WARS (gene)
Tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase, cytoplasmic is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the WARS gene.[5][6][7]
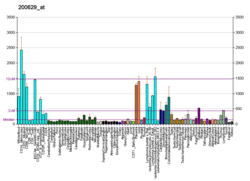
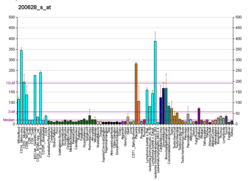
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyze the aminoacylation of tRNA by their cognate amino acid. Because of their central role in linking amino acids with nucleotide triplets contained in tRNAs, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are thought to be among the first proteins that appeared in evolution. Two forms of tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase exist, a cytoplasmic form, named WARS, and a mitochondrial form, named WARS2. Tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase (WARS) catalyzes the aminoacylation of tRNA(trp) with tryptophan and is induced by interferon. Tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase belongs to the class I tRNA synthetase family. Four transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene.[7]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000140105 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000021266 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Buwitt U, Flohr T, Bottger EC (Mar 1992). "Molecular cloning and characterization of an interferon induced human cDNA with sequence homology to a mammalian peptide chain release factor". EMBO J. 11 (2): 489–96. PMC 556479. PMID 1537332.
- Fleckner J, Rasmussen HH, Justesen J (Feb 1992). "Human interferon gamma potently induces the synthesis of a 55-kDa protein (gamma 2) highly homologous to rabbit peptide chain release factor and bovine tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 88 (24): 11520–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.24.11520. PMC 53167. PMID 1763065.
- "Entrez Gene: WARS tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase".
Further reading
- Ewalt KL, Schimmel P (2002). "Activation of angiogenic signaling pathways by two human tRNA synthetases". Biochemistry. 41 (45): 13344–9. doi:10.1021/bi020537k. PMID 12416978.
- Rasmussen HH, van Damme J, Puype M, et al. (1993). "Microsequences of 145 proteins recorded in the two-dimensional gel protein database of normal human epidermal keratinocytes". Electrophoresis. 13 (12): 960–9. doi:10.1002/elps.11501301199. PMID 1286667.
- Bange FC, Flohr T, Buwitt U, Böttger EC (1992). "An interferon-induced protein with release factor activity is a tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase". FEBS Lett. 300 (2): 162–6. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(92)80187-L. PMID 1373391.
- Rubin BY, Anderson SL, Xing L, et al. (1992). "Interferon induces tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase expression in human fibroblasts". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (36): 24245–8. PMID 1761529.
- Frolova LYu, Sudomoina MA, Grigorieva AYu, et al. (1992). "Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the structural gene encoding for human tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase". Gene. 109 (2): 291–6. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(91)90624-K. PMID 1765274.
- Frolova LY, Grigorieva AY, Sudomoina MA, Kisselev LL (1993). "The human gene encoding tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase: interferon-response elements and exon-intron organization". Gene. 128 (2): 237–45. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(93)90568-N. PMID 7685728.
- Popenko VI, Cherny NE, Beresten SF, et al. (1994). "Immunoelectron microscopic location of tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase in mammalian, prokaryotic and archaebacterial cells". Eur. J. Cell Biol. 62 (2): 248–58. PMID 7925483.
- Børglum AD, Flint T, Tommerup N, et al. (1996). "Assignment of the human tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase gene (WARS) to chromosome 14q32.2 --> q32.32". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 73 (1–2): 99–103. doi:10.1159/000134317. PMID 8646895.
- Sokolova IV, Narovlianskiĭ AN, Amchenkova AM, Turpaev KT (1996). "[Alternative splicing of 5'-terminal exons of the human tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase gene]". Mol. Biol. (Mosk.). 30 (2): 319–29. PMID 8724762.
- Krause SW, Rehli M, Kreutz M, et al. (1996). "Differential screening identifies genetic markers of monocyte to macrophage maturation". J. Leukoc. Biol. 60 (4): 540–5. PMID 8864140.
- Yuan W, Collado-Hidalgo A, Yufit T, et al. (1998). "Modulation of cellular tryptophan metabolism in human fibroblasts by transforming growth factor-beta: selective inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase gene expression". J. Cell. Physiol. 177 (1): 174–86. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199810)177:1<174::AID-JCP18>3.0.CO;2-D. PMID 9731757.
- Jensen LL, Nielsen MM, Justesen J, Hansen LL (2001). "Assignment of human NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 beta subcomplex 3 (NDUFB3) and of its four pseudogenes to human chromosomes 2q31.3, 1p13.3→p13.1, 9q32→q34.1, 14q22.3→q23.1 and 14q32.2 by radiation hybrid mapping". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 93 (1–2): 147–50. doi:10.1159/000056973. PMID 11474204.
- Otani A, Slike BM, Dorrell MI, et al. (2002). "A fragment of human TrpRS as a potent antagonist of ocular angiogenesis". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (1): 178–83. doi:10.1073/pnas.012601899. PMC 117535. PMID 11773625.
- Wakasugi K, Slike BM, Hood J, et al. (2002). "A human aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase as a regulator of angiogenesis". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (1): 173–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.012602099. PMC 117534. PMID 11773626.
- Sang Lee J, Gyu Park S, Park H, et al. (2002). "Interaction network of human aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and subunits of elongation factor 1 complex". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 291 (1): 158–64. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2002.6398. PMID 11829477.
- Guo Q, Gong Q, Tong KL, et al. (2002). "Recognition by tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetases of discriminator base on tRNATrp from three biological domains". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (16): 14343–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111745200. PMID 11834741.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.