Trellis (architecture)
A trellis (treillage) is an architectural structure, usually made from an open framework or lattice of interwoven or intersecting pieces of wood, bamboo or metal that is normally made to support and display climbing plants, especially shrubs.[1]


Types
There are many types of trellis for different places and for different plants, from agricultural types, especially in viticulture, which are covered at vine training systems, to garden uses for climbers such as grapevines, clematis, ivy, and climbing roses or other support based growing plants.
The rose trellis is especially common in Europe and other rose-growing areas, and many climbing rose varieties require a trellis to reach their potential as garden plants. Some plants will climb and wrap themselves round a trellis without much artificial help being needed while others need training by passing the growing shoots through the trellis and/or tying them to the framework.
Uses
Trellis can also be referred to as panels, usually made from interwoven wood pieces, attached to fences or the roof or exterior walls of a building. A pergola usually refers to trellis-work that is laid horizontally above head height to provide a partial "roof" in a garden (pergolas are also used in agricultural settings).
History
The trellis was originally intended to support vine stock – which gives its name: lat Trichila (greenery bower). Though it is unknown when and where the trellis was invented, the trellis has been mentioned in literature and botanical works throughout history. Pliny the Younger, in the first and second centuries, wrote about trellises in some of his letters about gardens. In the 19th century, Walt Whitman also mentioned a trellis in his poem Give me the Splendid, Silent Sun.[2]
Trellis was used to support shrubs in espalier, also to separate roads from thickets and diverse sections of vegetable gardens. These sorts of fences were made by the gardeners. When the art of gardening was perfected by André Le Nôtre and Jules Hardouin-Mansart, the treillis became an object of decoration and was entrusted to particular workers named treillageurs. They worked individually until 1769, when they joined the corporation of carpenters. The treillageur has to have at least some elementary notions and principles of architecture and l’art du trait.
A trellis could be designed as a gallery, portico, room or different element of architecture and thus evolved into garden architecture linked to landscaping. In the 20th century landscape architects such as Edouard François, Lewis Duncan, and Gilles Clément, uses trellis, as well as artists such as Nils Udo or Jean-Max Albert whose spatial creations belong to land art, Site specific art, or Environmental sculpture. Jean-Max Albert notes[3][4] the trellis possibilities in visual art: "The trellis permits a visual contact of external and internal elements. It allows [us] to observe together the inside and the outside of a construction. The semi-transparency of the plans permits a simultaneous reading of imbricated volumes".
Gallery
 Four styles of trelliswork
Four styles of trelliswork Trellis arcade supporting a vine in French India
Trellis arcade supporting a vine in French India- A trellis supporting speakers viewed from the Jay Pritzker Pavilion stage
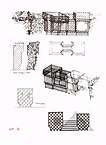 Project for Brancusi's studio, by Jean-Max Albert, 1978
Project for Brancusi's studio, by Jean-Max Albert, 1978 Jean-Max Albert, Pavillon de treillage, Hôtel de Sully, Paris, 1977
Jean-Max Albert, Pavillon de treillage, Hôtel de Sully, Paris, 1977 Creeping groundsel growing on a wooden trellis in Italy
Creeping groundsel growing on a wooden trellis in Italy
References
| Look up trellis in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Trellis. |
- The Book of Garden Furniture, C. Thonger, 1903
- Simpson, Rick. "History of the Trellis". Pergola Kits USA. Retrieved 18 January 2016.
- Hubert Beylier, Bénédicte Leclerc, Treillage de jardin du XIV au XX siècle, Éditions du patrimoine, Paris, 2000, p. 172-173
- Jean-Max Albert, L’espace de profil = Space in Profile, Les Éditions de La Villette, Paris, 1993.