Tsetlin machine
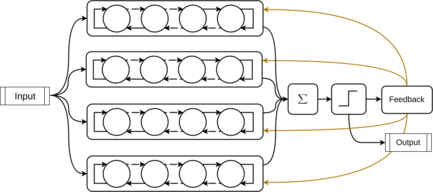
Overview
Tsetlin Machine, a state-of-the-art Artificial Intelligence algorithm based on propositional logic.
| Part of a series on |
| Machine learning and data mining |
|---|
|
Theory |
|
Machine-learning venues |
Background
A Tsetlin machine is a form of learning automaton based upon algorithms from reinforcement learning to learn expressions from propositional logic. Ole-Christoffer Granmo gave the method its name after Michael Lvovitch Tsetlin and his Tsetlin automata. The method uses computationally simpler and more efficient primitives compared to more ordinary artificial neural networks, but while the method may be faster it has a steep drop in signal-to-noise ratio as the signal space increases.[1]
As of April 2018 it has shown promising results on a number of test sets.[2][3]
Types
Original Tsetlin Machine
| Description | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Number of binary inputs | |
| Number of classes | |
| Number of clauses per class | |
| Number of automaton states | |
| Automaton decision boundary | |
| Automaton initialization state | |
| Feedback threshold | |
| Learning Sensitivity |
Tsetlin Automaton
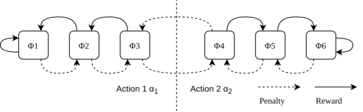
The Tsetlin Automaton is the fundamental 'learning unit' of the Tsetlin machine which able to store the generalized learning outcome based on the input feature. It can be seen as an FSM which changes its states based on the inputs. The FSM will generate its outputs based on the current states.
- The quintuple describes a two-action Tsetlin Automaton.
- The TA consists 6 states
Φ = {Φ1, Φ2, Φ3, Φ4, Φ5, Φ6}
- The FSM can be triggered by two input events
β = {β_Penalty, β_Reward}
- The rules of states migration of the FSM is stated as
- It includes two output actions
α = {α1, α2}
- Which can be generated by the algorithm
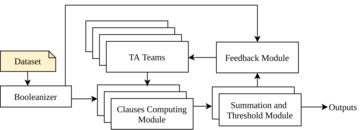
Clauses Computing Module
Summation and Threshold Module
Feedback Module
Implementations
Software
Hardware
- The one of first FPGA-based hardware implementation[14][15] of the Tsetlin Machine on Iris dataset had developed by µSystems (microSystems) Research Group at Newcastle University.
- They also presented the first ASIC [16] [17]implementation of the Tsetlin Machine focusing energy frugality, claims it could deliver 10 trillion operation per Joule[18]. The ASIC design had demoed on DATA2020 [19].
Additional Read
Videos
- Tsetlin Machine -- A new paradigm for pervasive AI [19]
- IOLTS Presentation: Explainability and Dependability Analysis of Learning Automata based AI hardware [20]
- FPGA and uC co-design: Tsetlin Machine on Iris demo [14][15]
- The-Ruler-of-Tsetlin-Automaton [21]
- Interpretable clustering and dimension reduction with Tsetlin automata machine learning. [22]
- Predicting and explaining economic growth using real-time interpretable learning [23]
- Early detection of breast cancer from a simple blood test[24]
- Recent advances in Tsetlin Machines [25]
Papers
- Learning Automata based Energy-efficient AI Hardware Design for IoT Applications [6]
Publications/News/Articles
- A low-power AI alternative to neural networks [26]
Partners
 The Centre for Artificial Intelligence Research (CAIR) at the University of Agder https://twitter.com/CairEnglish https://cair.uia.no/about-cair/
The Centre for Artificial Intelligence Research (CAIR) at the University of Agder https://twitter.com/CairEnglish https://cair.uia.no/about-cair/ uSystems Research Group at Newcastle University https://twitter.com/nclmicrosystems https://www.ncl.ac.uk/engineering/research/eee/microsystems/
uSystems Research Group at Newcastle University https://twitter.com/nclmicrosystems https://www.ncl.ac.uk/engineering/research/eee/microsystems/
Gallery
References
- Granmo, Ole-Christoffer (2018-04-04). "The Tsetlin Machine - A Game Theoretic Bandit Driven Approach to Optimal Pattern Recognition with Propositional Logic". arXiv:1804.01508 [cs.AI].
