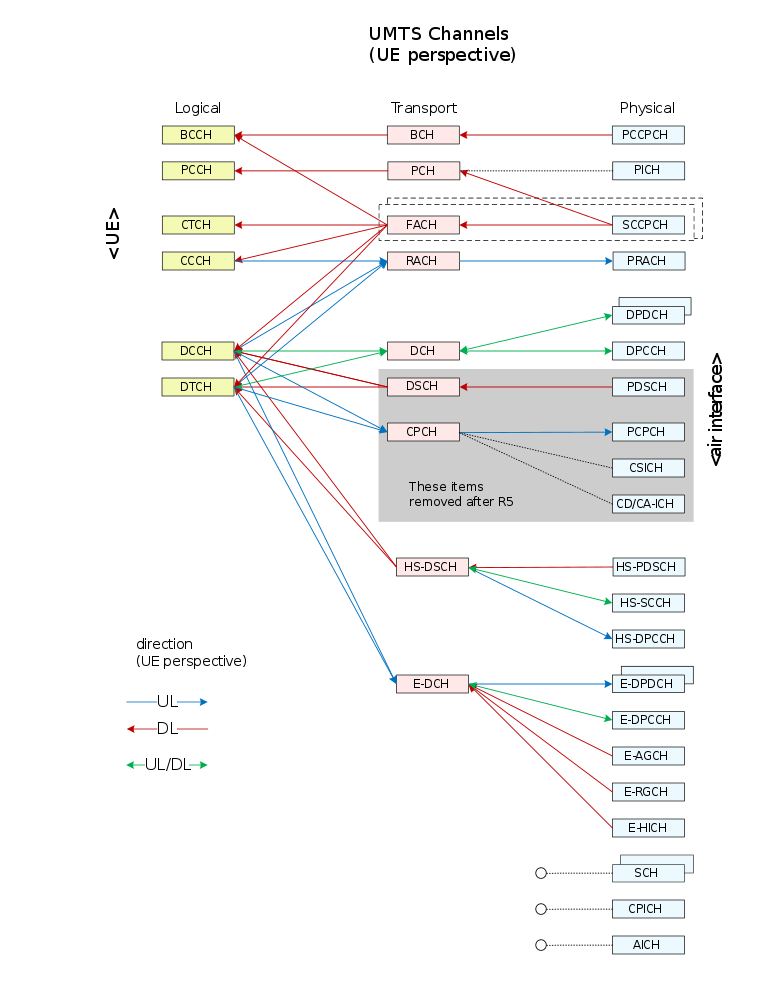
UMTS channels
The UMTS channels are communication channels used by third generation (3G) wireless Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) networks. [1][2][3] UMTS channels can be divided into three levels:
- Physical
- Transport
- Logical
List
| Level | Abrev. | Full Name | Description | UL/DL | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3_LOGICAL | BCCH | broadcast control channel | For broadcasting system control information | DL | 5.3.1.1.1[4] |
| 3_LOGICAL | CCCH | common control channel | Supports common procedures required to establish a dedicated link between the UE and the network. | UL/DL | 5.3.1.1.1[4] |
| 3_LOGICAL | CTCH | common traffic channel | A point-to-multipoint unidirectional channel for transfer of dedicated user information for all or a group of specified UEs. | DL | 5.3.1.1.1[4] |
| 3_LOGICAL | DCCH | dedicated control channel | A point-to-point dedicated channel for transmitting control information between a UE and the network. | UL/DL | 5.3.1.1.1[4] |
| 3_LOGICAL | DTCH | dedicated traffic channel | A point-to-point dedicated channel for transmitting user traffic information between a UE and the network. | UL/DL | 5.3.1.1.1[4] |
| 3_LOGICAL | PCCH | paging control channel | Transfers paging information. Used when the network does not know the location cell of the UE or the UE is in sleep mode. | DL | 5.3.1.1.1[4] |
| 2_TRANSPORT | BCH | broadcast channel | Used to broadcast cell and system information. | DL | 4.1.2.1[5] |
| 2_TRANSPORT | CPCH | common packet channel | Used for transmission of bursty data traffic. Shared by the UEs in a cell. Employs fast power control. NOTE - removed after R5. | UL | 4.1.2.5[6] |
| 2_TRANSPORT | DCH | dedicated channel | Allocated to an individual user and typically used to support a speech channel. | UL/DL | 4.1.1.1[5] |
| 2_TRANSPORT | DSCH | downlink shared channel | Carries dedicated user data or control information. May be shared by several UEs. Associated with a downlink DCH. NOTE - removed after R5. | DL | 4.1.2.6[6] |
| 2_TRANSPORT | E-DCH | enhanced dedicated channel | HSUPA Enhanced (high-speed) dedicated uplink transport channel. | UL | 4.1.1.2[5] |
| 2_TRANSPORT | FACH | forward access channel | Carries control information to UEs in a cell (may also be used to transmit packet data). Makes up the RACH/FACH pair. | DL | 4.1.2.2[5] |
| 2_TRANSPORT | HS-DSCH | high speed downlink shared channel | The HSDPA transport channel. Shared by several UEs. | DL | 4.1.2.7[5] |
| 2_TRANSPORT | PCH | paging channel | Carries paging procedure data (for sleep mode) used by network to establish connection to UE. Always transmitted over entire cell. | DL | 4.1.2.3[5] |
| 2_TRANSPORT | RACH | random access channel | Used to gain access to the system when first attaching to it (can also carry packet data). Makes up the RACH/FACH pair. Always received from entire cell. Entails a collision risk. Transmitted using open loop power control. | UL | 4.1.2.4[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | AICH | acquisition indicator channel | Carries acquisition indicators. AI corresponds to signature on the PRACH. Fixed rate (sf=256). | DL | 5.3.3.7[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | CD/CA-ICH | collision detection/channel assignment indicator channel | Carries CD Indicator (CDI) or CD Indicator/CA Indicator (CDI/CAI). Fixed rate (sf=256). NOTE - removed after R5. | DL | 5.3.3.9[6] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | CPICH | common pilot channel | Provides the default phase reference for demodulation of the other downlink channels and enables channel estimation. Uses a pre-defined bit sequence. Fixed rate (sf=256). | DL | 5.3.3.11[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | CSICH | cpch status indication channel | Carries CPCH status information. Fixed rate (sf=256). NOTE - removed after R5. | DL | 5.3.3.11[6] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | DPCCH | dedicated physical control channel | Carries physical layer control information including known pilot bits to support channel estimation, transmit power-control (TPC) commands, feedback information (FBI) and, optionally, transport-format combination indicator (TFCI). | UL/DL | 5.3.3.11[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | DPDCH | dedicated physical data channel | Carries DCH data. Used with DPCCH. May be multiple DPDCHs on each radio link. | UL/DL | 