Whewell (crater)
Whewell is a lunar impact crater that lies on a stretch of lava-resurfaced terrain to the west of Mare Tranquillitatis. Its diameter is 13 km. It was named after the 19th century philosopher and naturalist, William Whewell.[1] It is located to the east of the disintegrated crater Tempel and north-northwest of D'Arrest. To the east is Cayley, a slightly larger but very similar formation. To the North lies the Rima Ariadaeus, which is a linear rille that is 300 kilometers long and was formed when a section of the Moon's crust sank down between two parallel fault lines, producing a graben. Further north again, lies the 90 km wide crater Julius Caeser.
 Whewell crater, northeast is its satellite crater Whewell A | |
| Coordinates | 4.2°N 13.7°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 13 km |
| Depth | 2.3 km |
| Colongitude | 347° at sunrise |
| Eponym | William Whewell |
This is a circular, bowl-shaped crater with interior walls that slope down gently to a small interior floor. This crater has not been significantly eroded, and the rim is well-defined.
Satellite craters
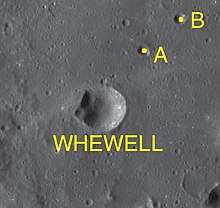
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Whewell.
| Whewell | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 4.7° N | 14.1° E | 4 km |
| B | 5.0° N | 14.5° E | 3 km |
References
- "Whewell (crater)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Whewell (crater). |
- Whewell at The Moon Wiki
- Wood, Chuck (December 12, 2006). "How Deep is That Hole". Lunar Photo of the Day. Archived from the original on June 14, 2011. - includes a couple of craters such as Whewell
- Wood, Chuck (March 17, 2013). "A Russian Masterpiece". Lunar Photo of the Day.