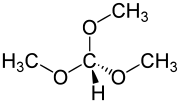
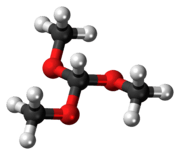
Trimethyl orthoformate
Trimethyl orthoformate is the simplest orthoester. It is a reagent used in organic synthesis for the introduction of a protecting group for aldehydes. The product of reaction of an aldehyde with trimethyl orthoformate is an acetal. In general cases, these acetals can be deprotected back to the aldehyde by using hydrochloric acid.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Trimethoxymethane | |
| Other names
2-Methoxyacetaldehyde dimethyl acetal; Methoxymethylal; Methyl orthoformate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.224 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 106.121 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | pungent |
| Density | 0.9676 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −53 °C (−63 °F; 220 K) |
| Boiling point | 100.6 °C (213.1 °F; 373.8 K) |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, ether |
| Vapor pressure | 1 kPa at 7 °C[2] |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.3773 |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R11 R36 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S9 S16 S26 |
| Flash point | 13 °C (55 °F; 286 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The industrial synthesis of this chemical is from hydrogen cyanide and methanol.[3]
Trimethyl orthoformate is a useful building block for creating methoxymethylene groups and heterocyclic ring systems. It introduces a formyl group to a nucleophilic substrate, e.g. RNH2 to form R-NH-CHO, which can undergo further reactions. It is used in the production of the fungicides, azoxystrobin and picoxystrobin, as well as for some members of the floxacin family of antibacterial drugs. A number of pharmaceutical intermediates are also made from trimethyl orthoformate.[3] Trimethyl orthoformate (TMOF) is an excellent reagent for the conversion of compatible carboxylic acids to the corresponding methyl esters. Refluxing such acids with excess neat TMOF until low-boilers cease evolution provides quantitative conversion to methyl esters, without need for catalysis. Ref. J.B. Paine III, J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 4929-4938. Alternatively, acid-catalyzed esterifications with methanol can be driven closer to completion by employing TMOF to convert water byproduct to methanol and methyl formate.
Preparation
Trimethyl orthoformate can also be prepared from the reaction between chloroform and sodium methoxide, an example of the Williamson ether synthesis.
See also
References
- Trimethyl orthoformate at Sigma-Aldrich
- Alfa Aesar SDS
- Ashford's Dictionary of Industrial Chemicals, Third edition, 2011, ISBN 978-0-9522674-3-0, page 9388