5.3.3.11[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | E-AGCH | enhanced absolute grant channel | [HSUPA] Establishes absolute power lever for UE transmission on E-DCH. Fixed rate (sf=256). | DL | 5.3.3.14[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | E-DPCCH | enhanced dedicated physical control channel | [HSUPA] Control information associated with E-DCH. Transmitted along with E-DPDCH. | UL/DL | 5.2.1.3[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | E-DPDCH | enhanced dedicated physical data channel | [HSUPA] Carries the E-DCH transport channel. Transmitted along with E-DPCCH. | UL | 5.2.1.3[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | E-HICH | enhanced hybrid indicator channel | [HSUPA] Dedicated channel which carries the E-DCH hybrid ARQ acknowledgement indicator. Fixed rate (sf=128). | DL | 5.3.2.5[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | E-RGCH | enhanced relative grant channel | [HSUPA] Carries the uplink E-DCH relative grants. Fixed rate (sf=128). | DL | 5.3.2.4[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | HS-DPCCH | high speed dedicated physical control channel | [HSDPA] Carries feedback signalling related to HS-DSCH including HARQ-ACK and CQI. | UL | 5.2.1.2[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | HS-PDSCH | high speed physical downlink shared channel | [HSDPA] Carries actual user data for HS-DSCH. | DL | 5.3.3.13[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | HS-SCCH | high speed shared control channel | [HSDPA] Contains downlink signalling information related to HS-DSCH. Fixed rate (sf=128). | DL | 5.3.3.12[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | P-CCPCH | primary common control physical channels | Carries BCH (Broadcast Channel). There is one P-CCPCH within a cell used to carry synchronization and broadcast information for all users. | DL | 5.3.3.3[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | PCPCH | physical common packet channel | Carries CPCH (Common Packet Channel). NOTE - removed after R5. | UL | 5.2.2.2[6] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | PDSCH | physical downlink shared channel | Carries DSCH. NOTE - removed after R5. | DL | 5.3.3.6[6] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | PICH | page indicator channel | Carries PCH. Fixed rate (sf=256). | DL | 5.3.3.10[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | PRACH | physical random access channel | Carries RACH (Random Access Channel). | UL | 5.2.2.1[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | S-CCPCH | secondary common control physical channels | Carries FACH (Forward Access Channel) and PCH (Paging Channel). | DL | 5.3.3.4[5] |
| 1_PHYSICAL | SCH | synchronization channel | Used for cell search and conveying synchronization information. Consists of two sub-channels - Primary and Secondary SCH. | DL | 5.3.3.5[5] |
gollark: Idea: Replace the overly specialized DDRn RAM interfaces with Ethernet
gollark: No, trousers are generally superior.
gollark: Idea: 1-bit GDDR6X interface.
gollark: http://sam.zeloof.xyz/category/semiconductor/
gollark: Just produce your own ICs, silly.
See also
- UMTS
- High Speed Packet Access
- 3GPP Long Term Evolution (aka 4G/LTE)
References
- Holma, Harry and Antti Toskala (2004). WCDMA for UMTS. Wiley. ISBN 0-470-87096-6.
- Harri Holma and Antti Toskala (2006). HSDPA/HSUPA for UMTS: High Speed Radio Access for Mobile Communications. ISBN 0-470-01884-4.
- Dahlman, Erik and Stefan Parkvall, Johan Skold, Per Beming (2006). 3G Evolution HSPA and LTE for Mobile Broadband. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-12-374538-5.
- "TS 25.301 Radio interface protocol architecture (FDD)" (PDF).
- "TS 25.211_PHYSICAL channels and mapping of transport channels onto physical channels (FDD) (R7)" (PDF).
- "TS 25.211_PHYSICAL channels and mapping of transport channels onto physical channels (FDD) (R5)" (PDF).
Sources
- 3GPP specification series 25—Radio aspects of 3G, including UMTS
- TS 25.101 User Equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception (FDD)
- TS 25.201 Description—Describes basic differences between FDD and TDD.
- TS 25.211_PHYSICAL channels and mapping of transport channels onto physical channels (FDD)
- TS 25.212 Multiplexing and channel coding (FDD)
- TS 25.213 Spreading and modulation (FDD)
- TS 25.214 Physical layer procedures (FDD)
- TS 25.215 Physical layer - Measurements (FDD)
- TS 25.301 Radio interface protocol architecture
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.