Trichohyalin
Trichohyalin is a protein that in mammals is encoded by the TCHH gene.[5]
| TCHH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | TCHH, THH, THL, TRHY, trichohyalin, UHS3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 190370 MGI: 2177944 GeneCards: TCHH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 1: 152.11 – 152.12 Mb | Chr 3: 93.44 – 93.45 Mb | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Discovery
In 1903 the name “trichohyalin” was assigned to the granules of the inner root sheath (IRS) of hair follicles discovered by H. Voerner.[6] In 1986 the name was reassigned to a protein isolated from sheep wool follicles.[7]
Gene location
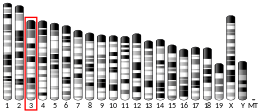
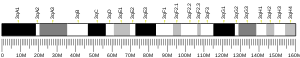
The human TCHH is located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 1 at region 2 band 1 sub-band 3 (1q21.3), from base pair 152,105,403 to base pair 152,116,368 (map).[8] This region in chromosome 1q21 is known as the epidermal differentiation complex, since it harbors over fifty other genes involved in keratinocyte differentiation.
Gene coding sequence contains 5829 nucleotides.[9] Gene orthologs were identified in most mammals including mice, chickens, rats, pigs, sheep, horses and other species.[10]
Protein localisation
Trichohyalin is highly expressed in the inner root sheath cells of the hair follicle and medulla.[11] It was also detected in the granular layer and stratum corneum of normal epidermis,[12] newborn human foreskin epidermis, the hard palate, in the nail matrix, the filiform papillae of dorsal tongue epithelium and in rodent forestomack.[13]
Function
The protein forms frequent links between the heads and tails of the keratin chains and, thus, participates in keratin intermediate filaments (KIF) inter-filamentous cross-linking. It also carries a function of a major reinforcement cross-bridging protein for the cell envelope (CE) barrier structure of the IRS and participates in coordination of CE structure.[11]
Overall, trichohyalin confers mechanical strength to the hair follicle inner root sheath and to other toughened epithelial tissues.[11]
Structure
Trichohyalin belongs to the S100-fused protein family. It is a monomer, containing 1943 amino acids,[14] and has elongated (>200 nm) single-stranded alpha-helical conformation based on its unusually high content of charged residues.[15]
Molecular mass of the human trichohyalin is 253925 Da.[14]
The protein includes nine domains. Domain 1 contains two EF-hand calcium-binding domains. Domains 2-4, 6, and 8 are almost entirely alpha-helical, configured as a series of peptide repeats of varying regularity, and are thought to form a single-stranded alpha-helical rod stabilised by ionic interactions. Domain 6 is the most regular and may bind KIF directly by ionic interactions. Domains 5 and 7 are less well organised and may induce folds in the molecule. Domain 9 contains the C-terminus, conserved among different species.[14][15]
Post-translational modifications
- Peptidylarginine deiminases (PAD) catalyse the deimination of arginine residues to citrullines.[16]
- Cross-linking by transglutaminase (TGase) enzymes results in the formation of an isopeptide bond between peptide-bound glutamine and lysine residues and provide insolubility and the rigid structure to trichohyalin.[16]
Interactions
TCHH protein is extensively cross-linked to itself in the IRS tissue as well as to keratin intermediate filaments (KIF). All TCHH-keratin links involved only domain 6 or 8 sequences.[11]
The protein can also form cross-links to all other CE proteins including involucrin, envoplakin, keratin, repetin, desmoplakin, SPR1, SPR2, and LEP.[11]
TCHH-TCHH and TCHH-CE protein links are distributed among domains 2–5, but are uncommon in domains 6 and 8. Most intra-THH cross-links occurred in the least organised domain 5 region at a 3.5-fold higher frequency.[11]
Clinical significance
Trichohyalin is associated with uncombable hair syndrome,[17] human alopecia areata [18] and also may be linked to curly hair phenotype in Europeans.[19]
A weak expression of the protein was discovered in the horny layer of psoriasis, ichthyosis, keratosis pilaris, porokeratosis, chronic dermatitis and callus.[20] The same level of trichohyalin expression was found in epidermal tumours (seborrheic keratosis, actinic keratosis, Bowen's disease, well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma) and follicular tumours (trichoepithelioma, keratotic basal cell epithelioma, proliferating trichilemmal tumour, trichilemmoma, pilomatricoma and keratoacanthoma).[20]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000159450 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000052415 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: Trichohyalin".
