UBTF
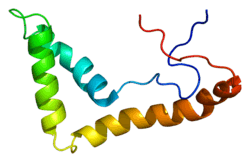
Nucleolar transcription factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBTF gene.[5][6]
Function
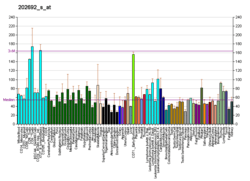
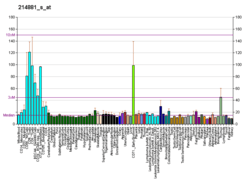
Upstream binding factor (UBF) is a transcription factor required for expression of the 18S, 5.8S, and 28S ribosomal RNAs, along with SL1 (a complex of TBP (MIM 600075) and three TBP-associated factors or 'TAFs'). Two UBF polypeptides, of 94 and 97 kD, exist in the human (Bell et al., 1988). UBF is a nucleolar phosphoprotein with both DNA binding and transactivation domains. Sequence-specific DNA binding to the core and upstream control elements of the human rRNA promoter is mediated through several HMG boxes (Jantzen et al., 1990).[supplied by OMIM][6]
Interactions
UBTF has been shown to interact with:
gollark: That would be fine, really?
gollark: I see.
gollark: Er, maximum.
gollark: Apparently, we are now expected to resolve all issues within the minimum response time.
gollark: Anyway; to clarify for nonstaff, palaiologos released a spreadsheet to fill out about timespans within staff were expected to respond (that).
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000108312 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020923 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
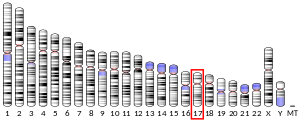
- Matera AG, Wu W, Imai H, O'Keefe CL, Chan EK (May 1997). "Molecular cloning of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor hUBF/NOR-90 (UBTF) gene and localization to 17q21.3 by fluorescence in situ hybridization and radiation hybrid mapping". Genomics. 41 (1): 135–8. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4647. PMID 9126496.
- "Entrez Gene: UBTF upstream binding transcription factor, RNA polymerase I".
- Voit R, Kuhn A, Sander EE, Grummt I (July 1995). "Activation of mammalian ribosomal gene transcription requires phosphorylation of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF". Nucleic Acids Res. 23 (14): 2593–9. doi:10.1093/nar/23.14.2593. PMC 307079. PMID 7651819.
- Hannan KM, Hannan RD, Smith SD, Jefferson LS, Lun M, Rothblum LI (October 2000). "Rb and p130 regulate RNA polymerase I transcription: Rb disrupts the interaction between UBF and SL-1". Oncogene. 19 (43): 4988–99. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203875. PMID 11042686.
- Voit R, Grummt I (November 2001). "Phosphorylation of UBF at serine 388 is required for interaction with RNA polymerase I and activation of rDNA transcription". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (24): 13631–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.231071698. PMC 61092. PMID 11698641.
- Zhai W, Comai L (August 2000). "Repression of RNA polymerase I transcription by the tumor suppressor p53". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (16): 5930–8. doi:10.1128/mcb.20.16.5930-5938.2000. PMC 86070. PMID 10913176.
- Lin CY, Tuan J, Scalia P, Bui T, Comai L (Dec 2002). "The cell cycle regulatory factor TAF1 stimulates ribosomal DNA transcription by binding to the activator UBF". Curr. Biol. 12 (24): 2142–6. doi:10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01389-1. PMID 12498690.
Further reading
- Chan EK, Imai H, Hamel JC, Tan EM (1991). "Human autoantibody to RNA polymerase I transcription factor hUBF. Molecular identity of nucleolus organizer region autoantigen NOR-90 and ribosomal RNA transcription upstream binding factor". J. Exp. Med. 174 (5): 1239–44. doi:10.1084/jem.174.5.1239. PMC 2119007. PMID 1940801.
- Jantzen HM, Admon A, Bell SP, Tjian R (1990). "Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins". Nature. 344 (6269): 830–6. doi:10.1038/344830a0. PMID 2330041.
- Bell SP, Learned RM, Jantzen HM, Tjian R (1988). "Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis". Science. 241 (4870): 1192–7. doi:10.1126/science.3413483. PMID 3413483.
- Voit R, Kuhn A, Sander EE, Grummt I (1995). "Activation of mammalian ribosomal gene transcription requires phosphorylation of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF". Nucleic Acids Res. 23 (14): 2593–9. doi:10.1093/nar/23.14.2593. PMC 307079. PMID 7651819.
