Tooth fusion
Tooth fusion arises through union of two normally separated tooth germs, and depending upon the stage of development of the teeth at the time of union, it may be either complete or incomplete. On some occasions, two independent pulp chambers and root canals can be seen. However, fusion can also be the union of a normal tooth bud to a supernumerary tooth germ. In these cases, the number of teeth is fewer if the anomalous tooth is counted as one tooth. In geminated teeth, division is usually incomplete and results in a large tooth crown that has a single root and a single canal. Both gemination and fusion are prevalent in primary dentition, with incisors being more affected.
| Tooth fusion | |
|---|---|
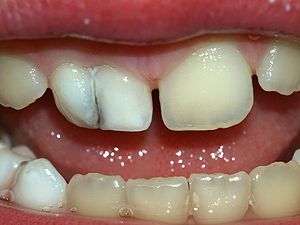 | |
| The fusion of two deciduous teeth. | |
| Specialty | Dentistry |
Tooth gemination, in contrast to fusion, arises when two teeth develop from one tooth bud. When the anomalous tooth appears to be two separate teeth, it appears that the patient has an extra tooth, although they have a normal number of tooth roots.
In contrast to fusion, concrescence is the roots of 2 or more teeth united by cementum alone after formation of tooth crowns.
Related abnormalities
- Amelogenesis imperfecta
- Dentinogenesis imperfecta
- Hyperdontia - More than the average number of teeth
- Anodontia - Lack of tooth development
References
- Peirera AJ, Fidel RA, Fidel SR. Maxillary Lateral Incisor with Two Root Canals: Fusion or Gemination? Braz Dent J (2000) 11(2): 141-146.