- Voerner, H. (1903). "On trichohyalin. A study of the anatomy of the hair root". Dermatol. Zeitschr. (Berlin). 10: 357–376.
- Rothnagel JA, Rogers GE (April 1986). "Trichohyalin, an intermediate filament-associated protein of the hair follicle". The Journal of Cell Biology. 102 (4): 1419–29. doi:10.1083/jcb.102.4.1419. PMC 2114164. PMID 3958055.
- "TCHH trichohyalin [Homo sapiens (human)] - Gene - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2018-11-10.
- Bank, RCSB Protein Data. "RCSB PDB - Gene View - TCHH - trichohyalin". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "ortholog_gene_7062[group] - Gene - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2018-11-10.
- Steinert PM, Parry DA, Marekov LN (October 2003). "Trichohyalin mechanically strengthens the hair follicle: multiple cross-bridging roles in the inner root shealth". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (42): 41409–19. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302037200. PMID 12853460.
- Hamilton EH, Payne RE, O'Keefe EJ (May 1991). "Trichohyalin: presence in the granular layer and stratum corneum of normal human epidermis". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 96 (5): 666–72. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12470590. PMID 1708794.
- O'Keefe EJ, Hamilton EH, Lee SC, Steinert P (July 1993). "Trichohyalin: a structural protein of hair, tongue, nail, and epidermis". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 101 (1 Suppl): 65S–71S. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12362866. PMID 7686953.
- "TCHH - Trichohyalin - Homo sapiens (Human) - TCHH gene & protein". www.uniprot.org. Retrieved 2018-11-10.
- Lee SC, Kim IG, Marekov LN, O'Keefe EJ, Parry DA, Steinert PM (June 1993). "The structure of human trichohyalin. Potential multiple roles as a functional EF-hand-like calcium-binding protein, a cornified cell envelope precursor, and an intermediate filament-associated (cross-linking) protein". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 268 (16): 12164–76. PMID 7685034.
- Tarcsa E, Marekov LN, Andreoli J, Idler WW, Candi E, Chung SI, Steinert PM (October 1997). "The fate of trichohyalin. Sequential post-translational modifications by peptidyl-arginine deiminase and transglutaminases". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (44): 27893–901. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.44.27893. PMID 9346937.
- Ü Basmanav FB, Cau L, Tafazzoli A, Méchin MC, Wolf S, Romano MT, Valentin F, Wiegmann H, Huchenq A, Kandil R, Garcia Bartels N, Kilic A, George S, Ralser DJ, Bergner S, Ferguson DJ, Oprisoreanu AM, Wehner M, Thiele H, Altmüller J, Nürnberg P, Swan D, Houniet D, Büchner A, Weibel L, Wagner N, Grimalt R, Bygum A, Serre G, Blume-Peytavi U, Sprecher E, Schoch S, Oji V, Hamm H, Farrant P, Simon M, Betz RC (December 2016). "Mutations in Three Genes Encoding Proteins Involved in Hair Shaft Formation Cause Uncombable Hair Syndrome". American Journal of Human Genetics. 99 (6): 1292–1304. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.10.004. PMC 5142115. PMID 27866708.
- Leung MC, Sutton CW, Fenton DA, Tobin DJ (October 2010). "Trichohyalin is a potential major autoantigen in human alopecia areata". Journal of Proteome Research. 9 (10): 5153–63. doi:10.1021/pr100422u. PMID 20722389.