- Christiansen, Atle. "The Tsetlin Machine outperforms neural networks - Center for Artificial Intelligence Research". cair.uia.no. Retrieved 2018-05-03.
- Øyvann, Stig. "AI-gjennombrudd i Agder | Computerworld". Computerworld (in Norwegian). Retrieved 2018-05-04.
- Granmo, Ole-Christoffer; Glimsdal, Sondre; Jiao, Lei; Goodwin, Morten; Omlin, Christian W.; Berge, Geir Thore (2019-12-27). "The Convolutional Tsetlin Machine". arXiv:1905.09688 [cs, stat].
- Abeyrathna, K. Darshana; Granmo, Ole-Christoffer; Shafik, Rishad; Yakovlev, Alex; Wheeldon, Adrian; Lei, Jie; Goodwin, Morten (2020-07-04). "A Novel Multi-Step Finite-State Automaton for Arbitrarily Deterministic Tsetlin Machine Learning". arXiv:2007.02114 [cs].
- Wheeldon, A.; Shafik, R.; Rahman, T.; Lei, J.; Yakovlev, A.; Granmo, O. C. (2020). "Learning Automata based Energy-efficient AI Hardware Design for IoT Applications". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A.
- cair/TsetlinMachineC, Centre for Artificial Intelligence Research (CAIR), 2019-04-18, retrieved 2020-07-27
- cair/pyTsetlinMachine, Centre for Artificial Intelligence Research (CAIR), 2020-07-07, retrieved 2020-07-27
- cair/TsetlinMachine, Centre for Artificial Intelligence Research (CAIR), 2020-07-27, retrieved 2020-07-27
- cair/pyTsetlinMachineParallel, Centre for Artificial Intelligence Research (CAIR), 2020-07-07, retrieved 2020-07-27
- cair/PyTsetlinMachineCUDA, Centre for Artificial Intelligence Research (CAIR), 2020-07-27, retrieved 2020-07-27
- "cair/convolutional-tsetlin-machine-tutorial". GitHub. Retrieved 2020-07-27.
- Phoulady, Adrian (2020-04-13), adrianphoulady/weighted-tsetlin-machine-cpp, retrieved 2020-07-27
- JieGH (2020-03-22), JieGH/Hardware_TM_Demo, retrieved 2020-07-22
- JieGH. "Tsetlin Machine on Iris Data Set Demo, Handheld #MignonAI". Youtube.
- "https://twitter.com/olegranmo/status/1279045633916182528". Twitter. Retrieved 2020-07-27. External link in
|title=(help) - "mignon". www.mignon.ai. Retrieved 2020-07-27.
- Bush, Steve (2020-07-27). "A low-power AI alternative to neural networks". Electronics Weekly. Retrieved 2020-07-27.
- "Tsetlin Machine -- A new paradigm for pervasive AI".
- "IOLTS Presentation: Explainability and Dependability Analysis of Learning Automata based AI hardware".
- "The-Ruler-of-Tsetlin-Automaton".
- "Interpretable Clustering & Dimension Reduction with Tsetlin Automata machine learning".
- "Predicting and explaining economic growth using real-time interpretable learning".
- "Early detection of breast cancer from a simple blood test".
- "Recent advances in Tsetlin Machines".
- Bush, Steve (2020-07-27). "A low-power AI alternative to neural networks". Electronics Weekly. Retrieved 2020-07-27.