Wandad Hurmuzd
Vindadhhurmuzd (Persian: هرمز ونداد), also known by the more correct form of Vandad Hormozd (ونداد هرمزد), was the ruler of the Qarinvand dynasty from 765 to 809.
| Vandad Hormozd | |
|---|---|
| 'Ispahbadh of the Qarinvand dynasty | |
| Reign | 765-809 |
| Predecessor | Unknown |
| Successor | Qarin ibn Vindadhhurmuzd |
| Born | Unknown Tabaristan |
| Died | 809 |
| House | House of Karen |
| Dynasty | Qarinvand dynasty |
| Father | Unknown |
| Religion | Zoroastrianism |
Background
In 760, during the reign of Vandad Hormozd's unnamed father, the Dabuyids, under Khurshid of Tabaristan, revolted against the Abbasid Caliphate. Khurshid was defeated, however, and fled to Daylam. From there he launched a counterattack against the Abbasids, but was once again defeated. After learning that his family was captured by the Abbasids, Khurshid poisoned himself.[1][2][3] This marked the end of the Dabuyid dynasty, but the other local dynasties such as the Qarinvands, Bavandids and Zarmihrids, who were all formerly subject to the Dabuyids, continued to control parts of Tabaristan, as tributary vassals of the Abbasid government.
Biography
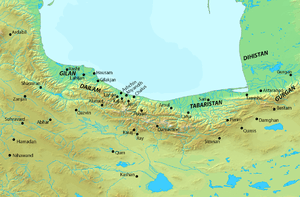
In 765, Vandad Hormozd became the ruler of the Qarinvand dynasty. In 772, Khalid ibn Barmak, the Abbasid governor of Tabaristan, left the region. Shortly after Khalid's departure, Vandad Hormozd sent the Bavand ruler Sharwin I a letter which urged him to revolt against the Abbasids. Sharwin I accepted,[4] and along with Vandad Hormozd, and the Zarmihrid ruler, rose in revolt. They then began destroying the cities built by the Muslims in the region, and in 782, Sharwin I along with Vandad Hormozd exterminated all the Muslims in Tabaristan. During the same period, Vandad Hormozd assumed the Dabuyid title of Gilgilan,[5] while Sharwin I assumed the title of Padashwargarshah ("king of the mountains").[6] The Abbasid caliph al-Mahdi, who had received the news about the Zoroastrian revolt in Tabaristan, sent one of his most distinguished officers, named Salim of Farghana, against the rebels, but Vandad Hormozd, with the aid of his brother Vinda-Umid, managed to defeat and kill Salim.[4] Al-Mahdi then sent Firasha, who was also defeated, captured and executed by Vandad Hormozd.
Vandad Hormozd continued to repel successive Arab invasions of Tabaristan until 785, when he and the other native rulers of Tabaristan were finally defeated, and once again agreed to pay tribute to the Abbasid caliphs.
In 805, the Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid visited Ray, where he met Vandad Hormozd and Sharwin I, who assured their submission to him and promised to pay tax. In order to ensure their loyalty, Harun took Sharwin's grandson Shahriyar I and Vandad Hormozd's son Qarin ibn Vindadhhurmuzd as hostages to Baghdad. The two princes were allowed to return to Tabaristan after Harun al-Rashid's death four years later.[7]
Vandad Hormozd died in 809, and was succeeded by his son Qarin ibn Vindadhhurmuzd.
References
- Rekaya (1986), pp. 68–70
- Madelung (1975), p. 200
- Pourshariati (2008), p. 317
- Ibn Isfandiyar, p. 128-132
- The Minor Dynasties of Northern Iran, C.E. Bosworth, The Cambridge History of Iran, Vol. 4, ed. W. Madelung, (Cambridge University Press, 1975), 201.
- Madelung (1984), pp. 747–753
- The Minor Dynasties of Northern Iran, C.E. Bosworth, The Cambridge History of Iran, Vol. 4, ed. W. Madelung, (Cambridge University Press, 1975), 204.
Sources
- Bosworth, C. E. (1968). "The Political and Dynastic History of the Iranian World (A.D. 1000–1217)". In Frye, R. N. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 5: The Saljuq and Mongol periods. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–202. ISBN 0-521-06936-X.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Frye, R. N. (1986). "Bāwand". The Encyclopedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume I: A–B. Leiden and New York: BRILL. p. 1110. ISBN 90-04-08114-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Madelung, W. (1975). "The Minor Dynasties of Northern Iran". In Frye, R. N. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 4: From the Arab Invasion to the Saljuqs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 198–249. ISBN 978-0-521-20093-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Madelung, W. (1984). "ĀL-E BĀVAND (BAVANDIDS)". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. I, Fasc. 7. London u.a.: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 747–753. ISBN 90-04-08114-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Rekaya, M. (1997). "Ḳārinids". The Encyclopedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume IV: Iran–Kha. Leiden and New York: BRILL. pp. 644–647. ISBN 90-04-05745-5.
- Mottahedeh, Roy (1975). "The ʿAbbāsid Caliphate in Iran". In Frye, R. N. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 4: From the Arab Invasion to the Saljuqs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 57–90. ISBN 978-0-521-20093-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ibn Isfandiyar, Muhammad ibn al-Hasan (1905). An Abridged Translation of the History of Tabaristan, Compiled About A.H. 613 (A.D. 1216). Trans. Edward G. Browne. Leyden: E.J. Brill.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
| Preceded by Unknown |
Qarinvand ruler 765–809 |
Succeeded by Qarin ibn Vindadhhurmuzd |