Timoleague
Timoleague (Irish: Tigh Molaige, meaning "house of Molaga") is a village in the eastern division of Carbery East in County Cork, Ireland. Located along Ireland's southern coast between Kinsale and Clonakilty. Nearby is the village of Courtmacsherry. It is about 17 km (11 mi) south of Bandon and 48 km (30 mi) from Cork on the R600 coastal road.
Timoleague Tigh Molaige | |
|---|---|
Village | |
 The ruins of Timoleague Abbey | |
 Timoleague Location in Ireland | |
| Coordinates: 51°38′33″N 8°46′1″W | |
| Country | Ireland |
| Province | Munster |
| County | Cork |
| Barony | Carbery East (East) |
| Elevation | 28 m (92 ft) |
| Population (2016)[1] | |
| • Total | 381 |
| Time zone | UTC+0 (WET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-1 (IST (WEST)) |
| Irish Grid Reference | W469437 |
| Website | www.timoleague.ie |
History
Timoleague gets its name from its original Irish name Tigh Molaga, meaning the Home/House of Molaga.[2] St. Molaga was reputed to have brought beekeeping/honey to Ireland. Honey production is still evident in the area. The village was formerly spelt Tagumlag, Tymulagy, Tymoleague. The town of Timoleague and much of the adjacent country belonged to the Hodnetts, an English family who settled in the area from Shropshire. Prior to this, it belonged to the O'Cowigs. In the reign of Henry III, a great battle was fought at Timoleague, between the Hodnetts, under Lord Phillip Hodnett, and the Barrys, under Lord Barrymore. The Hodnetts were routed, and their leader was killed. The Barrymores then became the owners of Timoleague, and they and their descendants retained possession until the 1800s, when it was purchased by the Travers family.
Places of interest

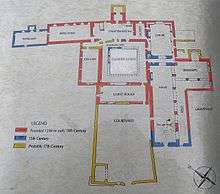
Timoleague Friary was founded by the Franciscan order in 1240. The abbey was built on the site of a monastic settlement founded by Saint Molaga in the 6th century. The Four Masters state that the Monastery of Timoleague was founded by MacCarthy Reagh, who lived near Kinsale, in 1240. The McCarthys were over-lords of Corca Laidhe, at least since the 13th century, and received tribute from the chiefs of the district. The abbey was extended by Donal Glas McCarthy in 1312, and by Irish and Norman patrons in the 16th century. The monks were dispersed by the Reformation, but returned in 1604. In 1612, the abbey was sacked by English soldiers who also smashed all of the stained glass windows, but much of the significant architecture remains. The friars remained in the abbey until 1642 when the friary and town were burnt by English soldiers under Lord Forbes.
In Abbeymahon, on the road to Courtmacsherry is the ruins of a Cistercian Abbey – Abbeymahon Abbey. The abbey was founded in 1172 by Dermot MacCormac MacCarthy, King of Desmond. The site was originally at Aghamanister and was colonized with a group of monks from Baltinglass. Almost a century lapsed before the monks decided to move to a new site. The monks moved to Abbeymahon in 1278 when Diarmuit MacCarthaig, son of Domnall Cairbreach, was buried in the new monastery.
The Church of Ireland church is also decorated internally in mosaic work carried out and paid for mainly by the then Maharajah of Gwalior (Madho Rao Scindia) of India about 1920 in memory of his doctor, Dr Crofts, who came from Timoleague. The church itself dates from 1811.[3]
Economy
Some of the local industries are based around tourism, agriculture and craft. One of the main employers in the local area is Stauntons Food a local producer of Pork/Bacon products. There are many other small and medium-sized businesses in the area including a small local maker of bespoke kitchens/furniture.
Timoleague Brown Pudding, a type of blood sausage, has been granted Protected Geographical Status under European Union law.[4]
Demographics
Timoleague has the highest proportion of Polish people of any settlement in Ireland at 25% of the population of the village, according to the 2011 census.[5]
Events
The Timoleague Harvest Festival is held every year in August.[6] In 2006 it attracted acts like Mundy and The Walls, and also hosts events in the village.
Sport
The local GAA club, Argideen Rangers, have won the 2005 Cork Intermediate Hurling Championship as well as a number of Junior Football and Hurling County Championships.
The club was home to Mark Foley, who scored an unprecedented 2–7 from play during the 1990 All-Ireland Hurling championship against All-Ireland champions (Tipperary) in the "Donkeys Don't Win Derbies" Munster Final in Thurles. He went on to score 1–1 in the All-Ireland Final against Galway in September of that year and brought the Liam MacCarthy Cup to the streets of Timoleague a few days later.
Transport
Timoleague railway station once connected the village to the West Cork Railway, by a branch onto the Clonakilty railway line, opened by the Ballinascarthy & Timoleague Junction Light Railway in 1890. The Timoleague & Courtmacsherry Extension Light Railway later extended this to Courtmacsherry in 1891 and its pier in 1892. It had three locomotives, Slaney, St. Molaga and Argadeen. Regular passenger traffic ceased in 1947 with post-war fuel shortages, and the line was closed completely by CIÉ in 1961. Timoleague railway station opened on 20 December 1890, closed for passenger traffic on 24 February 1947 and finally closed altogether on 1 April 1961.[7]
See also
- List of towns and villages in Ireland
- Market Houses in Ireland
- List of Harvest Festivals
References
- "Sapmap Area: Settlements Timoleague". Census 2016. Central Statistics Office. 2016.
- "Timoleague Friary Archived 2007-11-17 at the Wayback Machine". corkandross.org, November 01, 2009. Retrieved on 19 April, 2009.
- "Buildings of Ireland, Church of Ascension, Timoleague".
- Official list of IE protected foods. Accessed 22 December July 2011.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2015-11-17. Retrieved 2015-11-15.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- http://www.timoleague.ie/festival
- "Timoleague station" (PDF). Railscot - Irish Railways. Retrieved 2007-11-24.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Timoleague. |