Vector (epidemiology)
In epidemiology, a disease vector is any agent which carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism;[1][2] agents regarded as vectors are organisms, such as intermediate parasites or microbes.
Arthropods
.jpg)
Arthropods form a major group of pathogen vectors with mosquitoes, flies, sand flies, lice, fleas, ticks, and mites transmitting a huge number of pathogens. Many such vectors are haematophagous, which feed on blood at some or all stages of their lives. When the insects blood feed, the pathogen enters the blood stream of the host. This can happen in different ways.[3][4]
The Anopheles mosquito, a vector for malaria, filariasis, and various arthropod-borne-viruses (arboviruses), inserts its delicate mouthpart under the skin and feeds on its host's blood. The parasites the mosquito carries are usually located in its salivary glands (used by mosquitoes to anaesthetise the host). Therefore, the parasites are transmitted directly into the host's blood stream. Pool feeders such as the sand fly and black fly, vectors for pathogens causing leishmaniasis and onchocerciasis respectively, will chew a well in the host's skin, forming a small pool of blood from which they feed. Leishmania parasites then infect the host through the saliva of the sand fly. Onchocerca force their own way out of the insect's head into the pool of blood.
Triatomine bugs are responsible for the transmission of a trypanosome, Trypanosoma cruzi, which causes Chagas Disease. The Triatomine bugs defecate during feeding and the excrement contains the parasites which are accidentally smeared into the open wound by the host responding to pain and irritation from the bite.
Plants and fungi
Some plants and fungi act as vectors for various pathogens. For example, the big-vein disease of lettuce was long thought to be caused by a member of the fungal division Chytridiomycota, namely Olpidium brassicae. Eventually however, the disease was shown to be viral. Later it transpired that the virus was transmitted by the zoospores of the fungus and also survived in the resting spores. Since then, many other fungi in the Chytridiomycota have been shown to vector plant viruses.[5]
Many plant pests that seriously damage important crops depend on other plants, often weeds, to harbour or vector them; the distinction is not always clear. In the case of Puccinia graminis for example, Berberis and related genera act as alternate hosts in a cycle of infection of grain.[6]
More directly, when they twine from one plant to another, parasitic plants such as Cuscuta and Cassytha have been shown to convey phytoplasmal and viral diseases between plants.[7] [5]
World Health Organization and vector-borne disease
The World Health Organization (WHO) states that control and prevention of vector-borne diseases are emphasizing "Integrated Vector Management (IVM)",[8] which is an approach that looks at the links between health and environment, optimizing benefits to both.[lower-alpha 1][9]
In April 2014, WHO launched a campaign called “Small bite, big threat” to educate people about vector-borne illnesses. WHO issued reports indicating that vector-borne illnesses affect poor people, especially people living in areas that do not have adequate levels of sanitation, drinking water and housing.[10]
Vector-borne zoonotic disease and human activity
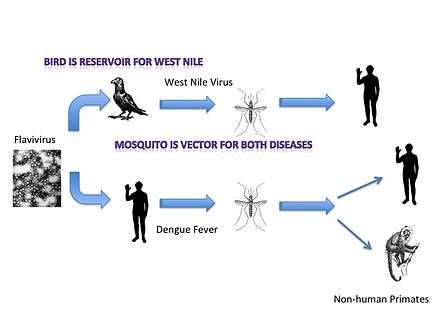
Several articles, recent to early 2014, warn that human activities are spreading vector-borne zoonotic diseases.[lower-alpha 2] Several articles were published in the medical journal The Lancet, and discuss how rapid changes in land use, trade globalization, and "social upheaval" are causing a resurgence in zoonotic disease across the world.[11]
Examples of vector-borne zoonotic diseases include:[12]
Many factors affect the incidence of vector-borne diseases. These factors include animals hosting the disease, vectors, and people.[12]
See also
- Airborne disease
- Asymptomatic carrier
- Fomite
- Globalization and disease
- Insect vectors of human pathogens
- Insect vectors of plant pathogens
- VectorBase: genomic database of invertebrate vectors of human pathogens
- List of diseases caused by insects
- Natural reservoir
- Waterborne disease
- 2007 Yap Islands Zika virus outbreak
Notes
- "IVM strategies are designed to achieve the greatest disease control benefit in the most cost-effective manner, while minimizing negative impacts on ecosystems (e.g. depletion of biodiversity) and adverse side-effects on public health from the excessive use of chemicals in vector control."[9]
- "Vector-borne zoonotic diseases are those that naturally infect wildlife and are then transmitted to humans through carriers, or vectors, such as mosquitoes or ticks."[11]
References
- "Vector". WordNet Search 3.1. Princeton University. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- Last, James, ed. (2001). A Dictionary of Epidemiology. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 185. ISBN 978-0-19-514169-6. OCLC 207797812.
- "Classification of Animal Parasites". plpnemweb.ucdavis.edu.
- Garcia, Lynne S. (August 15, 1999). "Classification of Human Parasites, Vectors, and Similar Organisms". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 29 (4): 734–736. doi:10.1086/520425. PMID 10589879 – via academic.oup.com.
- R. S. Mehrotra (2013). Fundamentals of Plant Pathology. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. pp. 342–. ISBN 978-1-259-02955-4.
- Peter W. Price (1980). Evolutionary Biology of Parasites. Princeton University Press. pp. 61–. ISBN 0-691-08257-X.
- Haynes, A R. et al. Comparison of two parasitic vines: Dodder (Cuscuta) and Woe vine(Cassytha). Florida Dept Agric & Consumer Services. Division of Plant Industry. Botany Circular No. 30. January/February 1996
- "Handbook for Integrated Vector Management" (PDF). World Health Organization. Retrieved 3 December 2015.
- "Vector-borne disease". The Health and Environment Linkages Initiative (HELI). Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- Parrish, Ryan (7 April 2014). "WHO focuses on vector-borne diseases for World Health Day 2014". Vaccine News Daily. Chicago, Illinois. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- Purlain, Ted (5 December 2012). "Lancet addresses emerging infectious vector-borne diseases". Vaccine News Daily. Chicago, Illinois. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- University of California - Santa Cruz (30 November 2012). "Emerging vector-borne diseases create new public health challenges". Science Daily. Rockville, Maryland. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
Bibliography
- "Better environmental management for control of dengue". The Health and Environment Linkages Initiative (HELI). Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- "Division of Vector-Borne Diseases (DVBD)" (Multimedia). Fort Collins, Colorado: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- "Issue Brief Series: Vector-borne Diseases" (PDF). Healthy Environments for Children Alliance. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- "Malaria control: the power of integrated action". The Health and Environment Linkages Initiative (HELI). Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- Pawan, J.L. (1936). "Transmission of the Paralytic Rabies in Trinidad of the Vampire Bat: Desmodus rotundus murinus Wagner, 1840." Annual Tropical Medicine and Parasitol, 30, April 8, 1936:137–156.
- Pawan, J.L. "Rabies in the Vampire Bat of Trinidad with Special Reference to the Clinical Course and the Latency of Infection." Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology. Vol. 30, No. 4. December 1936
- Quammen, David (4 April 2013). "Planet of the Ape; 'Between Man and Beast,' by Monte Reel". The New York Times. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- "Vector-borne diseases". Articles about vector-borne disease. Vaccine News Daily. Chicago.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Disease vectors. |
