Tunga, Leyte
Tunga, officially the Municipality of Tunga (Waray: Bungto han Tunga; Tagalog: Bayan ng Tunga), is a 6th class municipality in the province of Leyte, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 7,584 people.[3]
Tunga | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Tunga | |
 Seal | |
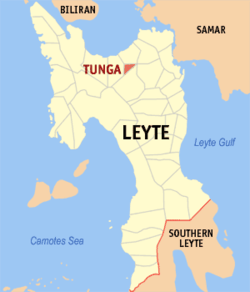 Map of Leyte with Tunga highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap 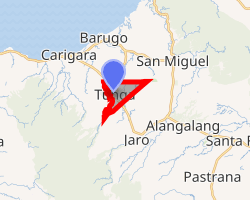
| |
.svg.png) Tunga Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 11°15′N 124°45′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Eastern Visayas (Region VIII) |
| Province | Leyte |
| District | 2nd district of Leyte |
| Founded | November 15, 1949 |
| Barangays | 8 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Catalina F. Agda |
| • Vice Mayor | Reinbert C. Costelo |
| • Congressman | Lolita T. Javier |
| • Municipal Council | Councilors
|
| • Electorate | 6,687 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 7.70 km2 (2.97 sq mi) |
| Population (2015 census)[3] | |
| • Total | 7,584 |
| • Density | 980/km2 (2,600/sq mi) |
| • Households | 1,590 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 6th municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 27.98% (2015)[4] |
| • Revenue (₱) | 37,078,567.95 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 6528 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)53 |
| Climate type | tropical rainforest climate |
| Native languages | Waray Tagalog |
| Website | www |
It is the smallest municipality in Leyte, both in population and area. [2]
History
The municipality of Tunga existed as early as 1860 as a barrio of Barugo. At that time only about fifty families were residing there, most of them coming from the different towns of Barugo, Carigara and Jaro. There are different versions that have been told as to why the place was called Tunga. Due to their stronger credibility, only two of these legends have been selected as the possible ones. One states that according to our forefathers, before Tunga became a barrio, people from Ormoc, Carigara, Barugo, Jaro and Tacloban engaged in trade with each other and they had to stop by or pass this place. Some of them even made it their contact point for conducting their business. Through their exchange of ideas and conversations, they concluded that this place was halfway between Ormoc and Tacloban or Carigara and Jaro. Since it had no name at the time, people started calling it Tunga, the dialect for half. When it became a barrio, the residents, due to their familiarity with the name christened the place Tunga.
On March 4, 1948, "Pag-urosa han mga Tunga-on", the association that led the campaign to make Tunga a municipality, was organized and it elected Domingo A. Ponferrada, President; Martino Ariza, 1st Vice President; Blas Uribe, 2nd Vice President; Vicente Catenza, 3rd Vice President; Primitivo Geraldo, Secretary; Norberto Quintana, treasurer; Ramón Santillan Sr (died on October 13, 2005, at age 101) and Juan Avila, auditors; Paulo Cotoner, Magno Buñales and Arsenio Carit, Sergeants-at-Arms.
These officers invited and apprised Atilano R. Cinco, Congressman for the 5th District of Leyte, of the desire of Tunga to become an independent municipality. Cinco promised to file a bill in congress when all supporting papers that he had suggested were ready. Thus, a committee on consensus was created. Martino Ariza was elected as chairman; the members being some of the students of Tunga Institute.
Subsequently, Philippine President Quirino issued Executive Order No. 266, dated September 24, 1949, creating the independent municipality of Tunga, however the appointed local officials had to assume their posts a few days after the elections.
On November 15, 1949, Provincial Board Secretary Ricardo Collantes, representing Leyte Governor Catalino Landia, proclaimed the Municipality of Tunga before a huge crowd of joyous Tunga-on and distinguished visitors.
The patron saint of Tunga is Saint Anthony of Padua. The Tunga-on celebrate their town's fiesta on August 13 every year.[5]
Geography
Barangays
Tunga is politically subdivided into 8 barangays: [2]
- Astorga (Barrio Upat)
- Balire
- Banawang
- San Antonio (Poblacion)
- San Pedro (Poblacion)
- San Roque (Poblacion)
- San Vicente (Poblacion)
- Santo Niño (Poblacion)
Climate
| Climate data for Tunga, Leyte | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 28 (82) |
28 (82) |
29 (84) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
29 (84) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22 (72) |
22 (72) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (74) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 73 (2.9) |
56 (2.2) |
75 (3.0) |
71 (2.8) |
114 (4.5) |
174 (6.9) |
172 (6.8) |
163 (6.4) |
167 (6.6) |
161 (6.3) |
158 (6.2) |
125 (4.9) |
1,509 (59.5) |
| Average rainy days | 15.2 | 12.5 | 16.2 | 17.3 | 23.9 | 27.3 | 28.4 | 26.9 | 26.9 | 27.1 | 23.8 | 19.3 | 264.8 |
| Source: Meteoblue [6] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority [3][7][8][9] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In the 2015 census, the population of Tunga, Leyte, was 7,584 people,[3] with a density of 980 inhabitants per square kilometre or 2,500 inhabitants per square mile.
Economy
The socio-economic situation in Tunga can be described as poor with little outside investment and few opportunities for most of the municipality's citizens to improve their economic status. Income per capita is very low and the poverty incidence is alarming. The magnitude of families living below the poverty threshold is much too high. The under-employment rate is high and most people hold informal jobs and carry out various activities daily to earn barely a subsistence income for their families. The percent of households without their own dwellings is high.
Elementary education participation is low, reflecting low incomes because families cannot afford to put their children through school and/or children are taken out of school to assist families with income-earning activities. As a result, the simple literacy rate is low.
Crop production indicates very low land productivity with the majority of farmers involved in coconut tree cultivation for copra as their main economic mainstay. Rice cultivation is the second main agricultural activity. Some farmers also raise pigs and chickens to sell to the local meat shop in the local market.
The fish catch, which is mainly Tilapia, in the Tunga River, which flows through the municipality, has decreased since 2005.
Education
There are a total of 4 Elementary Schools and 1 Secondary/High School in Tunga Leyte[10]
Grade School/Elementary Schools
- Astorga Elementary School
- Balire Elementary School
- Banawang Elementary School
- Tunga CS
Secondary/High School
- Gregorio C. Catenza National High School (Tunga National High School)
References
- "Municipality". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- "Province: Leyte". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region VIII (Eastern Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved 12 October 2019.
- . Mission http://www.mission.net/philippines/tacloban/page.php?lang=eng&pg_id=1761. Retrieved November 16, 2018. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "Tunga: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved 29 February 2020.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region VIII (Eastern Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region VIII (Eastern Visayas)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Leyte". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- . School Torkis Directory https://schools.trokis.com. Retrieved November 8, 2018. Missing or empty
|title=(help)