented by two auxiliary fins mounted on the upper wing, and a high mounted horizontal tail.[4][5]
Operational history

Although started later, the single-engined aircraft, the No. 2 Seaplane, flew first on 1 August 1914.[3] The No. 1 was still not ready when the Circuit of Britain race was cancelled on 4 August due to the outbreak of World War I. Initial attempts in September 1914 to fly the No. 1 proved unsuccessful, it proving unable to leave the water. After a great deal of modification, supervised by White & Thompson's new chief designer, Percy Beadle, culminating in the fitting of horizontal planing fins to the hull, for the aircraft to finally able to make its maiden flight during October.[6][7]
Although the No. 1 was impressed by the Royal Naval Air Service, it was never delivered, being retained by White & Thompson for testing,[6][8] and indeed it is possible that it never flew again following its maiden flight.[3]
Specifications
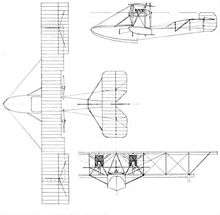
Data from The Norman Thompson File[9]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 32 ft 3 in (9.83 m)
- Upper wingspan: 52 ft 0 in (15.85 m)
- Lower wingspan: 40 ft 0 in (12.19 m)
- Height: 10 ft 6 in (3.20 m) (approx)
- Wing area: 500 sq ft (46 m2)
- Airfoil: RAF 6[10]
- Empty weight: 2,000 lb (907 kg)
- Gross weight: 3,000 lb (1,361 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 90 imp gallons (410 L)
- Powerplant: 2 × Curtiss OX water-cooled V-8 engine, 90 hp (67 kW) each
Performance
See also
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
Notes
- "1917: Norman Thompson Flight Co Ltd". Aviation Ancestry. Historic British Aviation Advertisements Archive. 2 May 1917. Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- Flight 17 July 1914, p.731.
- London 1996, p.71.
- Goodall 1995, pp. 25–26.
- Flight 9 October 1914, pp. 1014–1016.
- Goodall 1995, p. 27.
- London 2003, p. 13.
- London 2003, pp. 12–13.
- Goodall 1995, p. 32.
- Flight 9 October 1914, p. 1014
- London 2003, pp. 266–267.
References
.jpg)
- Bruce, J.M. British Aeroplanes 1914-18. London:Putnam, 1957.
- Goodall, Michael H. The Norman Thompson File. Tunbridge Wells, UK: Air-Britain, 1995. ISBN 0-85130-233-5.
- London, Peter. "Bognor's Boats: The Aircraft of Norman Thompson". Air Enthusiast, No. 66, November–December 1996. Stamford, UK:Key Publishing. ISSN 0143-5450. pp. 70–75.
- London, Peter. British Flying Boats. Stroud, UK:Sutton Publishing, 2003. ISBN 0-7509-2695-3.
- "The Royal Aero Club of the United Kingdom: Official Notices to Members", Flight, 17 July 1914, p. 731.
- "The "Round Britain" Machines". Flight, 9 October 1914, pp. 1014–1016.