Voice crossing
In music, voice crossing is the intersection of melodic lines in a composition, leaving a lower voice on a higher pitch than a higher voice (and vice versa). Because this can cause registral confusion and reduce the independence of the voices,[1] it is sometimes avoided in composition and pedagogical exercises.
History
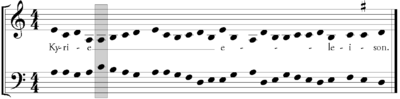
Voice crossing appears in free organum, with examples appearing as early as John Cotton's treatise De musica (1100).[2] Voice crossing is inherent in voice exchange, which became an important compositional technique in the 12th and 13th centuries. Later, as different voices were thought of occupying more distinct vocal ranges, crossing is less frequent. In the 15th-century English discant style, such as in the Old Hall manuscript, the three voices rarely cross.[3] In the three-part music of Guillaume Dufay, a special use of voice crossing at the cadence involves a Landini cadence but has lower voice crossing to give a bass progression as in the modern dominant-tonic cadence.[4] As four-part music became more established by the time of Johannes Ockeghem, the top and bottom parts were less likely to cross, but the inner voices continued to cross frequently.[5]
Voice crossing appears frequently in 16th-century music, to such a degree that Knud Jeppesen, in his analysis of Renaissance polyphony, said that without voice crossing "no real polyphony is possible."[6] Voice crossing is less common when it involves the lowest voice, as it creates a new bass line for the calculation of the upper voices, though still it is by no means uncommon.[7] Though it is common in the repertoire, voice crossing is sometimes avoided in strict counterpoint pedagogical exercises, especially when involving few voices.[8] This is not always the case, however; Gradus ad Parnassum (1725), probably the most famous species counterpoint instruction book, includes an example using crossed voices early in the text.[9]
In 18th-century contrapuntal writing, voices may cross freely, especially among voices in the same pitch location.[10] It is, however, quite restricted in invertible counterpoint, since it makes the crossing in the inversion impossible.[11] Canons at small harmonic intervals usually necessitate considerable voice crossing,[12] and in a crab canon it is inevitable at the midpoint.[13] For this reason, many authors find that canons sound better when performed by voices of different timbre.[14] In four-part chorale writing, voice crossing is infrequent, and again the most frequently crossed voices are the alto and tenor.[15] Voice crossing is usually forbidden in pedagogical exercises in common practice chorale-style voice-leading, especially when involving an outer voice.[1]
Examples from the Repertoire
An early example of medieval voice-crossing can be found in what Richard Taruskin (2009, p.394) calls “English twinsongs.” “These songs, among the earliest polyphonic vernacular settings to survive in any language, employ a more sophisticated sort of voice-leading, through contrary motion and voice crossings.”[16]

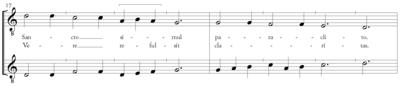
Further examples of voice crossing can be found in music of the fifteenth century, where “the voices overlap constantly.”[17]:
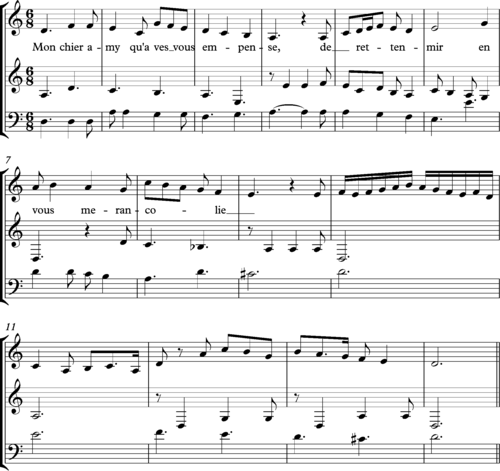

The early seventeenth century, as in this canon by Michael Praetorius:

The eighteenth century, as in Bach’s Concerto for Two Violins:

And the late nineteenth century , in the finale of Tchaikovsky's 6th Symphony “which begins with a composite melody that is shattered among the whole string section (no single instrumental group plays the tune you actually hear, an amazing, pre-modernist idea)”[18]

As Tom Service points out, Tchaikovsky's approach to instrumentation here was indeed prophetic. Some nineteen years after the première of the “Pathétique” symphony, Arnold Schoenberg was exploring a similar voice crossing technique involving flute, clarinet and violin in “Ein Blasse Wascherin”, a movement from his seminal melodrama Pierrot Lunaire (1912). Jonathan Dunsby cites this as an early example of Klangfarbenmelodie (sound-colour melody).[19]
Voice overlapping

A related phenomenon is "voice overlapping," where the voices do not cross per se, but they move together, and the lower voice passes where the upper voice was (or vice versa). For example, if two voices sound G and B, and move up to C and E. The overlapping occurs because the second note (C) in the lower voice is higher than the first note (B) in the upper voice. It leads to ambiguity, as the ear interprets the step from B to C in one voice, and is fairly consistently avoided in contrapuntal writing.[20] Voice overlaps are common in Bach chorales, but again are discouraged or forbidden by most theory texts. In keyboard works, however, voice overlapping is considered appropriate.[21]
Notes
- Edgar W. Williams, Jr., Harmony and Voice Leading, New York: Harper Collins, 1992, 63.
- Richard Hoppin, Medieval Music, New York: Norton, 1978, 196.
- Hoppin, 507 and 510.
- Donald Jay Grout and Claude Palisca, A History of Western Music, 5th ed., New York: Norton, 1996, 142.
- Grout and Palisca, 164.
- Jeppesen, Knud (1992) [1939]. Counterpoint: the polyphonic vocal style of the sixteenth century. trans. by Glen Haydon, with a new foreword by Alfred Mann. New York: Dover. pp. 113. ISBN 0-486-27036-X.
- Thomas Benjamin, The Craft of Modal Counterpoint: A Practical Approach, New York: Schirmer, 1979, 89.
- Arnold Schoenberg, Preliminary Exercises in Counterpoint, New York: St. Martin's, 1964, 11.
- Alfred Mann, tr. The Study of Counterpoint. Translated from Johann Joseph Fux, Gradus ad Parnassum, New York: Norton, 1971, 36.
- Walter Piston, Counterpoint, New York: Norton, 1947, 81.
- Piston, 170.
- Piston, 200.
- Piston, 210.
- Schoeberg, 166.
- Felix Salzer and Carl Schachter, Counterpoint in Composition, New York: McGraw-Hill, 1969, 266.
- Taruskin, R. (2009, p394) The Oxford History of Western Music: Music from the Earliest Notations to the Sixteenth Century. Oxford University Press.
- Fallows, D. (1982, p93) Dufay. London, Dent.
- Service, T. (2014) “Symphony Symphony guide: Tchaikovsky's Sixth ('Pathétique').” Guardian, 26 August.
- Dunsby, J. (1992, p.39) Schoenberg: Pierrot Lunaire. Cambridge University Press.
- Piston, 82.
- Williams, 64.