- Medland SE, Nyholt DR, Painter JN, McEvoy BP, McRae AF, Zhu G, Gordon SD, Ferreira MA, Wright MJ, Henders AK, Campbell MJ, Duffy DL, Hansell NK, Macgregor S, Slutske WS, Heath AC, Montgomery GW, Martin NG (November 2009). "Common variants in the trichohyalin gene are associated with straight hair in Europeans". American Journal of Human Genetics. 85 (5): 750–5. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.10.009. PMC 2775823. PMID 19896111.
- Lee SC, Lee JB, Seo JJ, Kim YP (March 1999). "Expression of trichohyalin in dermatological disorders: a comparative study with involucrin and filaggrin by immunohistochemical staining". Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 79 (2): 122–6. doi:10.1080/000155599750011336. PMID 10228630.
Further reading
- Eriksson N, Macpherson JM, Tung JY, Hon LS, Naughton B, Saxonov S, Avey L, Wojcicki A, Pe'er I, Mountain J (June 2010). Gibson G (ed.). "Web-based, participant-driven studies yield novel genetic associations for common traits". PLoS Genetics. 6 (6): e1000993. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000993. PMC 2891811. PMID 20585627.
- Yamamoto S, Hirai K, Hasegawa-Oka Y, Hirai Y (February 2009). "Molecular elements of the regulatory control of keratin filament modulator AHF/trichohyalin in the hair follicle". Experimental Dermatology. 18 (2): 152–9. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.2008.00777.x. PMID 18643848.
- Lee SC, Wang M, McBride OW, O'Keefe EJ, Kim IG, Steinert PM (January 1993). "Human trichohyalin gene is clustered with the genes for other epidermal structural proteins and calcium-binding proteins at chromosomal locus 1q21". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 100 (1): 65–8. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12354504. PMID 8423399.
- Steinert PM, Parry DA, Marekov LN (October 2003). "Trichohyalin mechanically strengthens the hair follicle: multiple cross-bridging roles in the inner root shealth". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (42): 41409–19. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302037200. PMID 12853460.
- O'Keefe EJ, Hamilton EH, Lee SC, Steinert P (July 1993). "Trichohyalin: a structural protein of hair, tongue, nail, and epidermis" (PDF). The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 101 (1 Suppl): 65S–71S. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12362866. PMID 7686953.
- Fietz MJ, Rogers GE, Eyre HJ, Baker E, Callen DF, Sutherland GR (November 1992). "Mapping of the trichohyalin gene: co-localization with the profilaggrin, involucrin, and loricrin genes". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 99 (5): 542–4. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12667301. PMID 1431214.
- Medland SE, Nyholt DR, Painter JN, McEvoy BP, McRae AF, Zhu G, Gordon SD, Ferreira MA, Wright MJ, Henders AK, Campbell MJ, Duffy DL, Hansell NK, Macgregor S, Slutske WS, Heath AC, Montgomery GW, Martin NG (November 2009). "Common variants in the trichohyalin gene are associated with straight hair in Europeans". American Journal of Human Genetics. 85 (5): 750–5. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.10.009. PMC 2775823. PMID 19896111.
- Leung MC, Sutton CW, Fenton DA, Tobin DJ (October 2010). "Trichohyalin is a potential major autoantigen in human alopecia areata". Journal of Proteome Research. 9 (10): 5153–63. doi:10.1021/pr100422u. PMID 20722389.
- Lee SC, Kim IG, Marekov LN, O'Keefe EJ, Parry DA, Steinert PM (June 1993). "The structure of human trichohyalin. Potential multiple roles as a functional EF-hand-like calcium-binding protein, a cornified cell envelope precursor, and an intermediate filament-associated (cross-linking) protein". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 268 (16): 12164–76. PMID 7685034.