Wadi Hammamat
Wadi Hammamat (English: Valley of Many Baths, Coptic: ⲣⲁϩⲱⲓⲙⲓ, ⲣⲁϩⲉⲛⲧⲟⲩ Route of waves, Indian route[1]) is a dry river bed in Egypt's Eastern Desert, about halfway between Al-Qusayr and Qena. It was a major mining region and trade route east from the Nile Valley in ancient times, and three thousand years of rock carvings and graffiti make it a major scientific and tourist site today.
Trade route
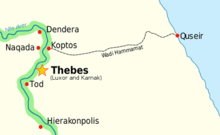
Hammamat became the major route from Thebes to the Red Sea and then to the Silk Road that led to Asia, or to Arabia and the horn of Africa. This 200 km journey was the most direct route from the Nile to the Red Sea, as the Nile bends toward the coast at the western end of the wadi.
The Hammamat route ran from Qift (or Coptos), located just north of Luxor, to Al-Qusayr on the coast of the Red Sea. Qift was an important center for administration, religion, and commerce. The cities at both ends of the route were established by the First Dynasty, although evidence of predynastic occupation also has been found along the route.[2]
Quarries
In Ancient Egypt Hammamat was a major quarrying area for the Nile Valley. Quarrying expeditions to the Eastern Desert are recorded from the second millennia BCE, where the wadi has exposed Precambrian rocks of the Arabian-Nubian Shield. These include Basalts, schists, bekhen-stone (an especially prized green metagraywacke sandstone used for bowls, palettes, statues, and sarcophagi) [3] and gold-containing quartz.[4] The Narmer Palette, 3100 BC, is one of a number of early and predynastic artifacts that were carved from the distinctive stone of the Wadi Hammamat.
Pharaoh Seti I is recorded as having the first well dug to provide water in the wadi, and Senusret I sent mining expeditions there.
The site is described in the earliest-known ancient geological map, the Turin Papyrus Map.[5]
Carvings
Today Hammamat is famous mostly for its ancient Egyptian graffiti, as well as that, in ancient times, it was a quarry that lay on the Silk Road to Asia, and is a common destination for modern tourists. The wadi contains many carvings and inscriptions dating from before the earliest Egyptian Dynasties to the modern era, including the only painted petroglyph known from the Eastern Desert and drawings of Egyptian reed boats dated to 4000 BCE.[6]
Common era
Occupying groups from the Roman-Byzantine Periods to the Late Ptolemaic Period operated gold mines near the well Bir Umm el-Fawakhir. Yet, the New Kingdom of Egypt gold mines at Wadi el-Sid were on a larger scale.[5]:129,136–141
A modern asphalt road, the Wadi Hammamat road now runs for 194 km through the wadi, making it a vital transport route, and enabling tourists to travel easily between the sites of nearby Luxor and Thebes.[7]
Modern European description
The first European descriptions of the Wadi Hammamat were from the Scottish traveler James Bruce in 1769, and the Russian Egyptologist Vladimir Golenishchev led the first modern study of the inscriptions in 1884-1885.
Biblical significance
Pi-hahiroth on the eastern shore of Sinai just south of the Gulf of Aqaba, near Thebes port of Elim, is recorded in the Book of Exodus as a stop on the flight of the Jews from Egypt, suggesting that their path was through the Wadi Hammamat.
Popular culture
In 1993, The Pogues wrote a song about it, entitled Girl From The Wadi Hammamat in their album Waiting for Herb.
References
- Meeks, Cf. D. Coptos et le chemin de Pount. p. 303.
- The Archaeology of the Eastern Desert, Appendix F: Desert Rock Areas and Sites. Andie Byrnes, University College London, June 2007. Retrieved September 2007.
- Survey of ancient Egyptian stone quarries (rock varieties and images, locations, and ages). James A. Harrell, Professor of Geology, Department of Environmental Sciences, University of Toledo. Retrieved September 2007.
- Dollinger, André, Mining, An introduction to the history and culture of Pharaonic Egypt. 2000. Retrieved September 2007.
- Klemm, Rosemarie; Klemm, Dietrich (2013). Gold and Gold Mining in Ancient Egypt and Nubia. Heidelberg: Springer. pp. 132–136. ISBN 9783642225079.
- Desert Boats Home Page Wadi Hammamat: Gallery and description of several dynastic and predynastic sites in the Wadi, by Francis Lankester. Retrieved June 2013.
- planetware, detailed modern travel description.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Wadi Hammamat. |
- Photograph Gallery of a visit to Wadi Hammamat
- Demotic Graffiti from the Wadi Hammamat, from Dr. Eugene Cruz-Uribe, Northern Arizona University
- Wadi Hammamat, The Road to the Sea, photographs by Yarko Kobylecky
- Hammamat Inscriptions, translated to English in An introduction to the history and culture of Pharaonic Egypt. André Dollinger, 2000. Retrieved September 2007.
- The Duke Databank of Documentary Papyri. O.Wadi Hamm.: Nouveaux textes grecs du Ouadi Hammamat, Database of Greek inscriptions in the Wadi Hammamat
- Aegyptias Museum, University of Leipzig, "Steine der Pharaonen in Leipzig": Guide to 2005 exhibit of stonework and photographs of the Wadi Hammamat
