Tinambac, Camarines Sur
Tinambac, officially the Municipality of Tinambac (Central Bicolano: Banwaan kan Tinambac; Tagalog: Bayan ng Tinambac), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 67,572 people.[3]
Tinambac | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Tinambac | |
San Pascual Baylon Parish Church | |
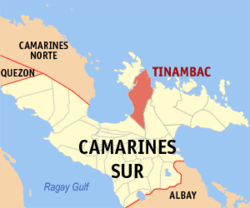 Map of Camarines Sur with Tinambac highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap 
| |
.svg.png) Tinambac Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 13°49′N 123°20′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Bicol Region (Region V) |
| Province | Camarines Sur |
| District | 4th district |
| Founded | 1888 |
| Barangays | 44 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Ruel B. Tuy |
| • Vice Mayor | Belyne B. Prades |
| • Congressman | Arnulf Bryan B. Fuentebella |
| • Electorate | 40,465 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 351.62 km2 (135.76 sq mi) |
| Population (2015 census)[3] | |
| • Total | 67,572 |
| • Density | 190/km2 (500/sq mi) |
| • Households | 13,277 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 1st municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 51.36% (2015)[4] |
| • Revenue (₱) | 164,015,557.77 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 4426 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)54 |
| Climate type | tropical rainforest climate |
| Native languages | Central Bikol Tagalog |
| Website | www |
Barangays
Tinambac is politically subdivided into 44 barangays.
- Agay-Ayan
- Antipolo
- Bagacay
- Banga
- Bolaobalite
- Bani
- Bataan
- Binalay (Poblacion)
- Buenavista
- Buyo
- Cagliliog
- Caloco
- Camagong
- Canayonan
- Cawaynan
- Daligan
- Filarca (Poblacion)
- La Purisima (Poblacion)
- Lupi
- Magsaysay (Camp 4)
- Magtang
- Mananao
- La Medalla (Mile 9)
- New Caaluan
- Olag Grande
- Olag Pequeño
- Old Caaluan
- Pag-Asa
- Pantat
- Sagrada (Camp 6)
- Salvacion
- San Antonio
- San Isidro (Poblacion)
- San Jose (Tiltilan)
- San Pascual (Poblacion)
- San Ramon (Camp 7)
- San Roque
- San Vicente
- Santa Cruz (Poblacion)
- Sogod
- Tambang
- Tierra Nevada
- Union
- Salvacion Poblacion
History
The town of Tinambac was considered to be a trading center of villages surrounding the eastern side of Mt. Isarog . It was in this place where tobacco, then a prohibited product, was exchanged by the townspeople of Tinambac.
Its establishment as a separate municipality occurred during the latter part of the 18th century and this was known as the mission post of Himoragat. In 1829 when the Spanish administration divided the province of Camarines Sur into four districts, Tinambac fall under the District of Isarog.
A church was built atop a hill which still stands at present where the residents of this simple town give way to the celebration of its fiesta every 17th day of May. St. Pascual Baylon is the patron saint of this town.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1939 | 10,921 | — |
| 1948 | 14,103 | +2.88% |
| 1960 | 28,897 | +6.16% |
| 1970 | 36,357 | +2.32% |
| 1975 | 34,415 | −1.09% |
| 1980 | 39,621 | +2.86% |
| 1990 | 46,570 | +1.63% |
| 1995 | 49,185 | +1.03% |
| 2000 | 55,608 | +2.67% |
| 2007 | 59,125 | +0.85% |
| 2015 | 67,572 | +1.68% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[3][5][6][7] | ||
In the 2015 census, the population of Tinambac was 67,572 people,[3] with a density of 190 inhabitants per square kilometre or 490 inhabitants per square mile.
Bikol is the predominant language.
Climate
| Climate data for Tinambac, Camarines Sur | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 31 (88) |
30 (86) |
33 (91) |
35 (95) |
36 (97) |
36 (97) |
35 (95) |
34 (93) |
35 (95) |
33 (91) |
32 (90) |
31 (88) |
33 (92) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 27 (81) |
27 (81) |
28 (82) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
28 (82) |
29 (84) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 62.63 (2.47) |
114.71 (4.52) |
41.44 (1.63) |
56.32 (2.22) |
105.22 (4.14) |
175.86 (6.92) |
192.89 (7.59) |
110.61 (4.35) |
130.78 (5.15) |
546.13 (21.50) |
232.90 (9.17) |
462 (18.2) |
2,231.49 (87.86) |
| Average rainy days | 21 | 25 | 14 | 17 | 23 | 29 | 31 | 23 | 27 | 29 | 29 | 31 | 299 |
| Source: World Weather Online[8] | |||||||||||||
Economy
Total agricultural area is estimated to be 17,230 hectares (42,600 acres), 96% of which are planted with coconut. Only around 4% are devoted to rice, corn, banana and root crops. Fishponds cover around 464 hectares (1,150 acres) or 1.8% of the total agricultural area.
Communication facilities:
- 1 Post Office located in the Poblacion, staffed by a Post Master and mail carriers
- Telegraph service offered by local branch of National Telecommunications Office
- Branches of RCPI and LBC Air Cargo
- Land line communication facilities
- Producers Bank
- Palawan Express( remittance center)
- Newly opened LCC supermarket and department store
References
- "Municipality". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- "Province: Camarines Sur". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region V (Bicol Region)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved 1 January 2020.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region V (Bicol Region)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region V (Bicol Region)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Camarines Sur". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- "Tinambac, Camarines Sur: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". World Weather Online. Retrieved 29 October 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tinambac. |