USS Washington (BB-47)
USS Washington (BB-47), a Colorado-class battleship, was the second ship of the United States Navy named in honor of the 42nd state. Her keel was laid down on 30 June 1919, at Camden, New Jersey, by the New York Shipbuilding Corporation. She was launched on 1 September 1921, sponsored by Miss Jean Summers, the daughter of Congressman John W. Summers of Washington.
 Incomplete hull of USS Washington (1922) | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Washington |
| Namesake: | State of Washington |
| Builder: | New York Shipbuilding Corporation |
| Laid down: | 30 June 1919 |
| Launched: | 1 September 1921 |
| Sponsored by: | Jean Summers |
| Stricken: | 8 February 1922 |
| Fate: | Sunk as target, 25 November 1924 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type: | Colorado class |
| Displacement: | 32,600 long tons (33,100 t) |
| Length: | 624 ft (190 m) |
| Beam: | 97 ft 6 in (29.72 m) |
| Draft: | 30 ft 6 in (9.30 m) |
| Speed: | 21 kn (39 km/h; 24 mph) |
| Complement: | 1,354 officers and men |
| Armament: | |
| Armor: |
|
On 8 February 1922, two days after the signing of the Washington Naval Treaty for the Limitation of Naval Armaments, all construction work ceased on the 75.9%-completed superdreadnought. She was sunk as a gunnery target on 26 November 1924, by the battleships New York and Texas.[1][2]
Design
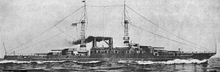
Washington was 624 feet (190 m) long, and had a beam of 97.5 feet (29.7 m) with a draft of 30.5 feet (9.3 m). She displaced 32,600 long tons (33,123 t). The ship's primary armament consisted of eight 16-inch (406 mm)/45 caliber Mark 1 guns in four twin gun turrets. This was augmented by a secondary battery of 20 5-inch (127 mm)/51 caliber guns. The ship was also armed with eight 3-inch (76 mm)/23 caliber antiaircraft guns.[3][4]
The new underwater protection scheme featured five compartments separated by bulkheads on either side of the ship: an outer empty one, three filled, and an empty inner one. In addition, the eight boilers were moved from their location in previous designs and placed in separate spaces to port and starboard of the turbo-electric power plant, forming another line of defense; the ship could still sail even if one or even an entire side of boilers was incapacitated due to battle damage. This new arrangement forced the chief aesthetic change between the New Mexicos and Tennessees; the single large funnel of the former was replaced by two smaller funnels in the latter.[3][4]
History

With fiscal year 1917 appropriations, bids on the four Colorados were opened on 18 October 1916; though Maryland's keel was laid on 24 April 1917. The other three battleships, including Washington, were not laid down until 1919–1920. With the cancellation of the first South Dakota class, the Colorados were the last U.S. battleships to enter service for nearly two decades. They were also the final U.S. battleships to use twin gun turrets—the North Carolina and second South Dakota classes used nine 16-inch/45 caliber Mark 6 guns and the Iowas used nine 16-inch/50 caliber Mark 7 guns[5][6][7] in three triple turrets. Washington was laid down on 30 June 1919.[8][2]
On 8 February 1922, two days after the signing of the Washington Naval Treaty for the Limitation of all Naval Armaments, all construction work was stopped on the 75.9 percent-completed superdreadnought.[1] By that time, she had her underwater armored protection in place.[9][10]
The ship was towed out in November 1924, to be used as a gunnery target. On the first day of testing, the ship was hit by two 400-pound (180 kg) torpedoes and three 1 tonne (1.1 short tons) near-miss bombs causing minor damage and a list of three degrees. She then had 400 pounds of TNT detonated on board, but remained afloat. Two days later, the ship was hit by fourteen 14-inch (356 mm) shells dropped from 4,000 feet (1,200 m), but only one penetrated. The ship was finally sunk by Texas and New York with fourteen more 14-inch shells. After the test, it was decided that the existing deck armor on battleships was inadequate, and that future battleships should be fitted with triple bottoms, which was underwater armor with three layers.[8]
The wreck of the USS Washington is quite popular with SCUBA divers. The wreck lies upside down with her keel reaching 240', the sand at 290'. The large inverted hull does not present many penetration opportunities. Furthermore, due to the scrapping prior to her sinking, there are most likely few artifacts or other interesting items at this site; while perhaps presenting an impressive sight, this wreck has few appealing features. This site has been known for decades unofficially as the “44 Fathom Wreck” and “the British Aircraft Carrier”.
Footnotes
- Ferguson 2007, p. 57.
- Graff 2010, p. 41.
- Gardiner & Gray 1985, p. 118.
- Friedman 1985, pp. 134, 137.
- Gardiner & Gray 1985, p. 118.
- Friedman 1985, pp. 137, 420–421.
- Gardiner & Chesneau 1980, pp. 97–100.
- Friedman 1985, p. 186.
- Kearns & Morris 2011, p. 47.
- Martin 1997, p. xi.
References
- Ferguson, John C. (2007). Historic Battleship Texas: The Last Dreadnought. Military History of Texas No. 4. Abilene, Texas: State House Press. ISBN 1-933337-07-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Friedman, Norman (1985). U.S. Battleships: An Illustrated Design History. United States Naval Institute. ISBN 0-87021-715-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Gardiner, Robert; Chesneau, Roger, eds. (1980). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships, 1922–1946. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-913-8. OCLC 18121784.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Gardiner, Robert; Gray, Randal, eds. (1985). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships, 1906–1921. Annapolis, Mayland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-907-3. OCLC 12119866.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Graff, Cory (2010). The Navy at Puget Sound. Charleston, SC: Arcadia Publishing. OCLC 700503123.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Kearns, Patricia M.; Morris, James M. (2011). Historical dictionary of the United States Navy (Second ed.). Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press. ISBN 0-8108-7229-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Martin, Robert J. (1997). USS West Virginia (BB-48). Nashville, Tennessee: Turner Publishing Company. ISBN 978-1-56311-341-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to USS Washington (BB-47). |
- Washington (BB-47), construction cancelled 1922
- MaritimeQuest USS Washington BB-47 Photo Gallery
- Photo gallery of Washington at NavSource Naval History (Keel Laying – Launching)
- Photo gallery of Washington at NavSource Naval History (Construction – Sinking)
- "Washington (Battleship No. 47)". DANFS. 23 February 2016. Retrieved 4 September 2018.
- DANFS photographs of USS Washington (BB-47)