- Hempel WM, Cavanaugh AH, Hannan RD, Taylor L, Rothblum LI (1996). "The species-specific RNA polymerase I transcription factor SL-1 binds to upstream binding factor". Mol. Cell. Biol. 16 (2): 557–63. doi:10.1128/MCB.16.2.557. PMC 231034. PMID 8552083.
- Hanada K, Song CZ, Yamamoto K, Yano K, Maeda Y, Yamaguchi K, Muramatsu M (1996). "RNA polymerase I associated factor 53 binds to the nucleolar transcription factor UBF and functions in specific rDNA transcription". EMBO J. 15 (9): 2217–26. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb00575.x. PMC 450146. PMID 8641287.
- Pluta AF, Earnshaw WC (1996). "Specific interaction between human kinetochore protein CENP-C and a nucleolar transcriptional regulator". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (31): 18767–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.31.18767. PMID 8702533.
- Whitehead CM, Winkfein RJ, Fritzler MJ, Rattner JB (1997). "ASE-1: a novel protein of the fibrillar centres of the nucleolus and nucleolus organizer region of mitotic chromosomes". Chromosoma. 106 (8): 493–502. doi:10.1007/s004120050271. PMID 9426281.
- Voit R, Hoffmann M, Grummt I (1999). "Phosphorylation by G1-specific cdk-cyclin complexes activates the nucleolar transcription factor UBF". EMBO J. 18 (7): 1891–9. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.7.1891. PMC 1171274. PMID 10202152.
- Liu CJ, Wang H, Lengyel P (1999). "The interferon-inducible nucleolar p204 protein binds the ribosomal RNA-specific UBF1 transcription factor and inhibits ribosomal RNA transcription". EMBO J. 18 (10): 2845–54. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.10.2845. PMC 1171365. PMID 10329630.
- Hannan KM, Hannan RD, Smith SD, Jefferson LS, Lun M, Rothblum LI (2000). "Rb and p130 regulate RNA polymerase I transcription: Rb disrupts the interaction between UBF and SL-1". Oncogene. 19 (43): 4988–99. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203875. PMID 11042686.
- Kalousek I, Krízková P (2000). "Lymphocyte mitogenic transformation is accompanied by phosphorylation of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF". Cell. Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand). 46 (7): 1163–71. PMID 11075946.
- Pelletier G, Stefanovsky VY, Faubladier M, Hirschler-Laszkiewicz I, Savard J, Rothblum LI, Côté J, Moss T (2000). "Competitive recruitment of CBP and Rb-HDAC regulates UBF acetylation and ribosomal transcription". Mol. Cell. 6 (5): 1059–66. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)00104-0. PMID 11106745.
- Miller G, Panov KI, Friedrich JK, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Lamond AI, Zomerdijk JC (2001). "hRRN3 is essential in the SL1-mediated recruitment of RNA Polymerase I to rRNA gene promoters". EMBO J. 20 (6): 1373–82. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.6.1373. PMC 145519. PMID 11250903.
- Seither P, Iben S, Thiry M, Grummt I (2001). "PAF67, a novel protein that is associated with the initiation-competent form of RNA polymerase I". Biol. Chem. 382 (8): 1163–70. doi:10.1515/BC.2001.146. PMID 11592397.
- Voit R, Grummt I (2001). "Phosphorylation of UBF at serine 388 is required for interaction with RNA polymerase I and activation of rDNA transcription". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (24): 13631–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.231071698. PMC 61092. PMID 11698641.
- Stefanovsky VY, Pelletier G, Hannan R, Gagnon-Kugler T, Rothblum LI, Moss T (2001). "An immediate response of ribosomal transcription to growth factor stimulation in mammals is mediated by ERK phosphorylation of UBF". Mol. Cell. 8 (5): 1063–73. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00384-7. PMID 11741541.
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, Leung AK, Lam YW, Steen H, Mann M, Lamond AI (2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus". Curr. Biol. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298.
- Dühr S, Torres-Montaner A, Astola A, García-Cozar FJ, Pendón C, Bolívar J, Valdivia MM (2001). "Molecular analysis of the 5' region of human ribosomal transcription factor UBF". DNA Seq. 12 (4): 267–72. doi:10.3109/10425170109025001. PMID 11916260.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.