Daylam
Daylam, also known in the plural form Daylaman (and variants such as Dailam, Deylam, and Deilam), was the name of a mountainous region of inland Gilan, Iran.[1][2][3][4][5] It was so named for its inhabitants, known as the Daylamites.[6]
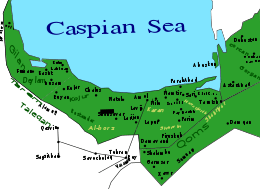
Map showing Daylam in western Tabaristan
The Church of the East established a metropolitan diocese for Daylam and Gilan around 790 under Shubhalishoʿ.[7]
See also
- Buyid dynasty
- Daylami language
- Gilaks
- al-Daylami
References
- Frye, Richard Nelson; Fisher, William Bayne; Madelung, W. (1975-06-26). The Cambridge History of Iran. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521200936.
- Frye, Richard Nelson; Fisher, William Bayne; Bosworth, C. E. (1975-06-26). The Cambridge History of Iran. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521200936.
- Tilman, Nagel (1990). "BUYIDS - Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. IV, Fasc. 6". www.iranicaonline.org. London u.a.: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 578–586. Retrieved 2017-03-04.
- Donohue, John J. (2003-01-01). The Buwayhid Dynasty in Iraq 334h., 945 to 403h., 1012: Shaping Institutions for the Future. BRILL. ISBN 9004128603. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- Kabir, Mafizullah (1964-01-01). The Buwayhid Dynasty of Baghdad, 334/946-447/1055. Iran Society. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- Wilferd Madelung, Wolfgang Felix (1995). "DEYLAMITES – Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. BII, Fasc. 4". www.iranicaonline.org. pp. 342–347. Retrieved 2017-03-04.
- David Wilmshurst (2011), The Martyred Church: A History of the Church of the East, East and West Publishing, p. 166.
Bibliography
- Amedroz, Henry F.; Margoliouth, David S., eds. (1921). The Eclipse of the ‘Abbasid Caliphate. Original Chronicles of the Fourth Islamic Century, Vol. V: The concluding portion of The Experiences of Nations by Miskawaihi, Vol. II: Reigns of Muttaqi, Mustakfi, Muti and Ta'i. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.